-
Posts
9255 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
371
Everything posted by anyweb
-
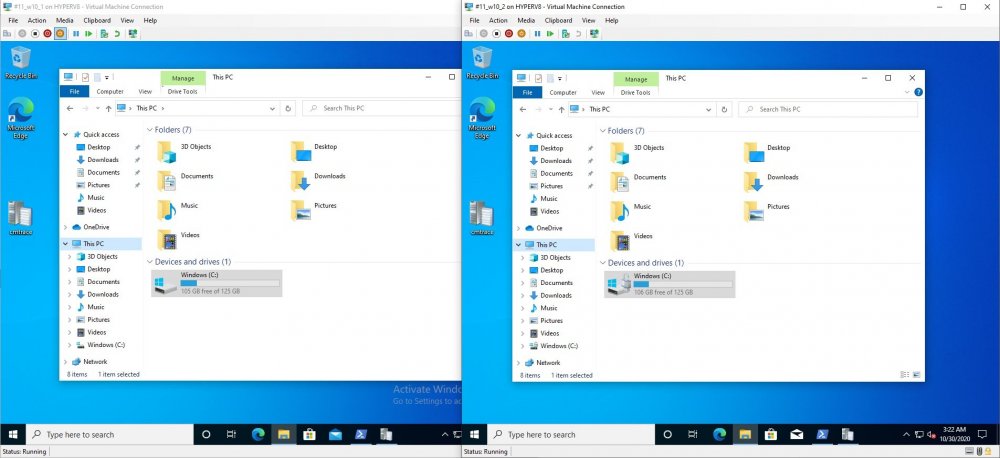
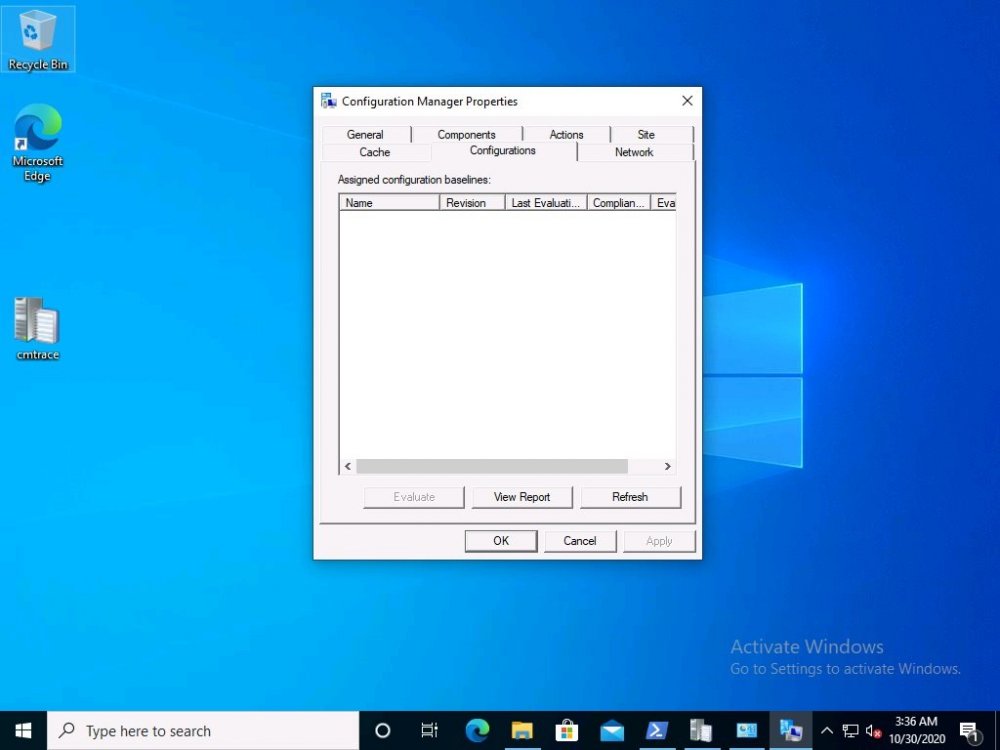
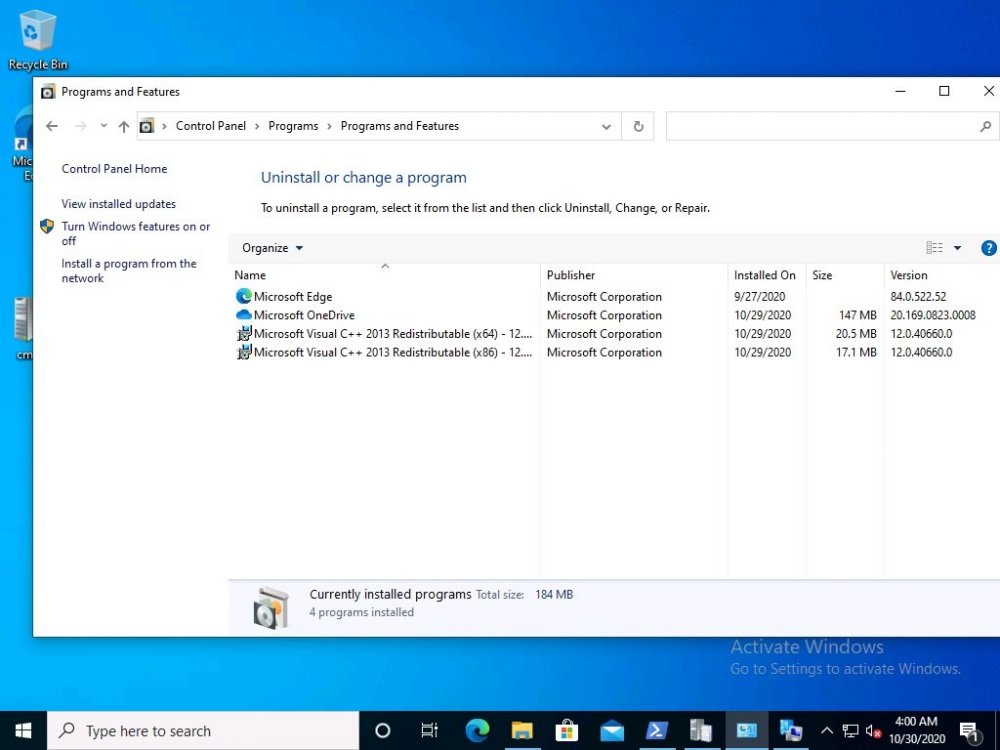
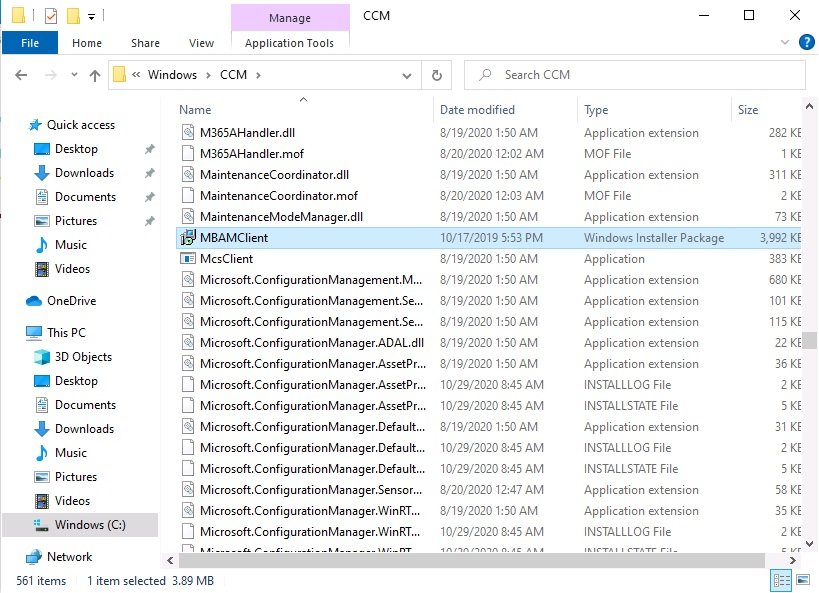
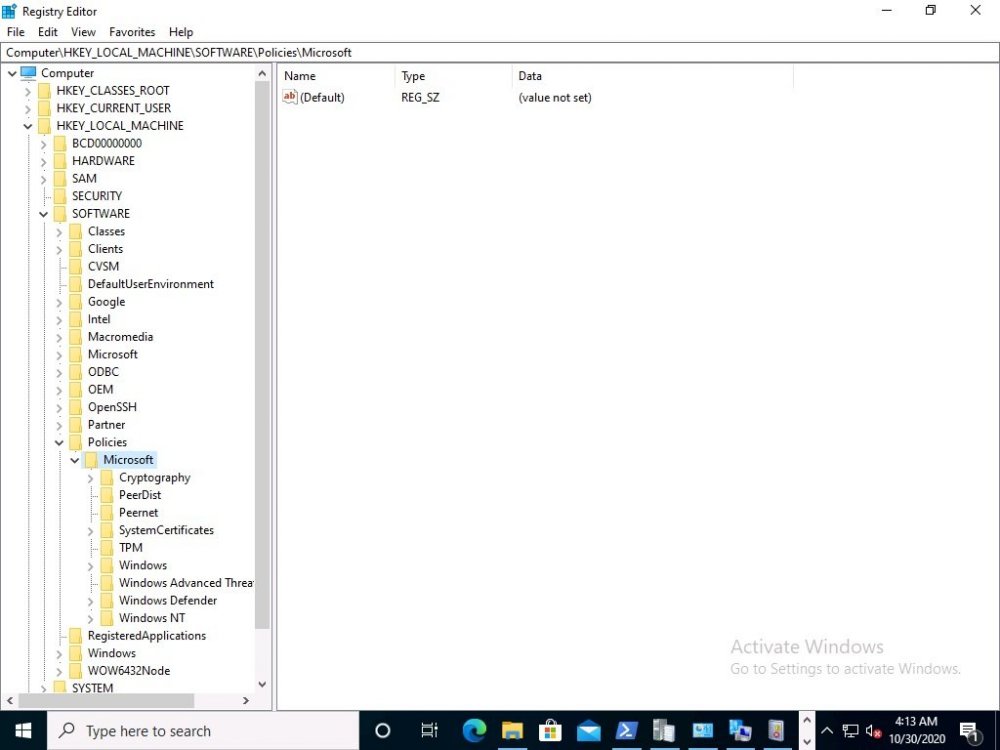
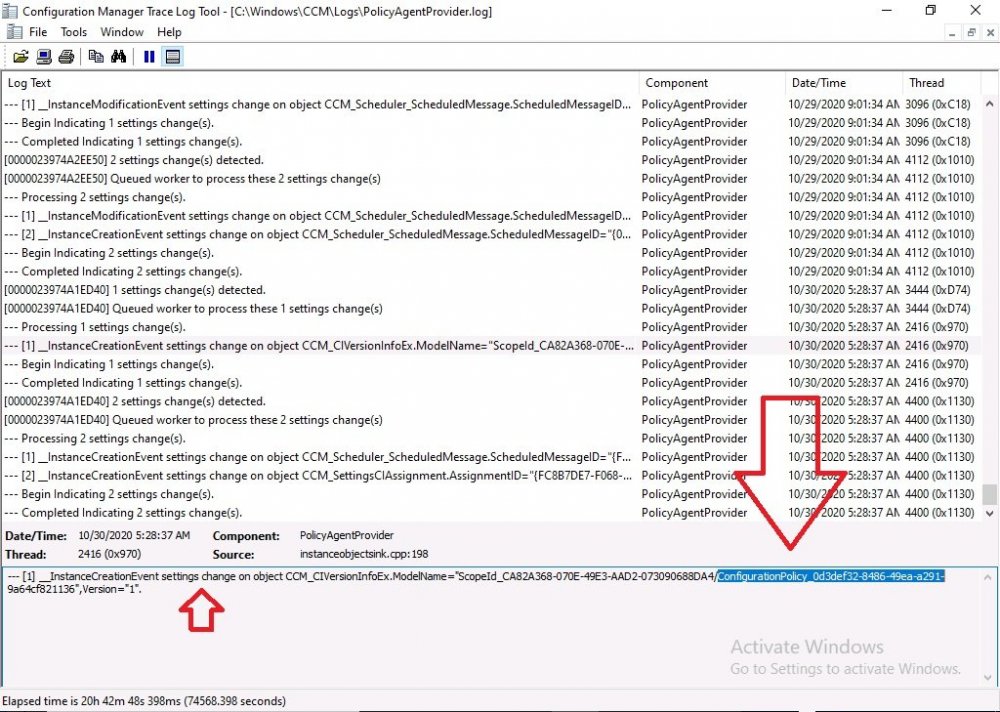
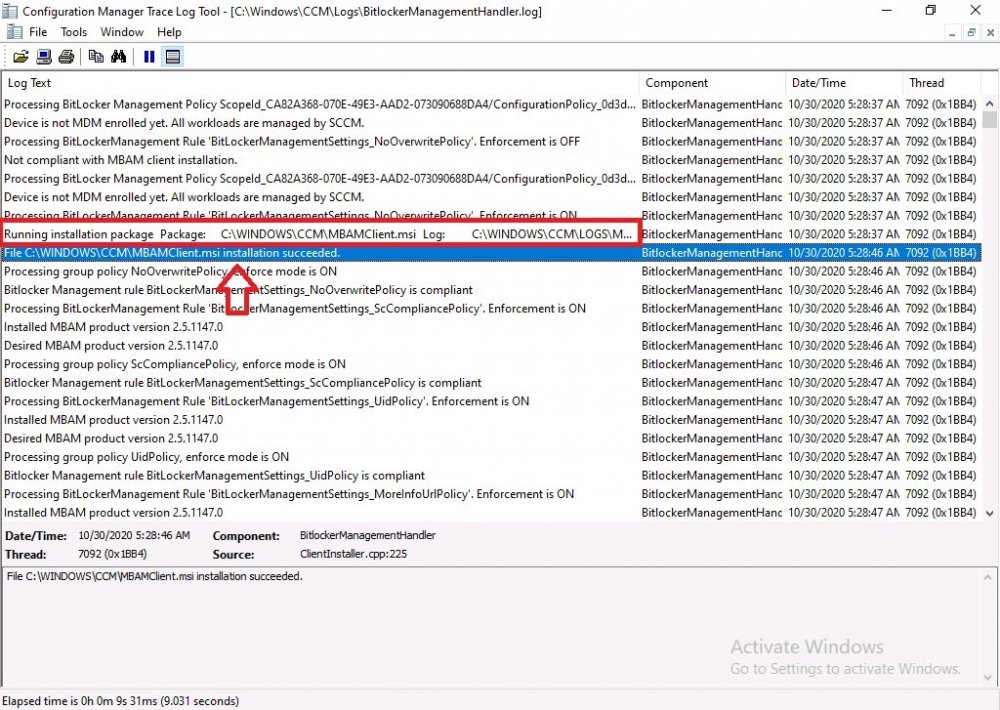
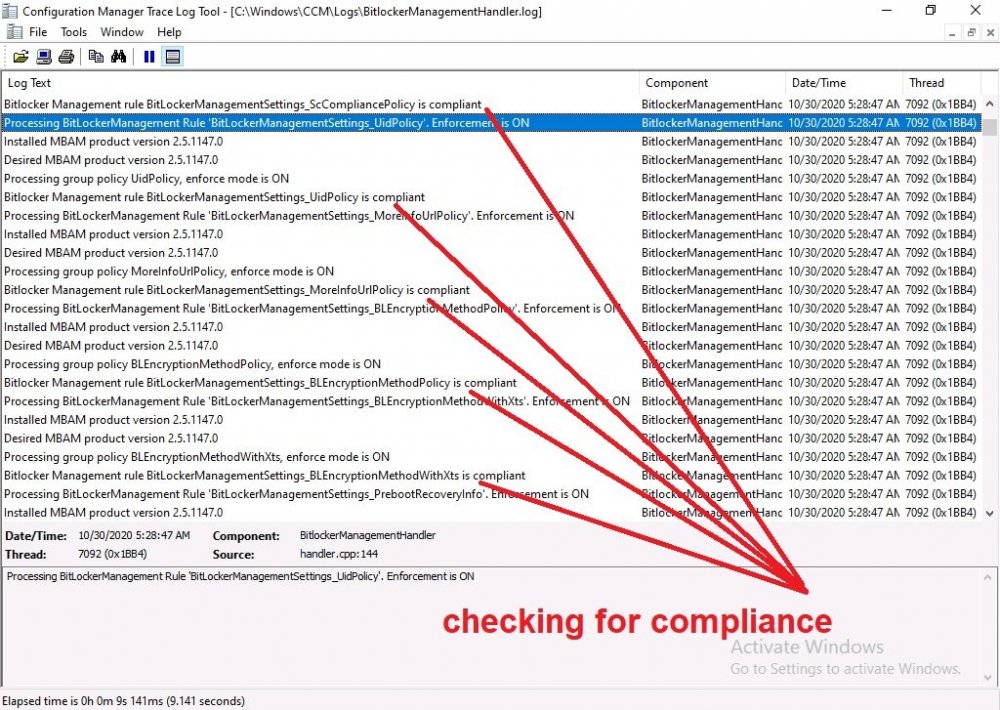
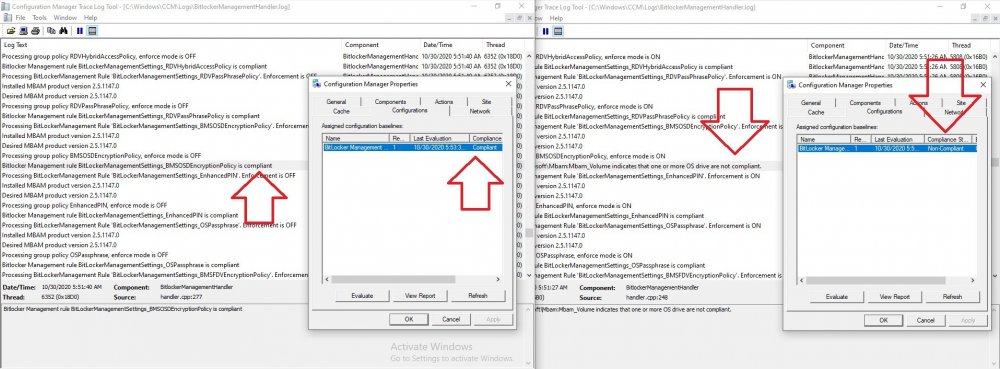
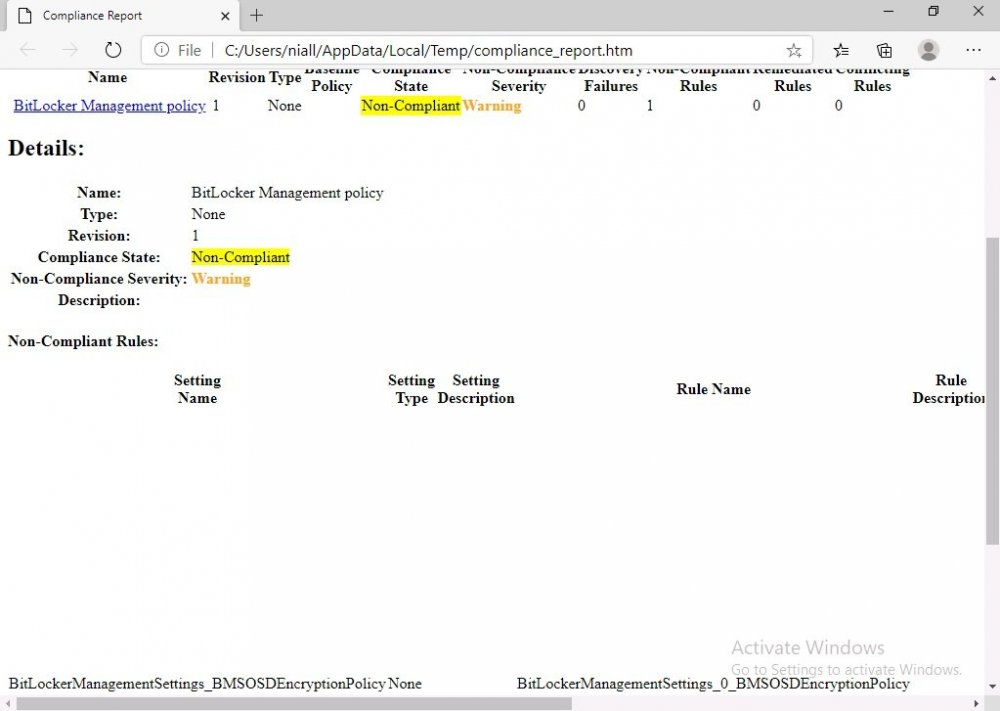
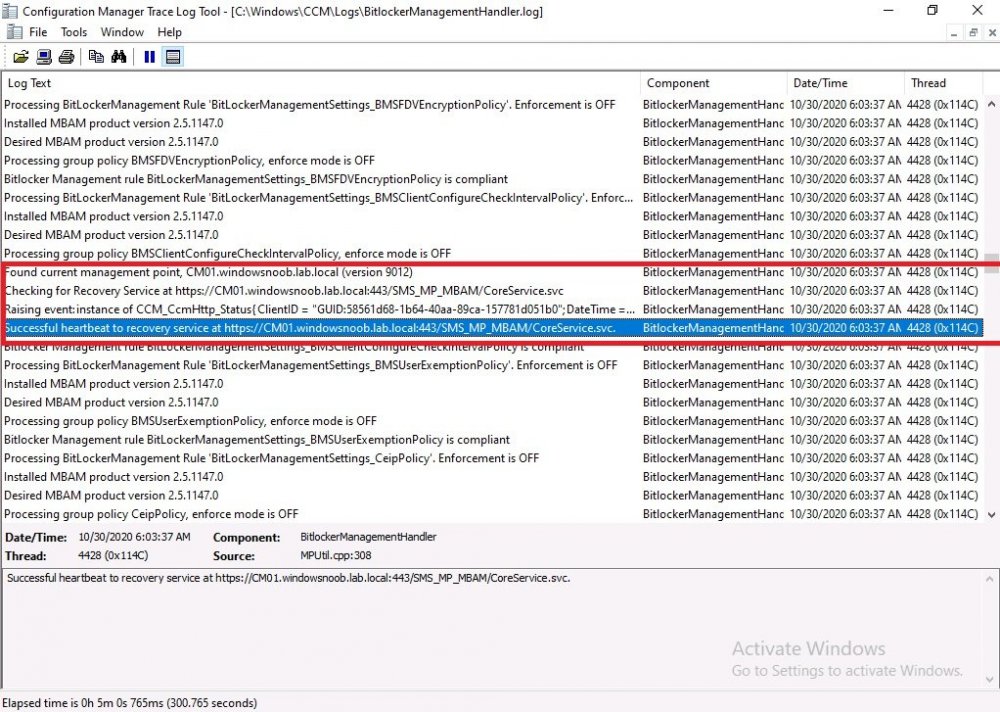
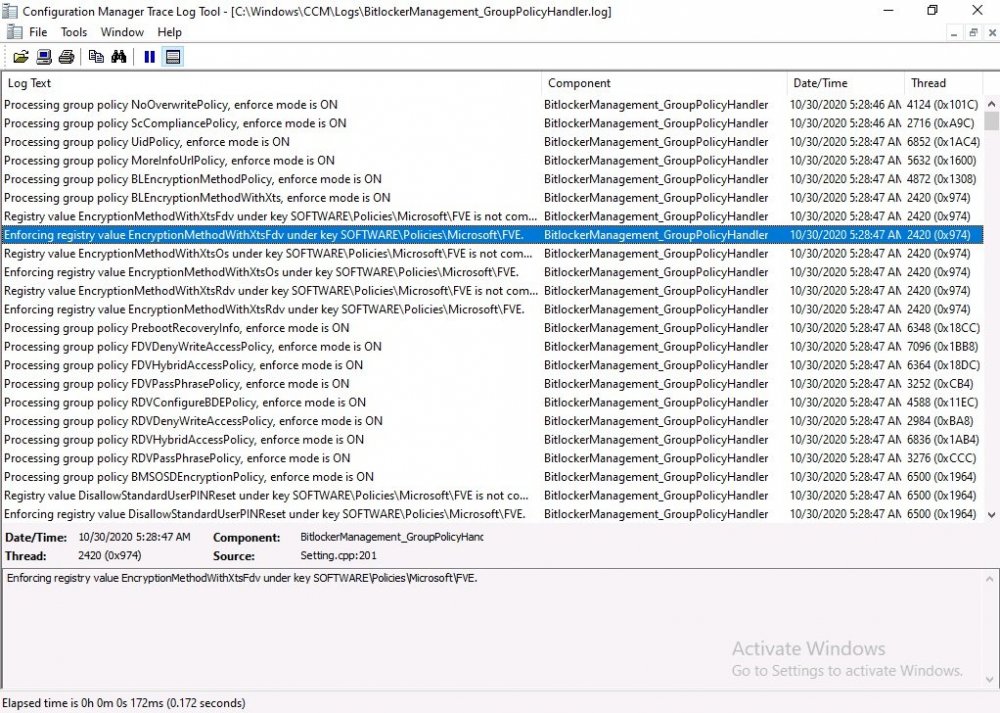
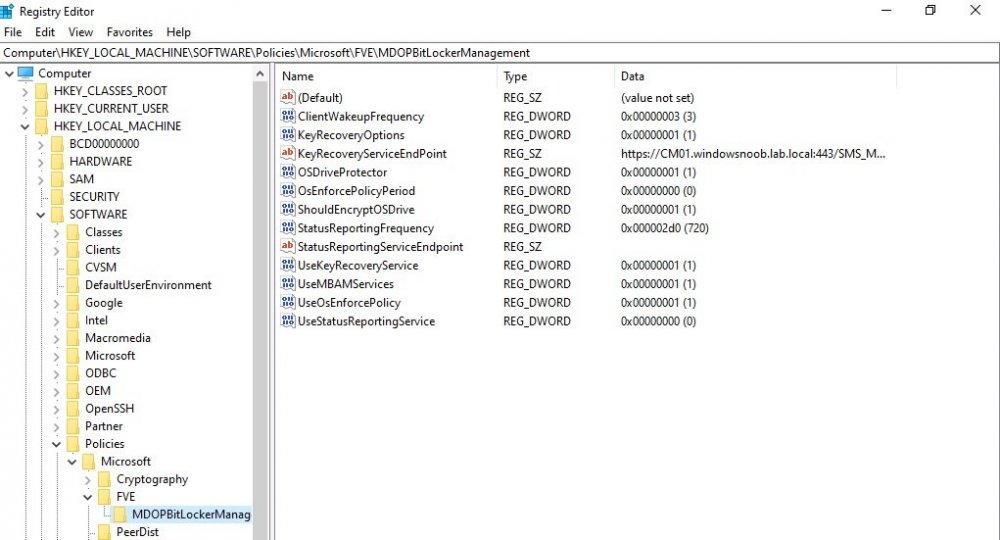
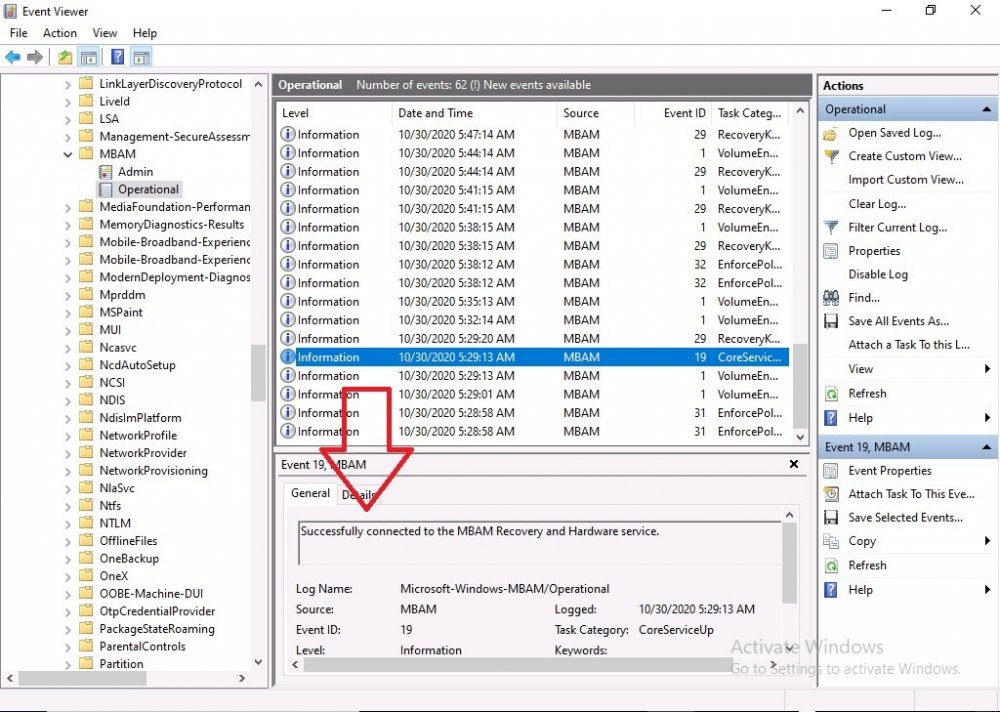
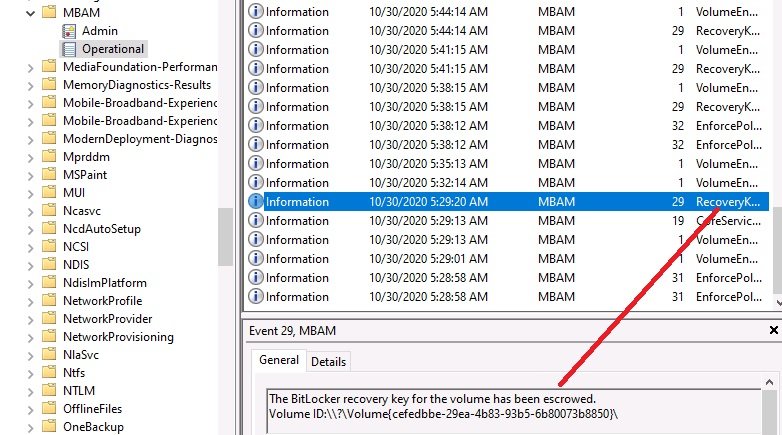
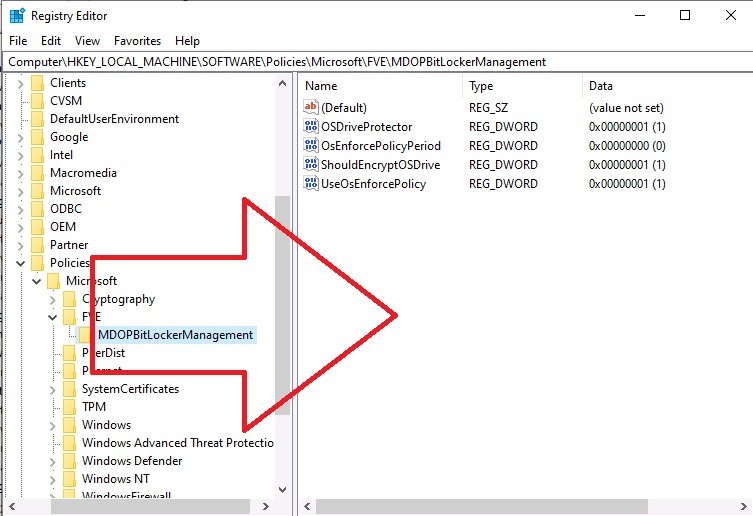
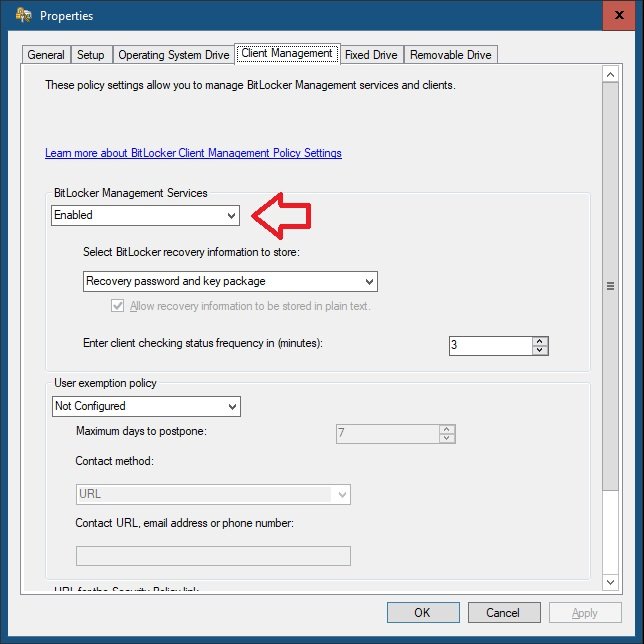
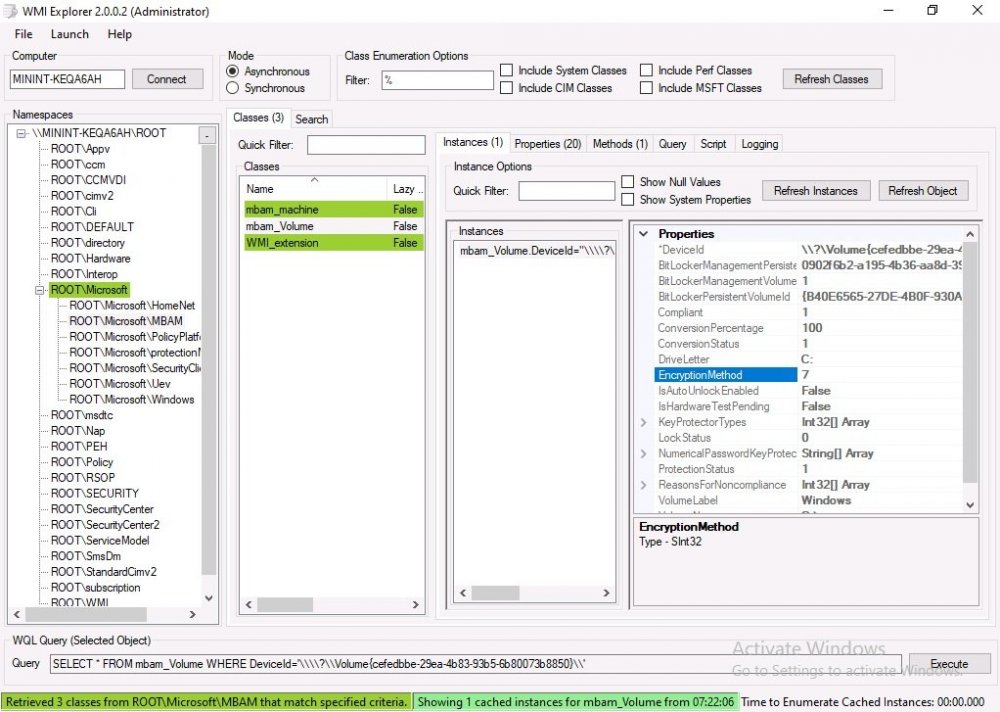
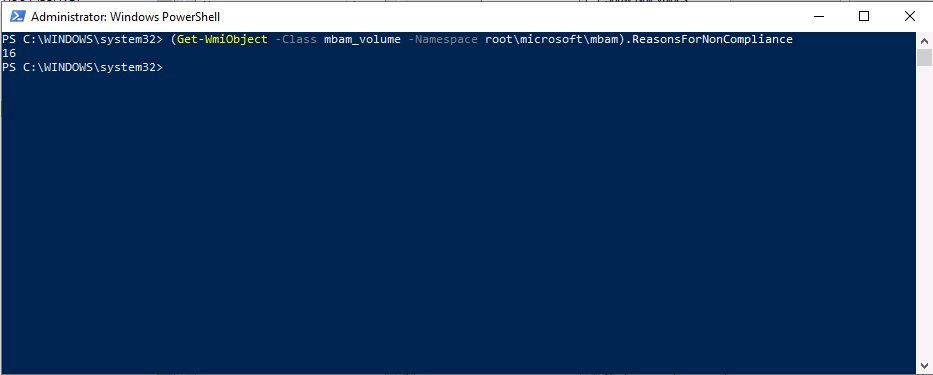
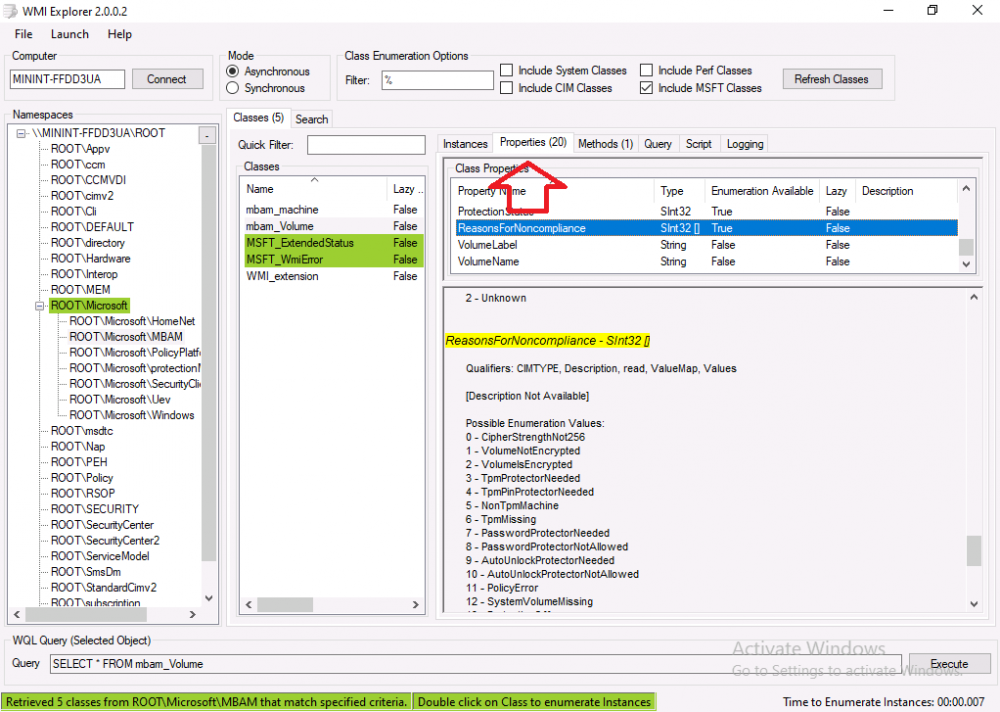
Introduction Microsoft blogged about Bitlocker Management capabilities back in May, 2019. They detailed how that would impact and evolve on the following three platforms. Cloud-based BitLocker management using Microsoft Intune On-premises BitLocker management using System Center Configuration Manager Microsoft BitLocker Administration and Monitoring (MBAM) And recently they've posted an updated blog post here where they go into detail about how BitLocker Management in Microsoft Endpoint Manager has evolved (both in Intune and ConfigMgr). This purpose