Leaderboard
Popular Content
Showing content with the highest reputation since 08/04/09 in Posts
-
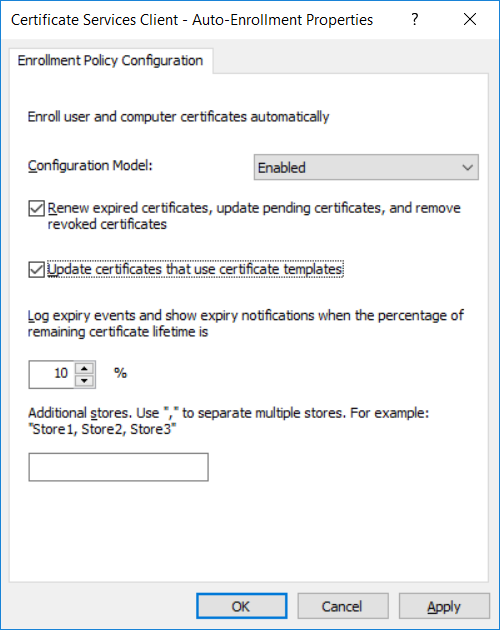
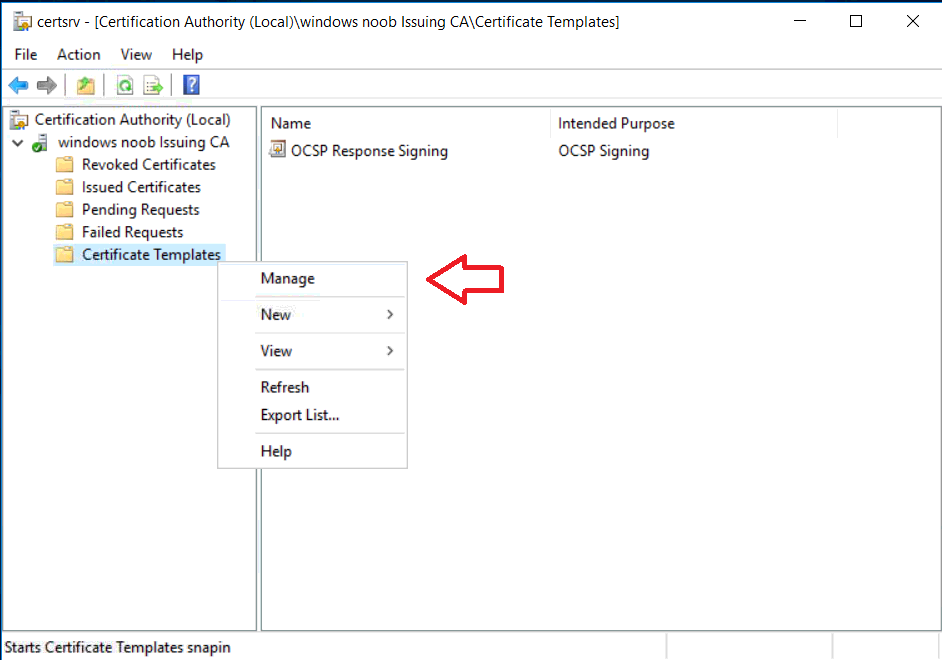
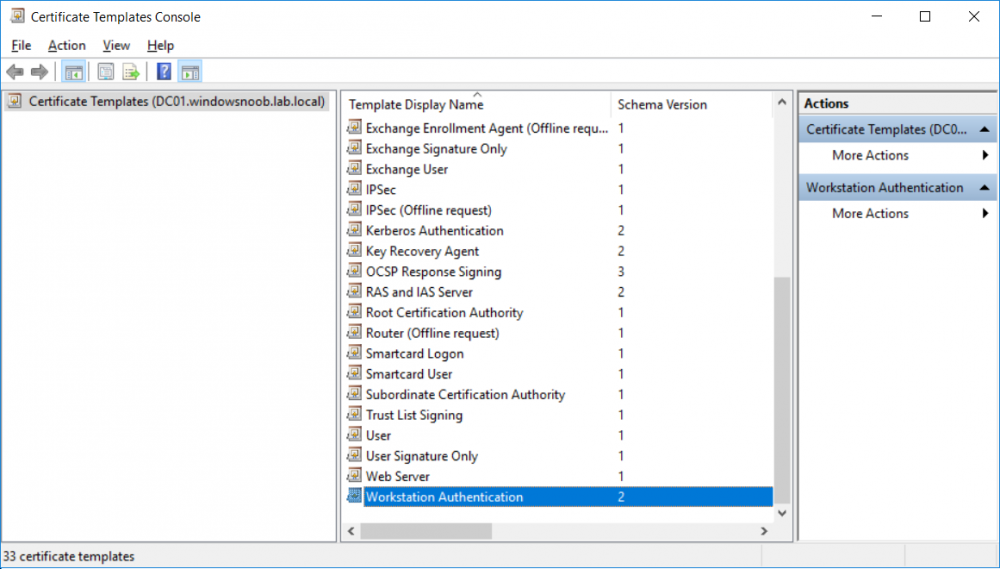
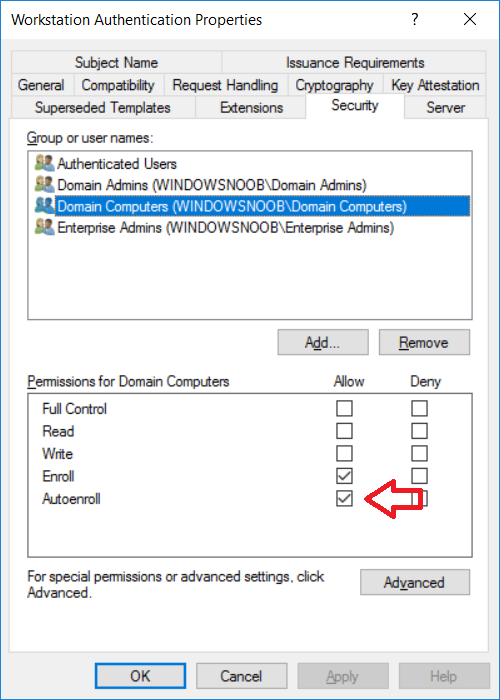
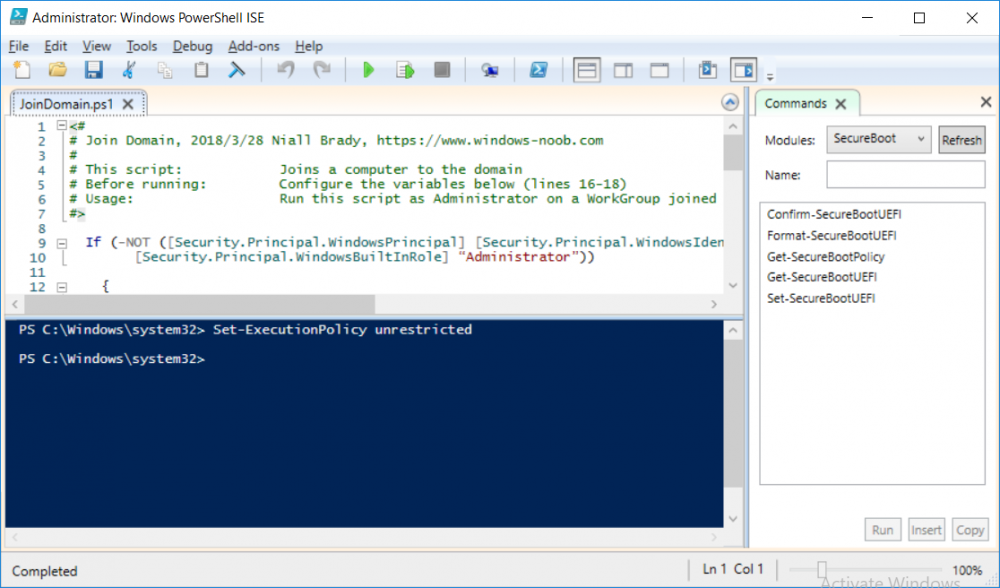
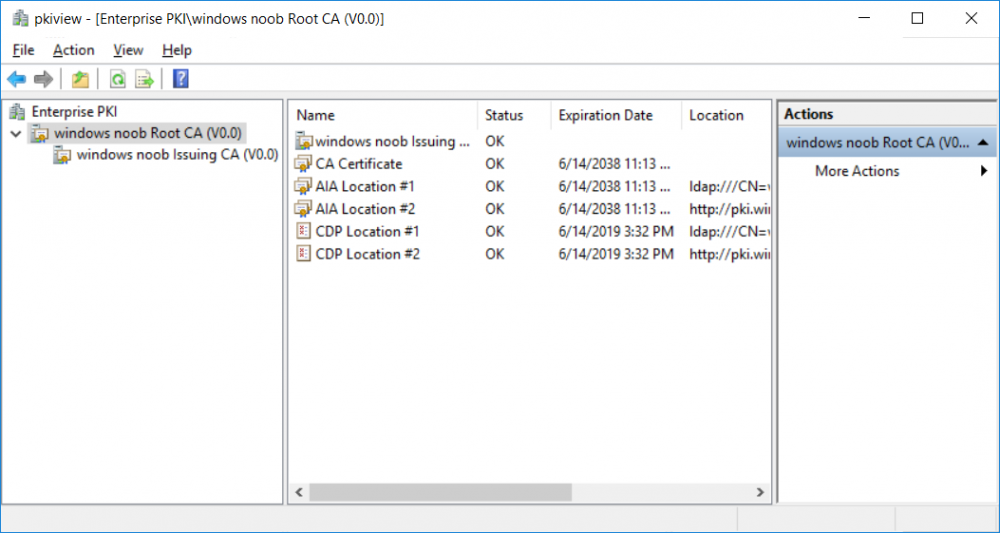
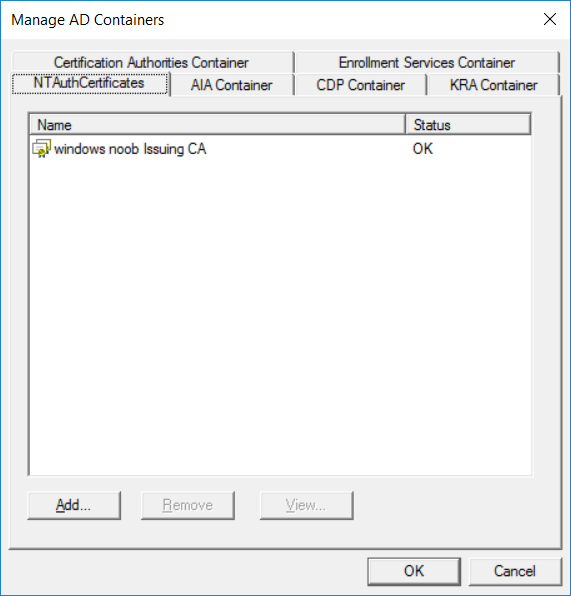
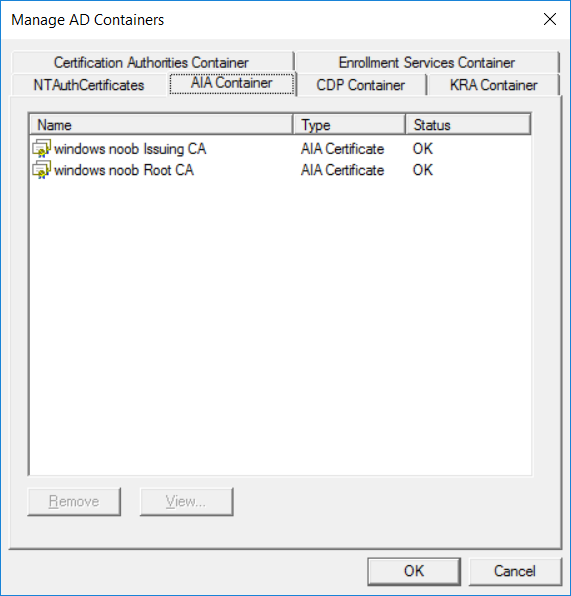
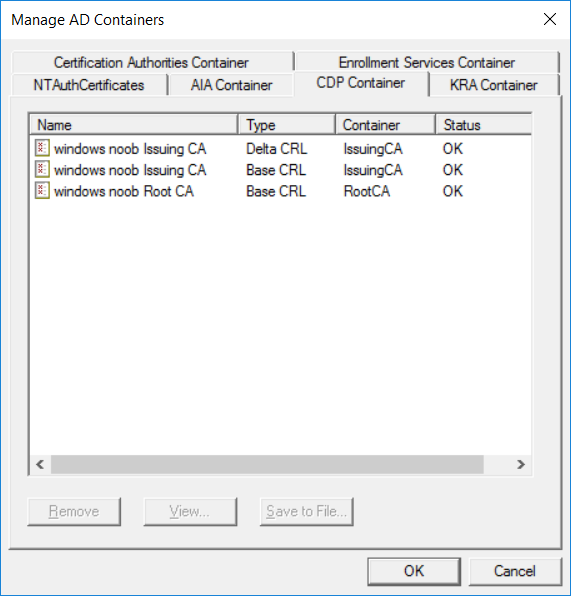
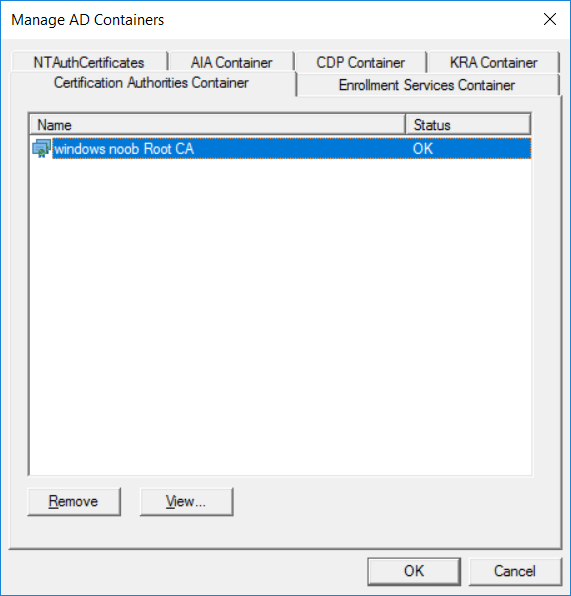
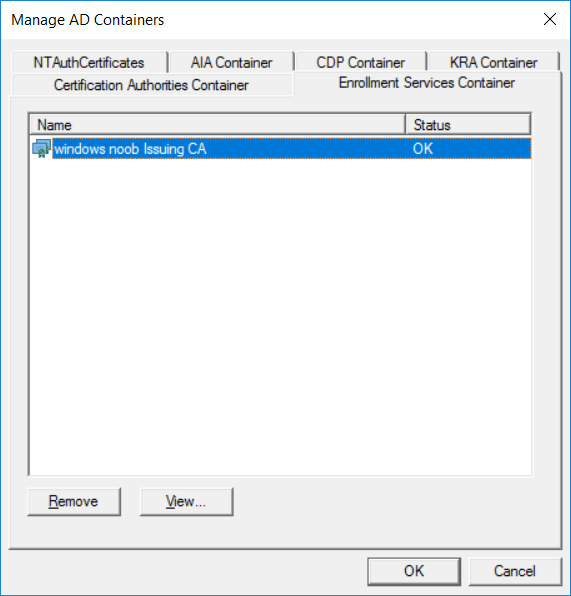
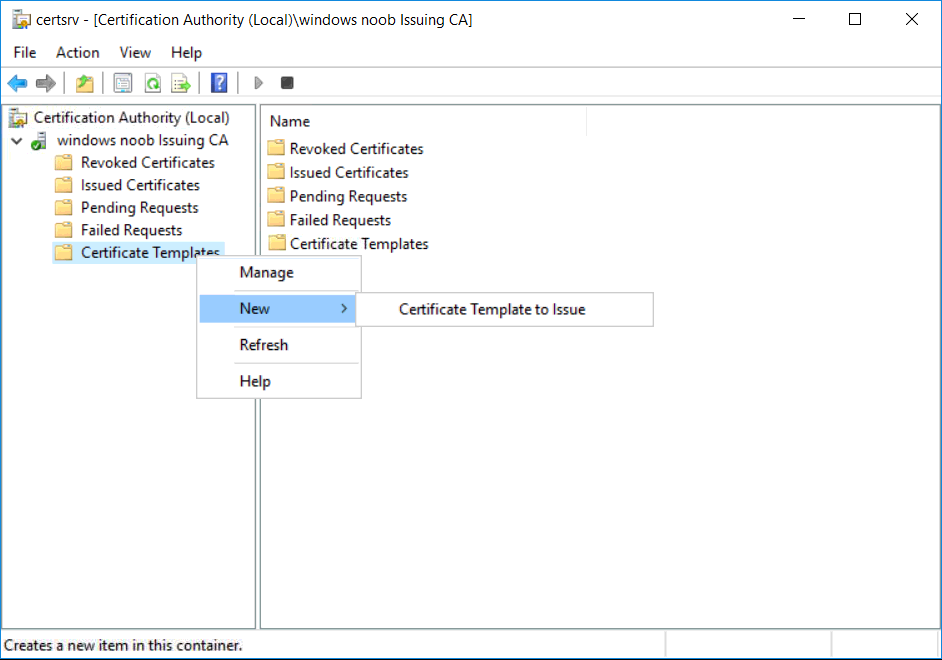
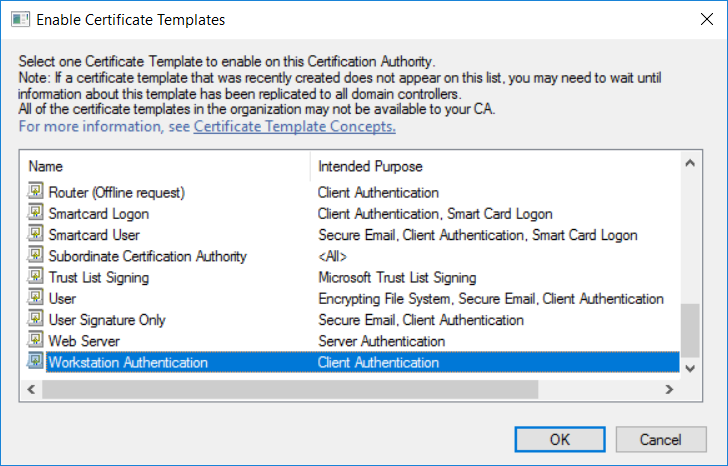
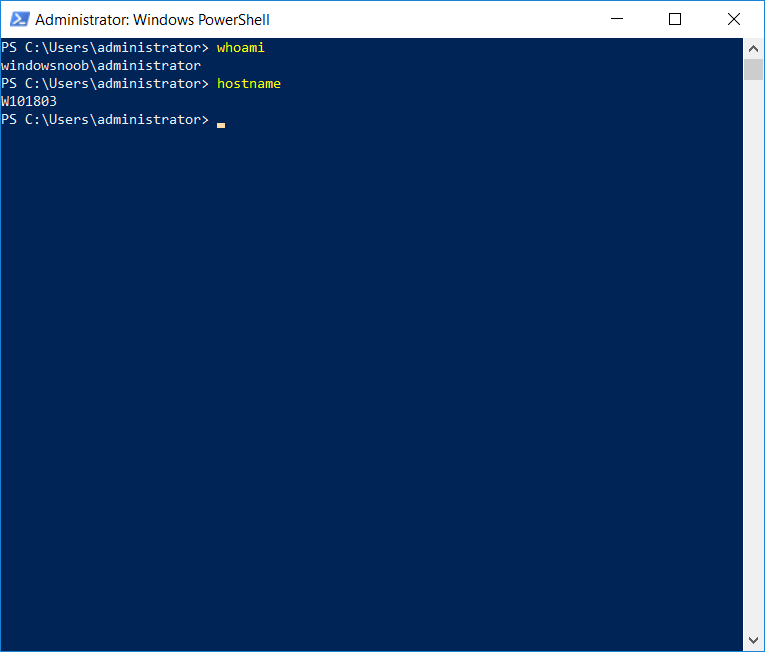
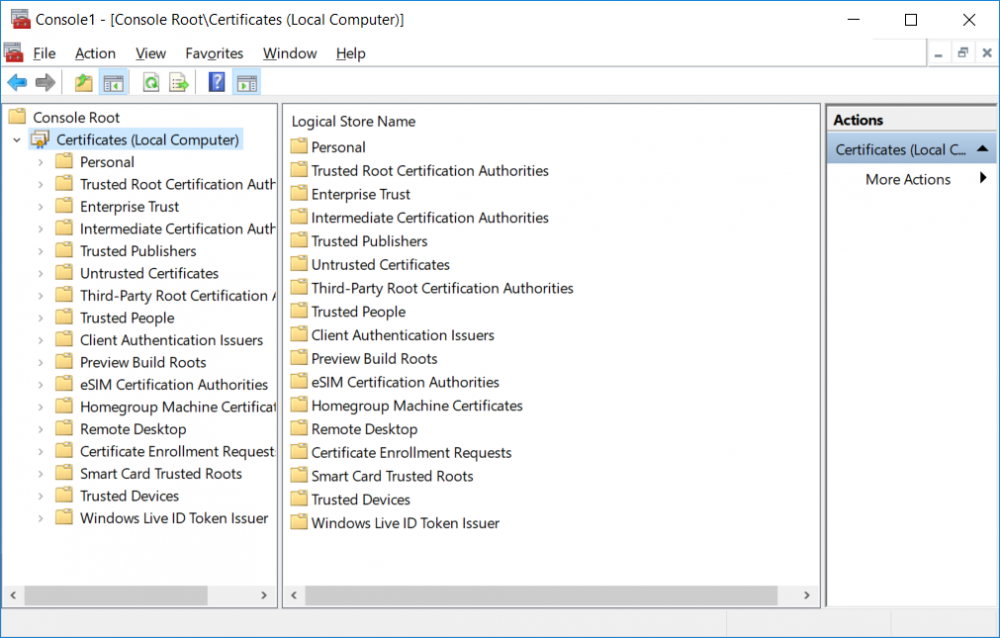
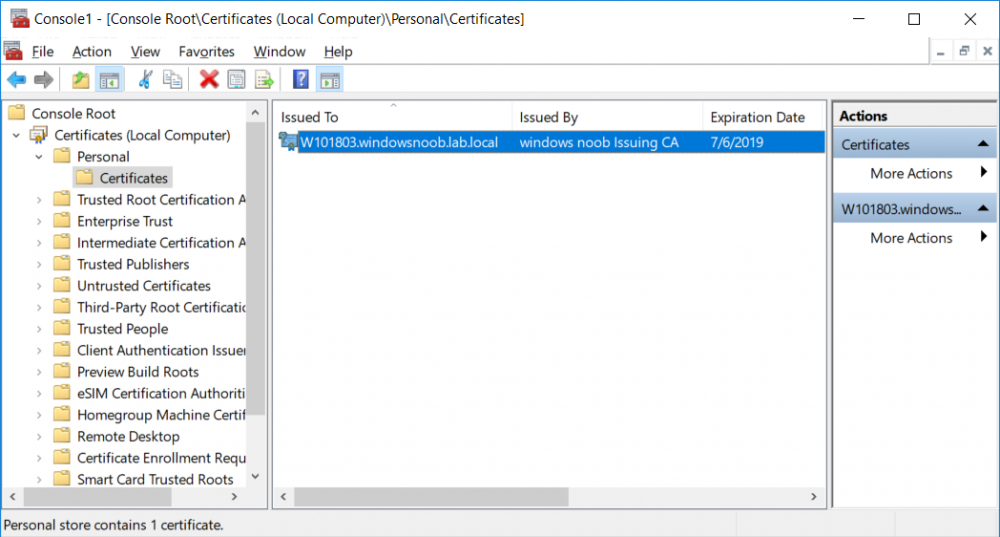
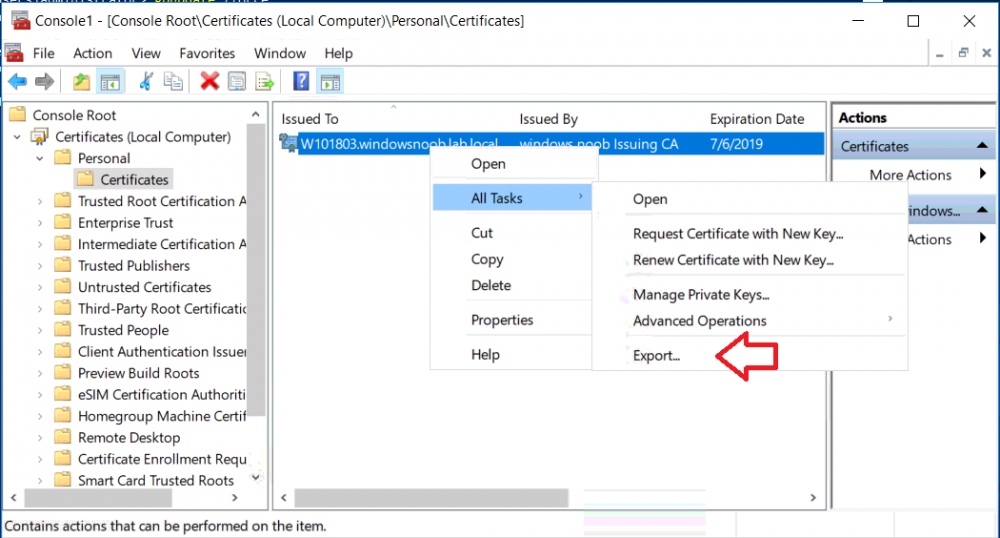
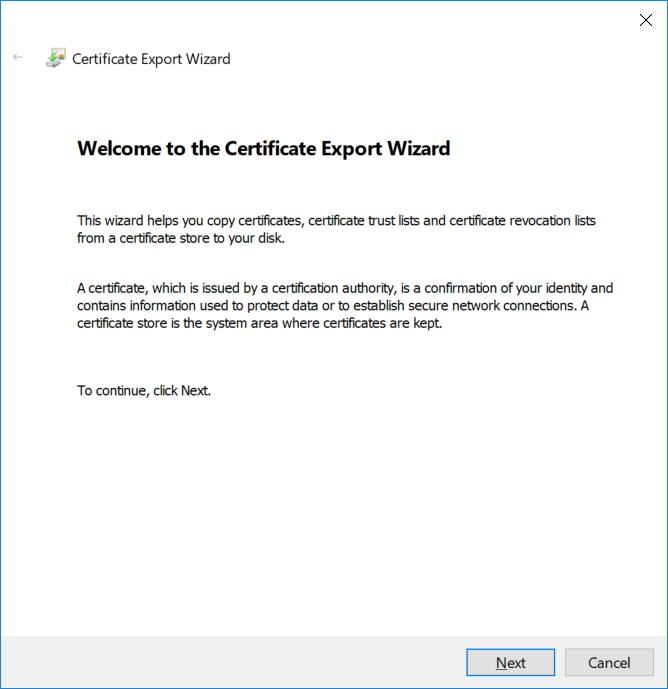
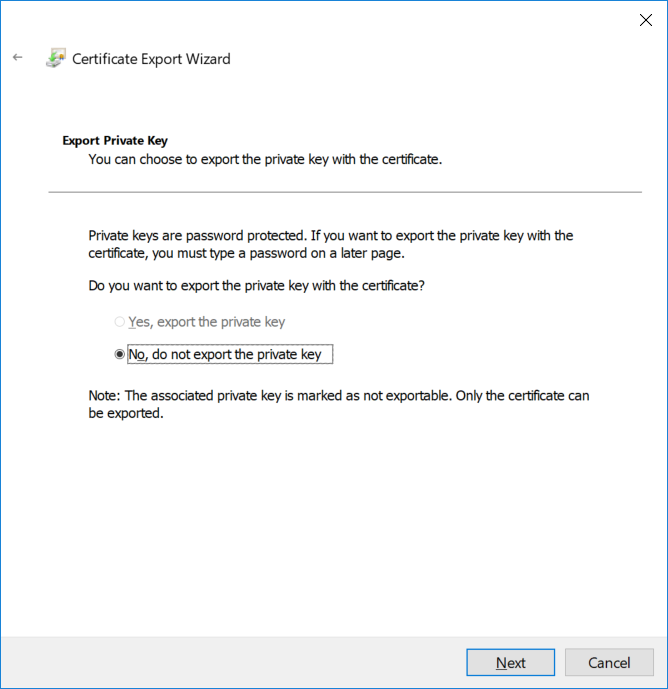
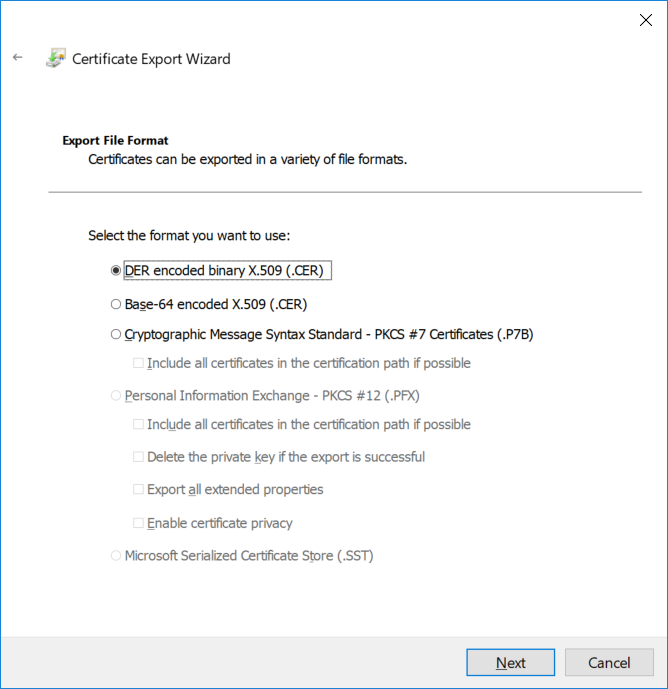
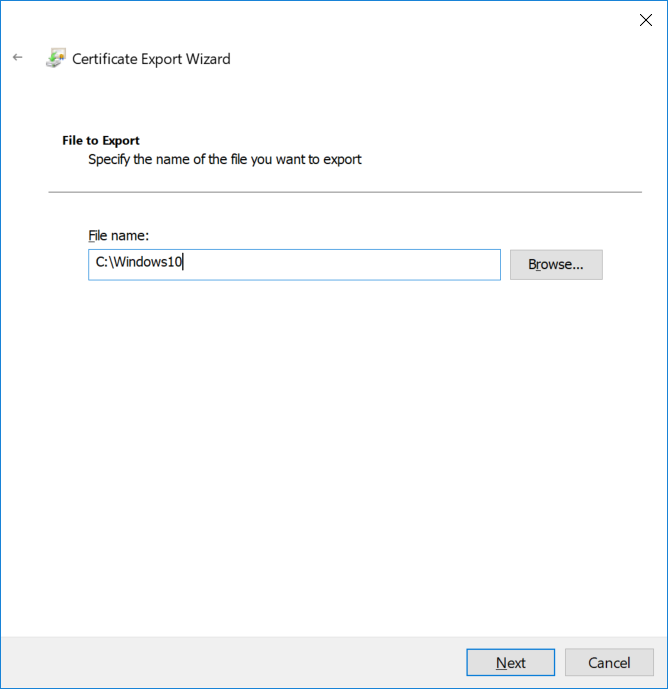
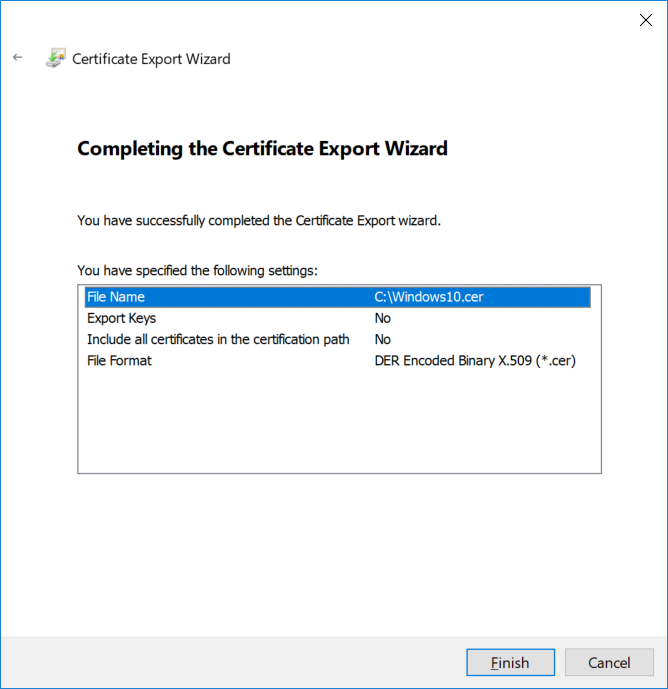
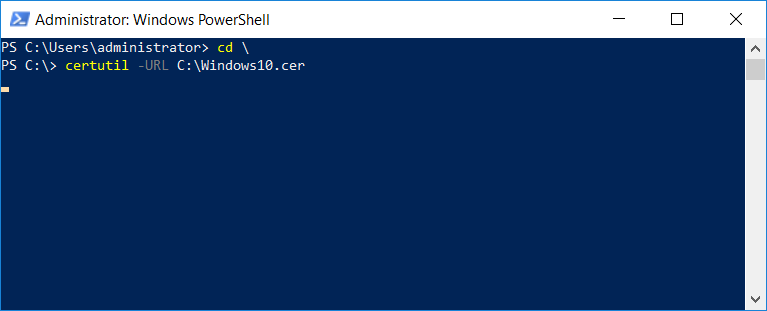
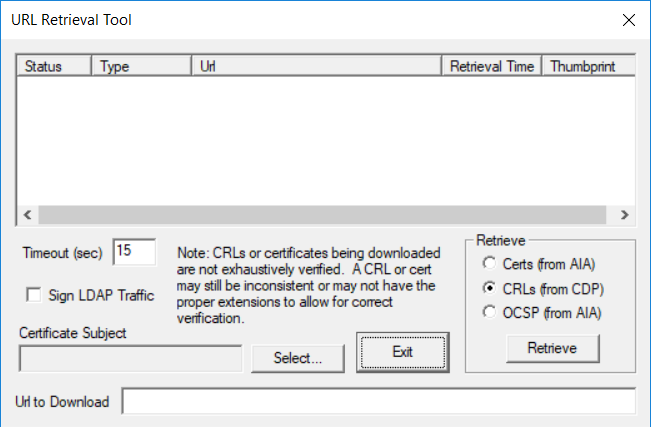
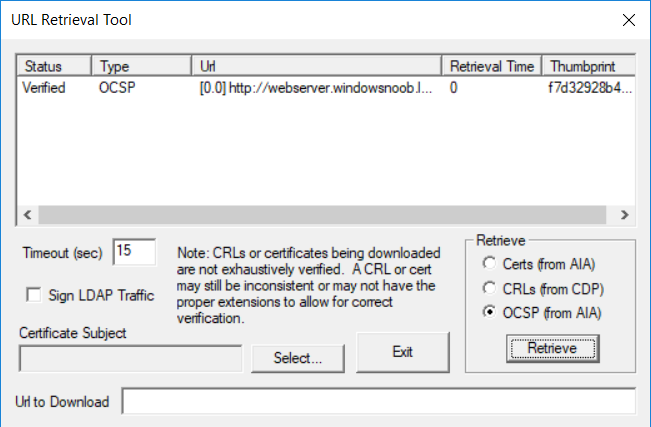
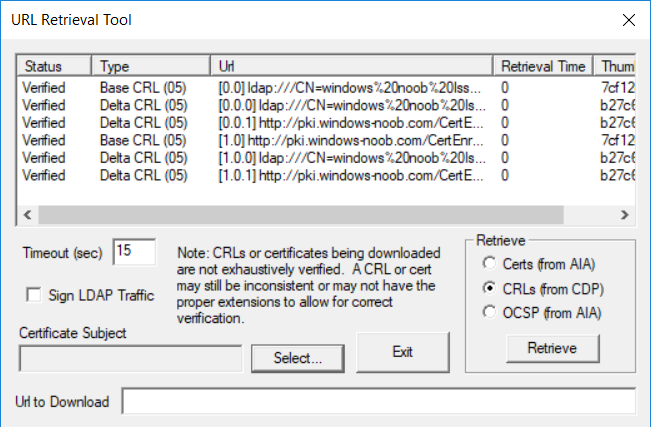
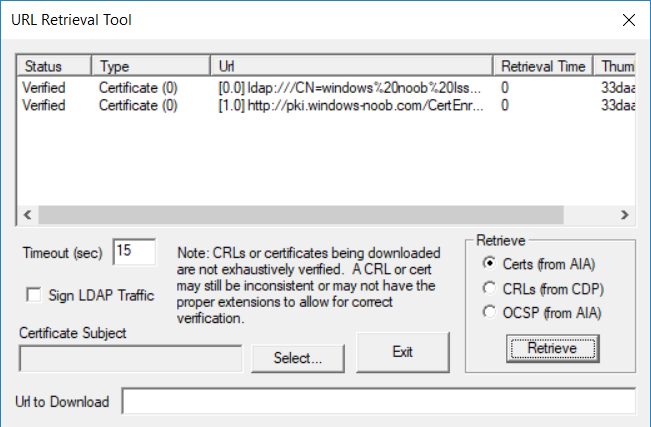
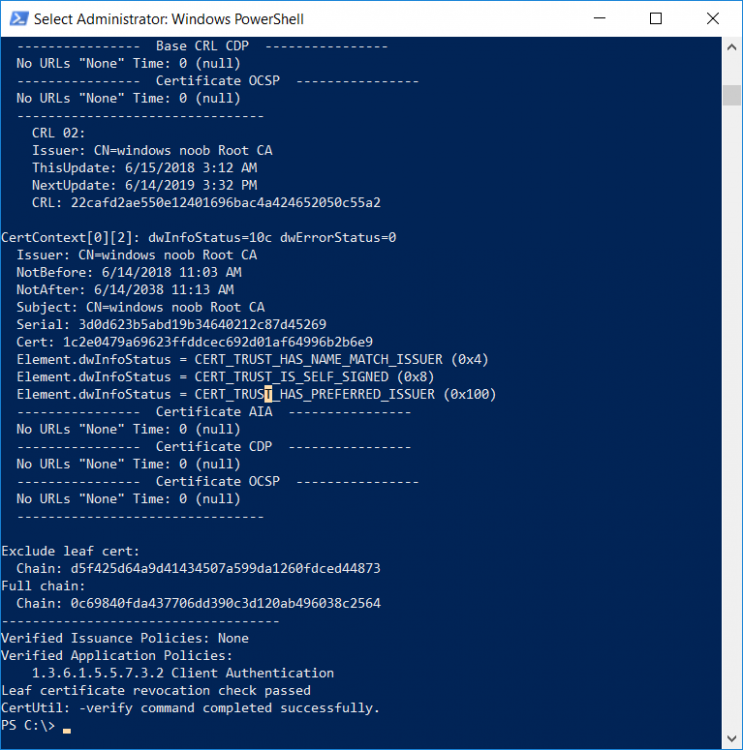
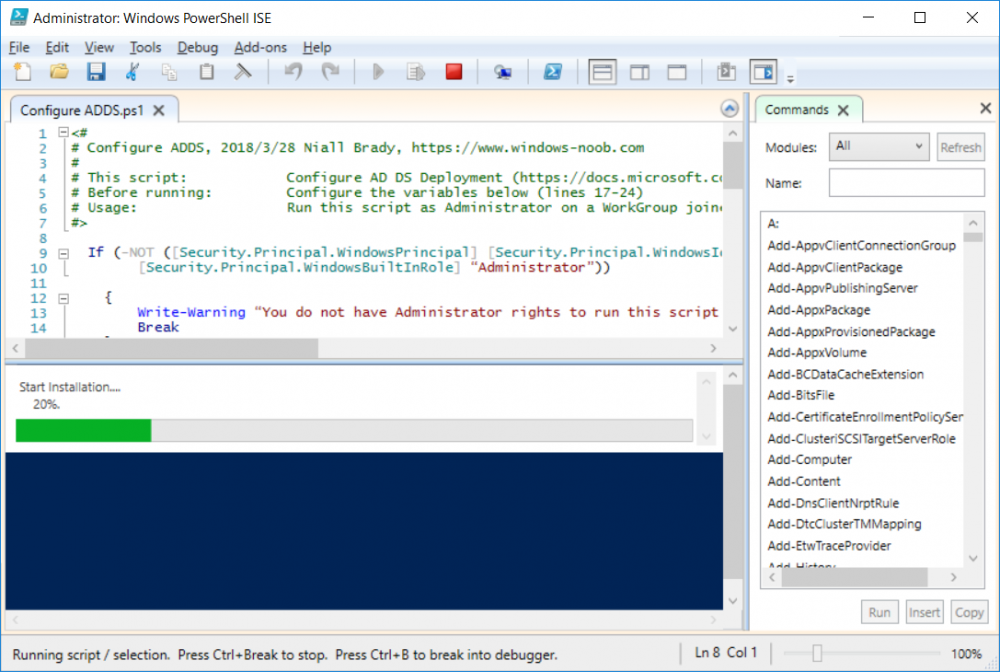
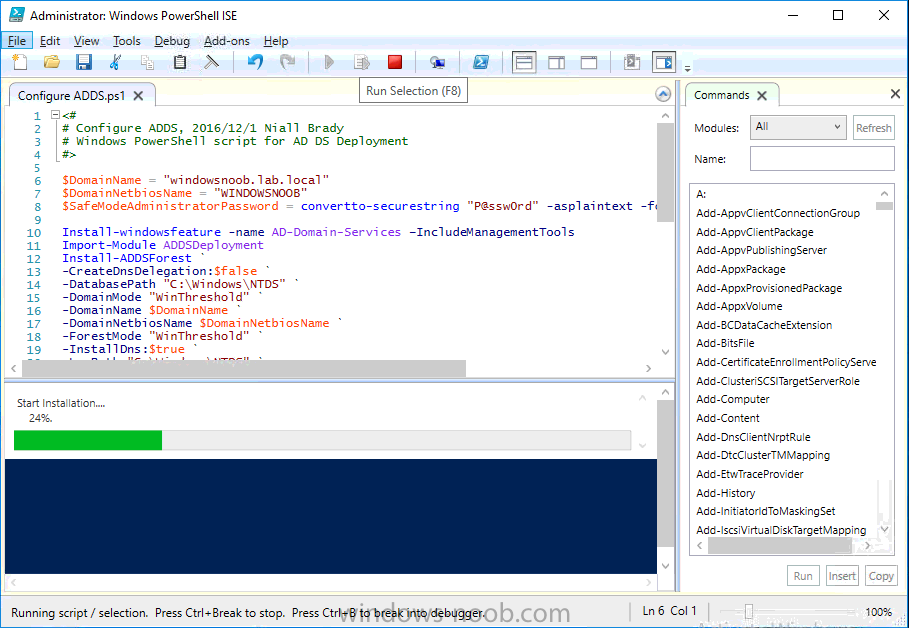
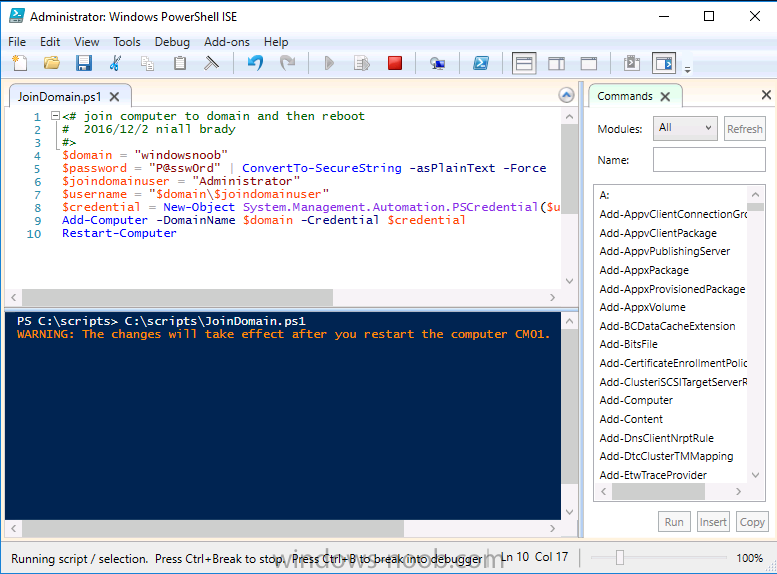
This series is comprised of different parts, listed below. Part 1 - Introduction and server setup Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication Part 4 - Post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 5 - Installing the Enterprise Issuing CA Part 6 - Perform post installation tasks on the Issuing CA Part 7 - Install and configure the OCSP Responder role service Part 8 - Configure AutoEnroll and Verify PKI health (this part) In part 1 of this series, you configured your LAB for a 2 tier PKI hierarchy running on Windows Server 2016. You used PowerShell to create some virtual machines, and then installed Windows Server 2016, Windows 10 Enterprise version 1803 and optionally Smoothwall 3.1 before configuring the IP address scheme and Computer Names on the virtual machines. Finally you configured ADDS on DC01 so that you have a working Domain Controller for the rest of this LAB. In part 2 you installed and did the initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA. In part 3 you prepared the HTTP Web Server for CDP and AIA Publication and you created a DNS record for the publicly available web server. In part 4 you performed post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA to set certificate revocation list (CRL) period registry settings using CertUtil, and then enabled object access Auditing and finally, you configured three locations for the Authority Information Access (AIA) and four locations for the Certificate revocation list Distribution Point (CDP), again using CertUtil. In part 5 you joined the IssuingCA computer to the windowsnoob domain before creating a new CAPolicy.inf file which was customized for the Issuing CA role. Next, you published the Root CA Certificate and CRL (both to Active Directory and the HTTP web server) and you installed the Enterprise Issuing CA before submitting a request to the StandAlone Offline Root CA. Next you installed the Issuing CA Certificate using the response files from the StandAlone Offline Root CA on the removable media. In part 6, you performed post installation and configuration of the IssuingCA server by configuring Certificate Revocation and CA Certificate Validity Periods, you then enabled auditing on the CA server, and configured the AIA and CDP. In part 7 you installed and configured the OCSP responder role service on the web server. Now you will configure Auto Enrollment and Verify PKI health. Step 1.Configure a GPO for Auto Enrollment Logon to to the Domain Controller (DC01) as windowsnoob\Administrator. Click Start, click Run, and then type gpmc.msc and press enter. Expand Forest, expand Domains, expand windowsnoob.lab.local, and then expand Group Policy Objects. Right click Default Domain Policy, then click Edit. Under Computer Configuration, expand Policies, expand Windows Settings, expand Security Settings, and then expand Public Key Policies. Select Certificate Services Client - Auto-Enrollment, right click and choose Properties. Change it from Not Configured to Enabled and enable the following 2 options. Renew expired certificates, update pending certificates, and remove revoked certificates Update certificate that use certificate templates As shown here. Click Apply when done, and close the Group Policy Management Editor and then close the Group Policy Management Console. Step 2. Configure AutoEnrollment for Workstation Authentication on the Issuing CA Ensure that you are logged on as windowsnoob\EntAdmin on the Issuing CA server (IssuingCA), start the Certification Authority console by entering certsrv.msc, ensure that windowsnoob Issuing CA is expanded. Right-click on Certificate Templates, then select Manage. In the Certificate Templates that appear, select Workstation Authentication. Right click it, and select Properties, click on the Security tab, select Domain Computers and ensure that AutoEnroll is selected, click Apply. Step 3. Join the Windows 10 computer to the domain Logon to Windows 10 version 1803 computer (Win101803) as Administrator, and copy the JoinDomain.ps1 script below to a folder called C:\Scripts. Open the script in PowerShell ISE as Administrator, then run Set-ExecutionPolicy to unrestricted before running the JoinDomain.ps1 PowerShell script by clicking on the Green Arrow in Windows PowerShell ISE. JoinDomain.ps1 Note: The computer will reboot by itself after joining the windowsnoob.lab.local domain. Step 4. Check PKI Health with Enterprise PKI To use the Enterprise PKI console to check PKI health, on the IssuingCA server, ensure that you are logged on as windowsnoob\entadmin. Run PKIView.msc from an administrative command prompt. Right click Enterprise PKI and then click Manage AD Containers. On the NTAuthCertificates tab, verify the windows noob Issuing CA certificate appears with a status of OK as shown below: On the AIA Container tab, verify both the windows noob Root CA and the windows noob Issuing CA certificates are present with a status of OK. On the CDP Container tab, verify that the windows noob Issuing CA has both Delta CRL and Base CRL, and that the windows noob Root CA has a Base CRL present and with a status of OK. On the Certification Authorities Container, verify that the windows noob Root CA certificate is present and with a status of OK. and finally on the Enrollment Services Container tab, verify that the windows noob Issuing CA certificate is present with a status of OK. Step 5. Configure Certificate Distribution on the Issuing CA To publish a certificate for computers in the enterprise do as follows. Logon to the IssuingCA computer as windowsnoob\EntAdmin. In the Certification Authority console (certsrv.msc), ensure that windows noob Issuing CA is expanded. Right-click Certificate Templates, select New and select Certificate Template to Issue. On the Enable Certificate Templates dialog box, select Workstation Authentication and then click OK. Step 6. verify certificate autoenrollment on the Windows 10 client To verify that autoenrollment of certificates on the Windows 10 compute do as follows. Log on to win101803.windowsnoob.lab.local as windowsnoob\Administrator. (Ensure that you switch user to log on as windowsnoob\Administrator) Click Start, type mmc and then press ENTER. Click File, and then click Add/Remove Snap-in. Click Certificates, then click Add, Select Computer Account, and then click Finish. Click OK. Expand Personal and select Certificates, if you do not see Certificates, in an Administrative Command prompt issue the following command gpupdate /force then refresh the view in the Certificates MMC. You should now see a Certificates folder and a certificate listed. This certificate was issued using AutoEnrollment which was configured above. Step 7. Verify PKI health on the issued certificate While logged on to W101803.windowsnoob.local.local as windowsnoob\Administrator, In the certificates console tree, expand Personal, click Certificates. In the details pane, right click the W101803.windowsnoob.lab.local certificate, click All Tasks, and then click Export. the Welcome to the certificate export wizard appears, click Next. Click Next at the No do not export the private key screen On the Export File Format page, click Next. [DER encoded binary X.509 (.CER) is the default selection]. in the File to Export, call it C:\Windows10 at the completing the certificate export wizard screen click Finish. you should be notified of the success of the export. Open an administrative command prompt and run the following commands: cd\ then certutil -URL C:\Windows10.cer The URL retrieval tool should appear. In the URL Retrieval Tool, select the OCSP (from AIA) option and then click Retrieve. Confirm that it shows status as Verified. In the URL Retrieval Tool, select the CRLs (from CDP) option and then click Retrieve. Confirm that it shows status as Verified. In the URL Retrieval Tool, select the Certs (from AIA) option and then click Retrieve. Confirm that it shows status as Verified. Click Exit to close URL Retrieval Tool. From the administrative command prompt run following command to thoroughly verify the certificate chain retrieval and revocation status. certutil -verify -urlfetch C:\Windows10.cer you'll see a lot of output similar to the following PS C:\> certutil -verify -urlfetch C:\Windows10.cer Issuer: CN=windows noob Issuing CA DC=windowsnoob DC=lab DC=local Name Hash(sha1): b500ca9b33a216fcc44492f25bb6e6b8bd6a5a78 Name