of this mini series is to help you troubleshoot problems related to the installation, configuration and usage of the new BitLocker Management capabilities in ConfigMgr and will be broken down into the following 3 parts. Troubleshooting BitLocker Management in ConfigMgr - Part 1. Server side Troubleshooting BitLocker Management in ConfigMgr - Part 2. Client side (this part) Troubleshooting BitLocker Management in ConfigMgr - Part 3. Common issues In the previous part we created a BitLocker Management policy, but we did not deploy it. This was enough to start the flow of how things work on the server side. But let's focus on the client side for now and in this blog post we will look at a Windows 10 20H2 client. As Windows 10 20H2 is a newly released operating system, we need to use ConfigMgr 2006 to remain supported. Let's take a look at some client computers both before and after they receive BitLocker Management policy from ConfigMgr. Before BitLocker Management policy Before a client receives BitLocker Management policy, it can be in one of 2 states with regards to encryption, namely fully encrypted or fully decrypted. If the computer has not been targeted with BitLocker policy and is for whatever reason decrypted, then the hard disc drives data will be readable at rest (not protected). I've prepared 2 virtual machines running Windows 10 20H2 and neither virtual machine has received our previously configured BitLocker Management policy yet, however one vm is encrypted using a different encryption algorithm than the one we created in the previous blog post, this is so that we can see what occurs when it receives that policy. Both are running Windows 10 version 20H2 with the ConfigMgr client agent version 5.00.9012.1020. Note: I manually encrypted one of the two virtual machines with XTS-AES 128 using the following: cmd /c reg.exe add HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\FVE /v EncryptionMethod /t REG_DWORD /d 6 /f & manage-bde -on c: Opening Windows File Explorer on both vm's show's that clearly the vm on the right is encrypted, while the vm on the left is not. Using manage-bde -status reveals details about the encryption (or decryption) on both vm's. Neither VM contains BitLocker Management policy based logs in C:\Windows\CCM\Logs and we can see that there is no BitLocker Management related policy shown in the ConfigMgr client agent on either of the two virtual machines A quick check of programs installed, reveals that the MDOP MBAM client Agent is not installed on either Virtual Machine. This agent is responsible for interpreting the BitLocker Mangement policy settings and acting accordingly. This MDOP MBAM client agent installation file (MSI) is present in the ConfigMgr client agent files path (C:\Windows\CCM\MBAMCLIENT.MSI) even when the no BitLocker Management policy is deployed to the client. There will be no MBAM related events (or folders) in the Event Viewer at the following