Hash(md5): b0c8a9c15f77c9e2b7af24718ab3f3ec Subject: EMPTY (DNS Name=W101803.windowsnoob.lab.local) Name Hash(sha1): f944dcd635f9801f7ac90a407fbc479964dec024 Name Hash(md5): a46c3b54f2c9871cd81daf7a932499c0 Cert Serial Number: 1e000000057a5838e2727d5162000000000005 dwFlags = CA_VERIFY_FLAGS_CONSOLE_TRACE (0x20000000) dwFlags = CA_VERIFY_FLAGS_DUMP_CHAIN (0x40000000) ChainFlags = CERT_CHAIN_REVOCATION_CHECK_CHAIN_EXCLUDE_ROOT (0x40000000) HCCE_LOCAL_MACHINE CERT_CHAIN_POLICY_BASE -------- CERT_CHAIN_CONTEXT -------- ChainContext.dwInfoStatus = CERT_TRUST_HAS_PREFERRED_ISSUER (0x100) ChainContext.dwRevocationFreshnessTime: 3 Weeks, 1 Hours, 35 Minutes, 37 Seconds SimpleChain.dwInfoStatus = CERT_TRUST_HAS_PREFERRED_ISSUER (0x100) SimpleChain.dwRevocationFreshnessTime: 3 Weeks, 1 Hours, 35 Minutes, 37 Seconds CertContext[0][0]: dwInfoStatus=102 dwErrorStatus=0 Issuer: CN=windows noob Issuing CA, DC=windowsnoob, DC=lab, DC=local NotBefore: 7/6/2018 4:04 AM NotAfter: 7/6/2019 4:04 AM Subject: Serial: 1e000000057a5838e2727d5162000000000005 SubjectAltName: DNS Name=W101803.windowsnoob.lab.local Template: Workstation Authentication Cert: 9eae120ea27c064e609df51cacda77e286a223d6 Element.dwInfoStatus = CERT_TRUST_HAS_KEY_MATCH_ISSUER (0x2) Element.dwInfoStatus = CERT_TRUST_HAS_PREFERRED_ISSUER (0x100) ---------------- Certificate AIA ---------------- Verified "Certificate (0)" Time: 0 33daad0a6923fdbd02300d703264d13d70eedf42 [0.0] ldap:///CN=windows%20noob%20Issuing%20CA,CN=AIA,CN=Public%20Key%20Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=windowsnoob,DC=lab,DC=local?cACertificate?base?objectClass=certificationAuthority Verified "Certificate (0)" Time: 0 33daad0a6923fdbd02300d703264d13d70eedf42 [1.0] http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/IssuingCA.windowsnoob.lab.local_windows%20noob%20Issuing%20CA.crt ---------------- Certificate CDP ---------------- Verified "Base CRL (05)" Time: 0 7cf12cea65a271e322dcd148dafca9890381d68c [0.0] ldap:///CN=windows%20noob%20Issuing%20CA,CN=IssuingCA,CN=CDP,CN=Public%20Key%20Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=windowsnoob,DC=lab,DC=local?certificateRevocationList?base?objectClass=cRLDistributionPoint Verified "Delta CRL (05)" Time: 0 b27c6e817abccb07e6d18c37c808013cc1377c1d [0.0.0] ldap:///CN=windows%20noob%20Issuing%20CA,CN=IssuingCA,CN=CDP,CN=Public%20Key%20Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=windowsnoob,DC=lab,DC=local?deltaRevocationList?base?objectClass=cRLDistributionPoint Verified "Delta CRL (05)" Time: 0 b27c6e817abccb07e6d18c37c808013cc1377c1d [0.0.1] http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/windows%20noob%20Issuing%20CA+.crl Verified "Base CRL (05)" Time: 0 7cf12cea65a271e322dcd148dafca9890381d68c [1.0] http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/windows%20noob%20Issuing%20CA.crl Verified "Delta CRL (05)" Time: 0 b27c6e817abccb07e6d18c37c808013cc1377c1d [1.0.0] ldap:///CN=windows%20noob%20Issuing%20CA,CN=IssuingCA,CN=CDP,CN=Public%20Key%20Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=windowsnoob,DC=lab,DC=local?deltaRevocationList?base?objectClass=cRLDistributionPoint Verified "Delta CRL (05)" Time: 0 b27c6e817abccb07e6d18c37c808013cc1377c1d [1.0.1] http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/windows%20noob%20Issuing%20CA+.crl ---------------- Base CRL CDP ---------------- OK "Delta CRL (07)" Time: 0 b27c6e817abccb07e6d18c37c808013cc1377c1d [0.0] ldap:///CN=windows%20noob%20Issuing%20CA,CN=IssuingCA,CN=CDP,CN=Public%20Key%20Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=windowsnoob,DC=lab,DC=local?deltaRevocationList?base?objectClass=cRLDistributionPoint OK "Delta CRL (07)" Time: 0 b27c6e817abccb07e6d18c37c808013cc1377c1d [1.0] http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/windows%20noob%20Issuing%20CA+.crl ---------------- Certificate OCSP ---------------- Verified "OCSP" Time: 0 f7d32928b44de5b419a11bac19cc56fad7d4f9ee [0.0] http://webserver.windowsnoob.lab.local/ocsp -------------------------------- CRL 05: Issuer: CN=windows noob Issuing CA, DC=windowsnoob, DC=lab, DC=local ThisUpdate: 7/3/2018 7:02 AM NextUpdate: 7/10/2018 7:22 PM CRL: 7cf12cea65a271e322dcd148dafca9890381d68c Delta CRL 07: Issuer: CN=windows noob Issuing CA, DC=windowsnoob, DC=lab, DC=local ThisUpdate: 7/5/2018 7:02 AM NextUpdate: 7/6/2018 7:22 PM CRL: b27c6e817abccb07e6d18c37c808013cc1377c1d Application[0] = 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2 Client Authentication CertContext[0][1]: dwInfoStatus=102 dwErrorStatus=0 Issuer: CN=windows noob Root CA NotBefore: 6/19/2018 4:34 AM NotAfter: 6/19/2028 4:44 AM Subject: CN=windows noob Issuing CA, DC=windowsnoob, DC=lab, DC=local Serial: 5600000002ff2362e624faf00a000000000002 Template: SubCA Cert: 33daad0a6923fdbd02300d703264d13d70eedf42 Element.dwInfoStatus = CERT_TRUST_HAS_KEY_MATCH_ISSUER (0x2) Element.dwInfoStatus = CERT_TRUST_HAS_PREFERRED_ISSUER (0x100) ---------------- Certificate AIA ---------------- Verified "Certificate (0)" Time: 0 1c2e0479a69623ffddcec692d01af64996b2b6e9 [0.0] ldap:///CN=windows%20noob%20Root%20CA,CN=AIA,CN=Public%20Key%20Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=windowsnoob,DC=lab,DC=local?cACertificate?base?objectClass=certificationAuthority Verified "Certificate (0)" Time: 0 1c2e0479a69623ffddcec692d01af64996b2b6e9 [1.0] http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/ROOTCA_windows%20noob%20Root%20CA.crt ---------------- Certificate CDP ---------------- Verified "Base CRL (02)" Time: 0 22cafd2ae550e12401696bac4a424652050c55a2 [0.0] ldap:///CN=windows%20noob%20Root%20CA,CN=ROOTCA,CN=CDP,CN=Public%20Key%20Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=windowsnoob,DC=lab,DC=local?certificateRevocationList?base?objectClass=cRLDistributionPoint Verified "Base CRL (02)" Time: 0 22cafd2ae550e12401696bac4a424652050c55a2 [1.0] http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/windows%20noob%20Root%20CA.crl ---------------- Base CRL CDP ---------------- No URLs "None" Time: 0 (null) ---------------- Certificate OCSP ---------------- No URLs "None" Time: 0 (null) -------------------------------- CRL 02: Issuer: CN=windows noob Root CA ThisUpdate: 6/15/2018 3:12 AM NextUpdate: 6/14/2019 3:32 PM CRL: 22cafd2ae550e12401696bac4a424652050c55a2 CertContext[0][2]: dwInfoStatus=10c dwErrorStatus=0 Issuer: CN=windows noob Root CA NotBefore: 6/14/2018 11:03 AM NotAfter: 6/14/2038 11:13 AM Subject: CN=windows noob Root CA Serial: 3d0d623b5abd19b34640212c87d45269 Cert: 1c2e0479a69623ffddcec692d01af64996b2b6e9 Element.dwInfoStatus = CERT_TRUST_HAS_NAME_MATCH_ISSUER (0x4) Element.dwInfoStatus = CERT_TRUST_IS_SELF_SIGNED (0x8) Element.dwInfoStatus = CERT_TRUST_HAS_PREFERRED_ISSUER (0x100) ---------------- Certificate AIA ---------------- No URLs "None" Time: 0 (null) ---------------- Certificate CDP ---------------- No URLs "None" Time: 0 (null) ---------------- Certificate OCSP ---------------- No URLs "None" Time: 0 (null) -------------------------------- Exclude leaf cert: Chain: d5f425d64a9d41434507a599da1260fdced44873 Full chain: Chain: 0c69840fda437706dd390c3d120ab496038c2564 ------------------------------------ Verified Issuance Policies: None Verified Application Policies: 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2 Client Authentication Leaf certificate revocation check passed CertUtil: -verify command completed successfully. PS C:\> Review the output and make sure all the chain retrieval and revocation status are successfully verified. Job done ! That's it for this mini-series about setting up PKI in a lab, thanks for joining me, I hope you completed everything successfully and have a better understanding of how PKI works and how to set it up in a lab. Next steps If you'd like to see how SCCM works with HTTPS, see below:- How can I configure System Center Configuration Manager in HTTPS mode (PKI) - Part 1 How can I configure System Center Configuration Manager in HTTPS mode (PKI) - Part 2 cheers niall.3 points
-
Thanks for your guidance, it is a very helpful! I did all the steps on my test infrastructure, though I had a reduced set of virtual machines. It seems to me that there is an error in section 5 (maybe my comment will help other people) You suggest to execute the command: certutil -f -dspublish "E: \ ROOTCA_windows noob Root CA.crt" RootCA Where RootCA , as you write, is the host name of offline Root CA, however certutil helps us: CertUtil [Options] -dsPublish CertFile [NTAuthCA | RootCA | SubCA | CrossCA | KRA | User | Machine] ... CertFile - certificate file to publish NTAuthCA - Publish cert to DS Enterprise store RootCA - Publish cert to DS Trusted Root store SubCA - Publish CA cert to DS CA object CrossCA - Publish cross cert to DS CA object ... So RootCA in this case is not the host name here, but the store name. Your host name matches the store name, and your command has been executed. My Root CA name was different, and when I will have tried to execute the command certutil -f -dspublish "C:\from_RCA\RCA01_My-CA.crt" RCA01 i got an error CertUtil: -dsPublish command FAILED: 0x80070057 (WIN32: 87 ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER) CertUtil: The parameter is incorrect. however command certutil -f -dspublish "C:\from_RCA\RCA01_My-CA.crt" RootCA performed correctly. Next command in your manual certutil -f -dspublish "E: \ windows noob Root CA.crl" RootCA is correct, because to publish CRL you must specify the host name: CertUtil [Options] -dsPublish CRLFile [DSCDPContainer [DSCDPCN]] .... CRLFile - CRL file to publish DSCDPContainer - DS CDP container CN, usually the CA machine name3 points
-
glad to hear it, to summarize Microsoft is aware of the issue and has produced a fix3 points
-