path Applications and services logs\Microsoft\Windows\ And there will be no FVE\MDOPBitLockerManagement registry entries in Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft After BitLocker Management policy So now that we've seen what client computers look like when not targeted with BitLocker Management policy, let's go ahead and deploy policy the previously created policy to them. And once done, we can see things happening on the two clients. The first indication that there's a change comes from the PolicyAgentProvider.log on the client, where it see's the new policy and refers to it via it's ScopeID. You can confirm that this is indeed the policy by enabling the CI_Unique_ID column in the Configuration Manager console for your respective BitLocker Management policy. very shortly after the client receives and interprets the policy, the following two logs are created on the client in the following order. BitlockerManagementHandler.log BitlockerManagement_GroupPolicyHandler.log The BitlockerManagementHandler.log records details about BitLocker management policies, the installation of the MBAMClient.msi (MDOP MBAM client agent) and whether the configured policy is compliant or not. Below you can see the BitlockerManagementHandler.log showing the installation of the MBAMClient.msi. Below you can see the BitlockerManagementHandler.log showing that it's checking for compliance and after the MDOP MBAM agent is done enforcing policy the computer will be marked Compliant or Non-Compliant. On this vm everything was compliant so the configuration baseline was marked as compliant. If you remember in the start of this blog post we had two virtual machines, one had no encryption configured (vm1) while the second had XTS-AES 128 configured, and that does NOT match our BitLocker Management policy of XTS-AES 256 therefore it is marked as non compliant even though it is encrypted. You can also look at the built in report for the Configuration Baseline by clicking on View report to see why it's not compliant, it's not that clear but if you see at the bottom of this report it's referring to the BMSOSDEncryptionPolicy and that's because the algorithm is different to the policy. After checking for compliance the log reports on whether or not it can reach the BitLocker Management recovery service. Below you can see a successful connection to the recovery service. The BitlockerManagement_GroupPolicyHandler.log records information about the presence of Local Group Policy settings which are written to the registry and if appropriate, enforces them. Below you can see the registry settings are now populated. if it looks like there are several registry keys missing (such as in the example below) then double-check that you've configured and enabled the BitLocker Management Settings in the Client Management setting of the configured BitLocker Management policy Once the registry keys are populated correctly, they'll be