To piggy back off this, talked to HP about this earlier today as well. Pre-release BIOS are available but they need to have it approved/signed off before providing it for testing purposes. I was told mid-April is their tentative release date for this. Anything with a kaby lake processor is having the UEFI PXE boot issues according to them or have had reports. They pointed to the G4 model laptops and the G3+ model desktop machines.3 points
-
This list of guides is a living index covering Windows 365 Cloud PC, Microsoft Intune or Configuration Manager. The Configuration Manager Current Branch releases are meant for your production deployments and the Technical Preview releases are for testing new upcoming features in the product, and are aimed at Lab use only. The PKI guides are added as https communication within ConfigMgr and Intune is desired. These guides are broken down into different sections: Windows 365 Microsoft Intune Configuration Manager - Current Branch Configuration Manager - Technical Preview Setting up PKI Note: The guides in each section are (mostly) sorted in the direction of oldest first. Windows 365 How can I delete a Windows 365 Cloud PC How can I use multiple monitors with Windows 365 Using Windows 365 with Linux Introducing the Windows 365 App How can I resize a Windows 365 Cloud PC USA Windows 365 User Group session – video available Windows 365 – Your connection failed – Error Code 0x3000047 How can I configure alerts for Windows 365 activity in Intune Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 1. Introduction Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 2. Provisioning an Azure Ad Joined Cloud PC Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 3. Provisioning a Hybrid Azure Ad Joined Cloud PC Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 4. Connecting to your Cloud PC Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 5. Managing your Cloud PC Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 6. Point in time restore Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 7. Patching your Cloud PCs with Windows Autopatch Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 8. Windows 365 boot Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 9. Windows 365 switch Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 10. Windows 365 offline Windows 365 app not connecting try this Using alternate ANCs in your Windows 365 provisioning policy Location redirection with Windows 365 Troubleshooting Windows 365 connection issues via the troubleshoot option in the Windows 365 app A quick look at some of the new features in the Windows 365 app An update about location redirection on Windows 365 Cloud PCs Windows 365 end user improvements - open in browser, open in desktop app Windows 365 web client can now use your camera New video: Windows 365 Switch in action Windows 365 boot and Windows 365 switch go GA! Automating Windows 365 part 1 - Introducing Graph and setting up Visual Studio code Automating Windows 365 part 2 - Using Graph X-Ray Automating Windows 365 part 3 - Provisioning Cloud PC's Automating Windows 365 part 4 - Managing your Cloud PC Automating Windows 365 part 5 - Cloud PC reports A quick look at Windows 365 Boot dedicated mode A quick look at Windows 365 Boot shared mode Microsoft Intune How can I find out version info about Intune Preview in Azure ? How can I unlock Windows Holographic for Business features in Intune Preview? How can I determine how long a blade loads in Intune Preview in Azure ? How can I check the status of my Intune service ? Intune Preview in Azure get’s a new look and Software Updates for Windows 10 ! What is Windows Information Protection and how can I use it to protect Enterprise data on Windows 10 devices using Intune Using Intune to enable WIP to protect Enterprise data on Windows 10 devices (MAM-WE) Getting started with Microsoft Graph and using PowerShell to automate things in Intune How can I integrate Microsoft Store for Business with Intune in Azure How can I create a dynamic group containing all Windows 10 version 1709 in Intune in Azure ? How can I enable MDM auto-enrollment in Azure How can I customize the start screen in Windows 10 using Intune How can I use Windows AutoPilot with a Proxy ? Troubleshooting “Something went wrong error 801c0003” during enrollment via Windows AutoPilot and Microsoft Intune Configuring BitLocker in Intune - Part 1. Configuring BitLocker Configuring BitLocker in Intune - Part 2. Automating Encryption Configuring BitLocker in Intune - Part 3. Testing the scripts How can I send notification messages using PowerShell in Microsoft Intune How can I deploy custom favorites in Microsoft Edge to Windows 10 devices using Microsoft Intune Managing devices with Microsoft Intune: What’s new and what’s next – my notes (Part 1 – new features) Managing devices with Microsoft Intune: What’s new and what’s next – my notes (Part 2 – iOS) Managing devices with Microsoft Intune: What’s new and what’s next – my notes (Part 3 – Android) Managing devices with Microsoft Intune: What’s new and what’s next – my notes (Part 4 – macOS) Managing devices with Microsoft Intune: What’s new and what’s next – my notes (Part 5 – Windows) Learn how to leverage Intune support for Microsoft Graph and PowerShell to enable powerful automation and IT security- my notes How Microsoft uses Intune internally to manage Windows devices Android device management with Microsoft Intune – Part 1. Partnerships Android device management with Microsoft Intune – Part 2. Deployment Scenarios Android device management with Microsoft Intune – Part 3. Dedicated device management Android device management with Microsoft Intune – Part 4. Coming soon and what’s new How can I create dynamic groups for different HoloLens devices in Microsoft Intune Troubleshooting app deployment in Windows Autopilot Configuring the Registered Owner and Organization in Windows Autopilot delivered PCs Removing company data from Endpoint Manager enrolled phones Office 365 issues after Windows Autopilot Displaying a welcome page after Windows Autopilot completes Adding devices to an Azure AD group after Windows Autopilot is complete - part 1 Adding devices to an Azure AD group after Windows Autopilot is complete - part 2 Gathering logs and sending an email when resetting Windows Autopilot - part 1 Gathering logs and sending an email when you need to reset Windows Autopilot - part 2 Gathering logs and sending an email when you need to reset Windows Autopilot - part 3 Adding devices or users to an Azure AD group after Windows Autopilot is complete but only when the device is marked as Compliant Using the updated & secure Retire My PC app via Company Portal Prompting standard users to confirm or change Regional, Time Zone and Country settings after Windows Autopilot enrollment is complete Encrypting devices during Windows Autopilot provisioning (WhiteGlove) - Part 1 Encrypting devices during Windows Autopilot provisioning (WhiteGlove) - Part 2 Encrypting devices during Windows Autopilot provisioning (WhiteGlove) - Part 3 Deploying KB5030310 to devices as a Win32 app for Copilot Using remediation scripts to automate a setting for Copilot How can I disable Copilot ? Configuration Manager Current Branch Installation - How can I install System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Configuring Discovery - How can I configure discovery for System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Configuring Boundaries - How can I configure boundaries in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Using Updates and Servicing in Offline mode - How can I use Updates and Servicing in Offline mode in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Using Updates and Servicing in Online mode - How can I use Updates and Servicing in Online mode in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Setting up the Software Update Point - How can I setup Software Updates in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Installing the Client agent - How can I configure client settings and install the ConfigMgr client agent in System Center Configuration Manager Current Branch Upgrading to System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1602 from System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1511 How can I use the Upgrade Task Sequence in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) ? How can I use servicing plans in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) to upgrade Windows 10 devices ? How can I deploy Windows 10 with MDT 2013 Update 2 integrated with System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Setting up PKI Part 1 - Introduction and server setup Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication Part 4 - Post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 5 - Installing the Enterprise Issuing CA Part 6 - Perform post installation tasks on the Issuing CA Part 7 - Install and configure the OCSP Responder role service Part 8 - Configure AutoEnroll and Verify PKI health How can I configure System Center Configuration Manager in HTTPS mode (PKI) - Part 1 How can I configure System Center Configuration Manager in HTTPS mode (PKI) - Part 2 New video: Fixing expired Root CA CDP and Crypt_E_REVOCATION_OFFLINE problems cheers niall3 points
-