reflected in Local Group Policy settings on the clients. Lastly, the MDOP MBAM agent logs the success or failure of it's actions to the event viewer and includes information about whether or not it can reach the Recovery Service as you can see in the example below: and it will also log the escrowing of recovery keys. Reviewing Policy using WMI Explorer You can also use WMI Explorer 2.0 to take a closer look at policy on the client computers, browse to ROOT\Microsoft\MBAM as shown here (ran as Local Administrator). and below you can see the two virtual machines side by side showing compliant versus non-compliant in WMI Explorer Using PowerShell to determine non-compliance You can use Powershell to determine non compliance, for example: (Get-WMIObject -Class mbam_Volume -NameSpace root\microsoft\mbam).ReasonsForNonCompliance and the results returned (16) match what was seen in WMI Explorer on the already encrypted client. To get a list of these Reasons For Non Compliance see here https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-desktop-optimization-pack/mbam-v25/determining-why-a-device-receives-a-noncompliance-message 0 Cipher strength not AES 256. 1 MBAM Policy requires this volume to be encrypted but it is not. 2 MBAM Policy requires this volume to NOT be encrypted, but it is. 3 MBAM Policy requires this volume use a TPM protector, but it does not. 4 MBAM Policy requires this volume use a TPM+PIN protector, but it does not. 5 MBAM Policy does not allow non TPM machines to report as compliant. 6 Volume has a TPM protector but the TPM is not visible (booted with recover key after disabling TPM in BIOS?). 7 MBAM Policy requires this volume use a password protector, but it does not have one. 8 MBAM Policy requires this volume NOT use a password protector, but it has one. 9 MBAM Policy requires this volume use an auto-unlock protector, but it does not have one. 10 MBAM Policy requires this volume NOT use an auto-unlock protector, but it has one. 11 Policy conflict detected preventing MBAM from reporting this volume as compliant. 12 A system volume is needed to encrypt the OS volume but it is not present. 13 Protection is suspended for the volume. 14 AutoUnlock unsafe unless the OS volume is encrypted. 15 Policy requires minimum cypher strength is XTS-AES-128 bit, actual cypher strength is weaker than that. 16 Policy requires minimum cypher strength is XTS-AES-256 bit, actual cypher strength is weaker than that. or simply click on the Properties tab in WMI Explorer, and look what it reveals for that Property. Recommended reading https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/protect/deploy-use/bitlocker/deploy-management-agent https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/protect/tech-ref/bitlocker/about-event-logs Well that's it for this part, join me in the next part where we'll look at some common problems seen in BitLocker Management and how to resolve them. cheers niall.