figure this out for anyone interested, found an article from 2012 that outlines some registry key changes you need to make on you cluster nodes. https://forum.red-gate.com/discussion/15396/error-monitoring-clustered-sql-server snippet taken from the article above. Of the tests we conducted above the root cause of the short file name error during the Pre-req checks was found to be the fact that we were not able to remotely access the registry using the SQL Virtual name which we should have been able to do. On contacting Microsoft Support we were informed that there are known issues around NoRemap registry key needing to be set if you are using Network Name resource that is dependent on a separate new IP Address resource – see http://support.microsoft.com/?id=306985 The final solution was to add a new REG_MULTI_SZ registry key to BOTH cluster nodes called:- NoRemapPipes to:- HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\lanmanserver\parameters\ This key should contain the values of:- WINREG EVENTLOG svcctl After adding the above key and values we needed to reboot both cluster nodes and then we were able to connect to the SQL Virtual names (CLUSQL02 + CLUSQL01) using Regedit (Remote registry). Running the SCCM Pre –req checker now returns no errors. Hope this soluton helps someone else.2 points
-
if this is a lab i'd suggest you rebuild the lab (doesn't take long) and before converting the lab to PKI take snapshots of the virtual machines, so you have different states (http/https/e-http) if you cannot do that then you'll have to experiment with removing bindings in IIS for https, removing the certificates to the dp role and more, and removing certificate services, quite a mess, you could basically undo all the settings where you switched to HTTPS back to HTTP2 points
-
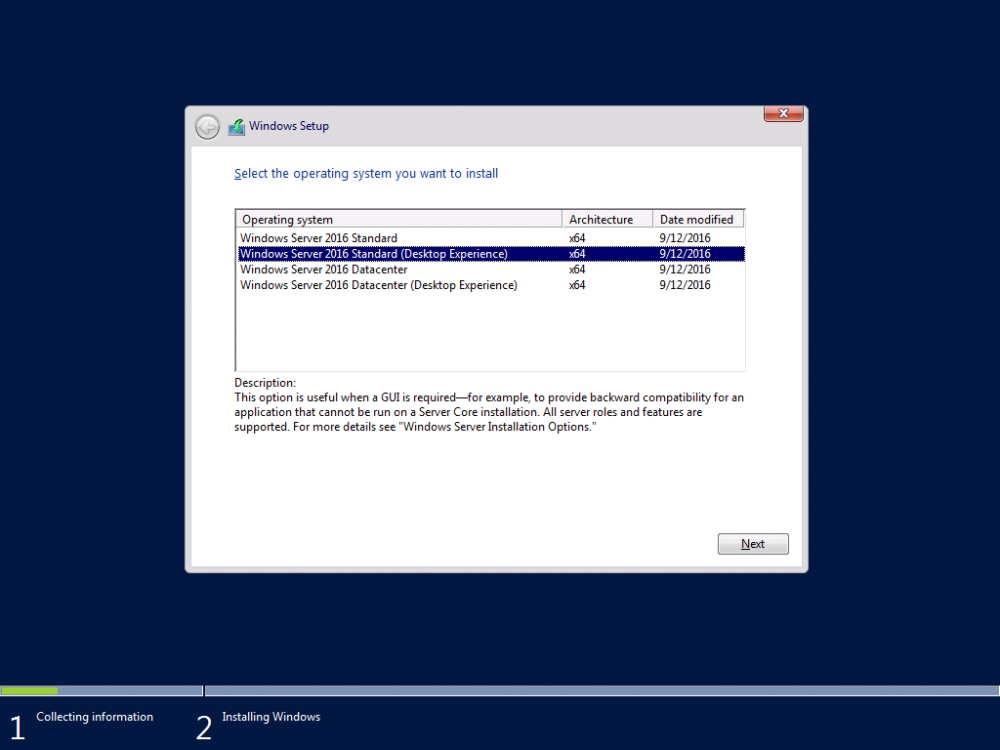
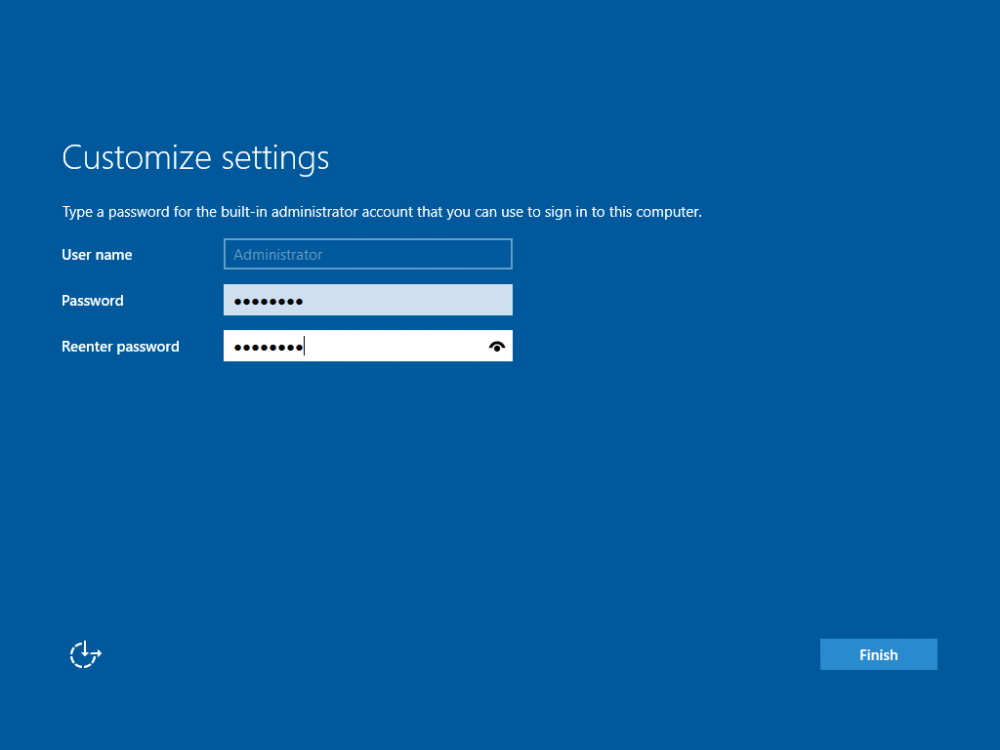
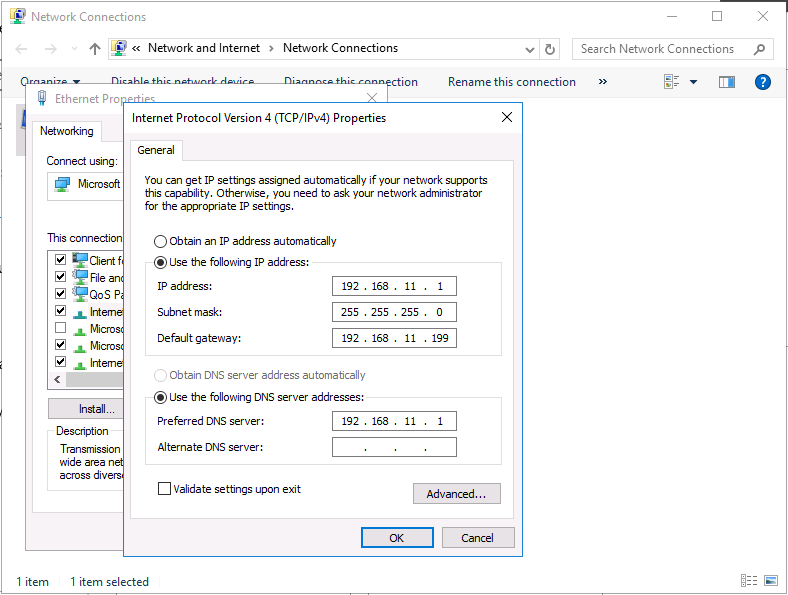
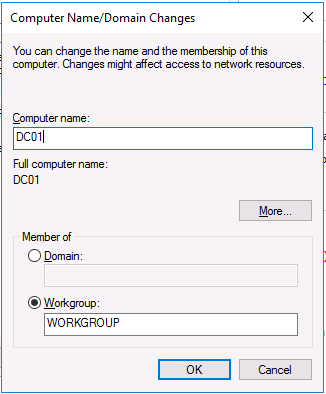
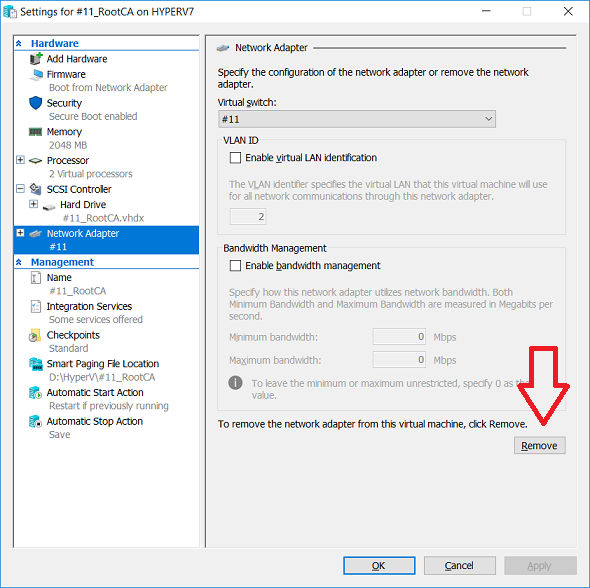
This series is comprised of different parts, listed below. Part 1 - Introduction and server setup (this part) Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication Part 4 - Post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 5 - Installing the Enterprise Issuing CA Part 6 - Perform post installation tasks on the Issuing CA Part 7 - Install and configure the OCSP Responder role service Part 8 - Configure AutoEnroll and Verify PKI health Introduction Security is everywhere, and a core component of security is certificates. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store, and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption (1). In this series of guides I will show you how to set up a 2 tier PKI hierarchy running on Windows Server 2016 and you can use this to set up your own LAB so that you can learn about PKI and later use it for related System Center Configuration Manager roles such as Co-Management (3). Note: I don't claim to be an expert on PKI and would absolutely advise you to consult with a PKI expert if you plan on setting up PKI in production. This guide is designed to help you setup your LAB, it's based on a Windows Server 2012 R2 PKI guide on Technet from here and kudos to those guys for writing it (2). The difference here is you'll be using Windows Server 2016 and you'll see more screenshots and hints to guide you through the experience. I'd highly recommend you go through this entire series at least twice, just to get a feel for how PKI works and to become familiar with the terms involved. The first time you complete this series will probably feel laborious, however the second time you do it things will start to make sense and you'll have a better understanding of why you are doing it. This series will be tough to wrap your head around especially if you are new to PKI, but take it one part at a time, one step at a time, methodically. If in any doubt, about any of the content then please ask your questions here by starting a new thread. By the end of this series of guides you'll have the following setup and running in your windowsnoob.lab.local PKI LAB. Domain Controller (Windows Server 2016) - 192.168.11.1 Issuing CA (Windows Server 2016) - 192.168.11.2 Webserver (Windows Server 2016) - 192.168.11.3 Offline Root CA (Windows Server 2016) Windows 10 (Windows 10 Enterprise, version 1803) - 192.168.11.4 (Optional) Smoothwall NAT (linux) - 192.168.11.199 and MMC based applications like this screenshot from the Enterprise Issuing CA will become familiar to you Before we start the series let's list some of the terms you'll see popping up over and over. I will try to explain them as we move through the guide. PKI - Public Key Infrastructure AIA - Authority Information Access CDP - Certificate revocation list Distribution Point CRL - Certificate Revocation List OCSP - Online certificate status protocol CA - Certificate Authority Note: I'd recommend that you snapshot (checkpoint) the Virtual Machines at the end of each part of this series, so if you make a mistake, you can always back track to a known good state. Step 1. Create the Virtual Machines I use Hyper-V for my labs, as it's a role built into Windows Server 2016 (and even Windows 10), so as long as your computer is relatively new and the hardware supports virtualization, you can use it (simply enable the role, reboot, and start using it). You should have at least 16GB