-

MECM 2006 +MDT +PXE Boot
anyweb replied to bigbro.pro's topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
it's only necessary to deploy to the Unknown computers collection if those are your target, for example, in a New Computer type of scenario, if however you want to deploy to existing (known) computers then you can do so to via whatever collections they are members of. -

MBAM portals cannot access
anyweb replied to hannah's topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
can you confirm that you've met these prerequisites To use the self-service portal or the administration and monitoring website, you need a Windows server running IIS. You can reuse a Configuration Manager site system, or use a standalone web server that has connectivity to the site database server. Use a supported OS version for site system servers. Only install the self-service portal and the administration and monitoring website with a primary site database. In a hierarchy, install these websites for each primary site. On the web server that will host the self-service portal, install Microsoft ASP.NET MVC 4.0 and .NET Framework 3.5 feature before staring the install process. Other required Windows server roles and features will be installed automatically during the portal installation process. The user account that runs the portal installer script needs SQL Server sysadmin rights on the site database server. During the setup process, the script sets login, user, and SQL Server role rights for the web server machine account. You can remove this user account from the sysadmin role after you complete setup of the self-service portal and the administration and monitoring website.- 23 replies
-

MBAM portals cannot access
anyweb replied to hannah's topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
ok still very hard to see the output from your powershell but if there's no errors then that's better, what type of environment do you have, is it a single primary with the helpdesks installed on the same server or something more complex, please explain... can you do a remote session so i can take a look (teamviewer ?)- 23 replies
-

MBAM portals cannot access
anyweb replied to hannah's topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
well it's hard to make out from your screenshot but it appears you had errors installing the portals, what cmdline did you use to install them ?- 23 replies
-

MECM 2006 +MDT +PXE Boot
anyweb replied to bigbro.pro's topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
have you created and deployed a task sequence in ConfigMgr yet ? -

MBAM portals cannot access
anyweb replied to hannah's topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
have you seen my guide here- 23 replies
-
have you tried to reinstall the helpdesk webportal as it's more than likely still tied to your original SQL server setup, here's the command line I used in my labs .\MBAMWebSiteInstaller.ps1 -SqlServerName cm01.windowsnoob.lab.local -SqlInstanceName MSSQLSERVER -SqlDatabaseName CM_P01 -ReportWebServiceUrl http://cm01.windowsnoob.lab.local/Reportserver -HelpdeskUsersGroupName "windowsnoob\MBAM_HD" -HelpdeskAdminsGroupName "windowsnoob\MBAM_HD_Adv" -MbamReportUsersGroupName "windowsnoob\MBAM_HD_Report" -SiteInstall Both that would be the first thing i'd do, uninstall your current help desk (as you've moved SQL) and then reinstall the helpdesk portal pointing to the new SQL server
-
Interesting, I haven't tested it yet with a CMG scenario, but now that you've mentioned it I guess I should so i'll try and replicate this in my lab and see what happens, time willing, i'll report back after that cheers niall
- 242 replies
-
- 1702
- forced upgrade
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-

Altaro FREE ebook - SysAdmin Horror Stories Vol.2
anyweb posted a topic in Official Forum Supporters
Last year’s ebook, SysAdmin Horror Stories Vol1 by Altaro, highlighted some of SysAdmins’ funniest and most horrifying stories. It proved so successful, that Altaro decided to produce a second edition this year: they’ve gathered some more real-life stories to share with you, that are both funny and horrific! We all know that a SysAdmin’s job is no easy task, and apart from constantly having systems to update, bugs to fix and users to please, SysAdmins encounter all sorts of situations throughout their careers. From tech situations to funny anecdotes, terrible mishaps or incidents with colleagues, this eBook includes real stories of what SysAdmins go through on a daily basis. It’s very easy to download as no registration is required. Click on Download and it’s yours. It includes more than 20 short stories but this one is my personal favorite. Download your FREE copy today & Happy Halloween! -

Dont Have Application Website Catalog
anyweb replied to honestvip's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
they are not there because they have been removed, see https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/plan-design/changes/deprecated/removed-and-deprecated-cmfeatures- 1 reply
-
- 1
-

-

ADR not downloading updates
anyweb replied to kesh's topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
which version of configmgr ? -
what type of headphones are they and are you using bluetooth or wired to use them ?
-
hi Mike used space only in a task sequence occurs when you have enabled the Pre-Provision BitLocker step and have not configured it (or the enable bitlocker step) to use Full disk encryption I blogged about that in the following posts, please take a look: How can we utilize the Bitlocker Management feature during OSD with Endpoint Manager Full disk encryption (in ConfigMgr 1910) – a closer look using real hardware Enabling Full Disk Encryption in Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager 1910 in a task sequence if none of this helps then let me know and i'll investigate in my lab
-

Autologon.exe task sequence SCCM2012r2
anyweb replied to Xavier62's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
hi and welcome, first i'd recommend you use the Current Branch release of ConfiMgr, today that would be anything from version 2006 and later (you install the baseline version first CM2002) then upgrade. next, your error 0x8007052e translates to " The user name or password is incorrect. Source: Windows ----- so you should verify you are settings the username/password correctly cheers niall "