of ram and 500GB of SSD storage to set this lab up comfortably. To quickly create the virtual machines I use a PowerShell script which I wrote, you can download it here. Download the script - Create HyperV VMv2.ps1 Virtual Machine Names For this LAB, please use the following naming convention for your virtual machines (note this is not the computer name but the virtual machine name). #11_DC01 #11_IssuingCA #11_RootCA #11_W10_1803 #11_Webserver #11_Smoothwall Note: The #11 prefix is simply a method I use in Hyper-V to separate my labs visually in Hyper-v manager, so #11 is one lab, and #10 is another (and so on). You don't have to use the same convention as I do, but it would make it easier for you to follow the entire series. I use the Smoothwall linux based NAT to provide Port Forwarding capability and to share internet into my various LABs. Virtual Machine Roles The Virtual Machines created will have the following functions #11_DC01 Roles: DC, DNS, LDAP CDP,AIA #11_IssuingCA Roles: Enterprise Issuing CA #11_RootCA Roles: Standalone Offline Root CA #11_W10_1803 Roles: A Windows client #11_Webserver Roles: Webserver HTTP CDP, AIA #11_Smoothwall Roles: Port Forward, Internet sharing Note: When prompted for a network switch, create a unique one (#11) for the first VM created, and use the same one for each of the other vm's (we will remove the network from the Offline Root CA). For generation type, use Gen 2. Below is how I created the virtual machines listed above. Note: After creating the virtual machines and before installing Windows Server 2016 on the Offline Root CA, you must remove the Network Card for the Offline Root CA virtual machine as it should not be connected to any network. Step 2. Install the virtual machines Install Server 2016 On DC01, RootCA, IssuingCA and Webserver, install Windows Server 2016. It's up to you how to do this, you can use an Automated MDT PowerShell script, or install them manually. To install all Windows Server 2016 on all 4 servers as WorkGroup joined computers do as follows.. Choose Windows Server 2016 Standard (Desktop Experience) Continue through the installation wizard until prompted for a password, use P@ssw0rd as the Administrator password Click Finish. And then logon using the Administrator username and password configured above. Once Windows is installed, set the IP address for each virtual machine as shown below. Note: Below are the Computer Name and IP addresses used in this guide. For the Offline Root CA, you must remove the Network card in the Hyper-V virtual machine settings. Computer Name: DC01, IP address: 192.168.11.1, Subnet mask 255.255.255.0, Default gateway: 192.168.11.199, Preferred DNS server: 192.168.11.1 Computer Name: IssuingCA, IP address: 192.168.11.2, Subnet mask 255.255.255.0, Default gateway: 192.168.11.199, Preferred DNS server: 192.168.11.1 Computer Name: Webserver, IP address: 192.168.11.3, Subnet mask 255.255.255.0, Default gateway: 192.168.11.199, Preferred DNS server: 192.168.11.1 Computer Name: RootCA, IP: <NO NETWORK> Computer Name: W101803, IP address: 192.168.11.4, Subnet mask 255.255.255.0, Default gateway: 192.168.11.199, Preferred DNS server: 192.168.11.1 Computer Name: smoothwall11, IP address: (Green, static) 192.168.11.199 (Red, DHCP internet IP) x.x.x.x Here's how you can set the IP address for DC01. And configure the Computer Name as per the list (in this example it's for the Domain Controller) Reboot when prompted. Install Windows 10 Enterprise version 1803 Install Windows 10 Enterprise, version 1803 on the remaining virtual machine (#11_W10_1803). Configure the Computer Name and IP address as specified. Leave it WorkGroup joined. Optionally install Smoothwall To learn how to setup Smoothwall express as a firewall see this blog post. Step 3. Configure ADDS on DC01 Now that you've installed the servers, it's time to make DC01 a domain controller, to do that we'll install Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) and to do that we'll use this PowerShell script, simply run the script as Administrator in Windows PowerShell ISE on DC01. Download the script -Configure ADDS.ps1 After running the script, DC01 is prompted to a Domain Controller and is ready for the next part of this series. Note: Please only run this script on the DC01 virtual machine. After running the script, the Domain Controller is ready for Part 2 (configured as dc01.windowsnoob.lab.local) and internet is working (via the Smoothwall) To continue with Part 2 of this series, click here. Recommended reading (1) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_key_infrastructure (2) - https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/15037.ad-cs-step-by-step-guide-two-tier-pki-hierarchy-deployment.aspx (3) - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/clients/manage/co-management-overview2 points
-
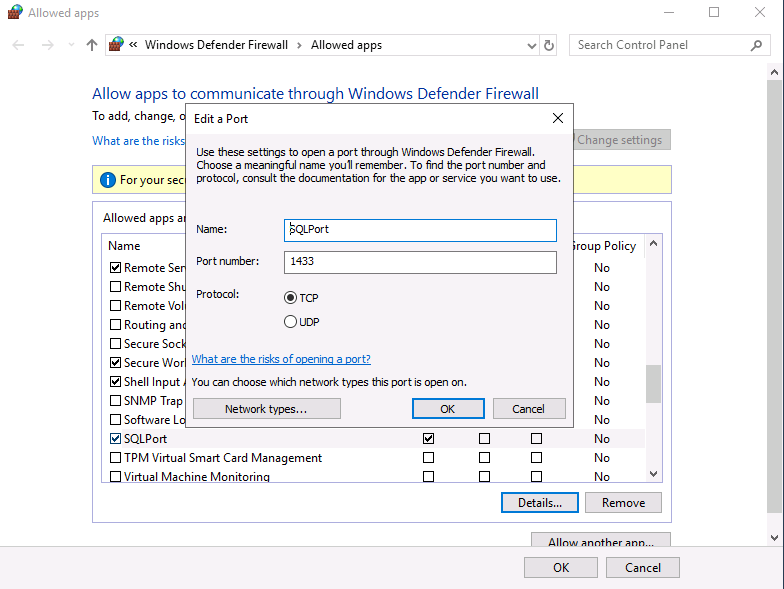
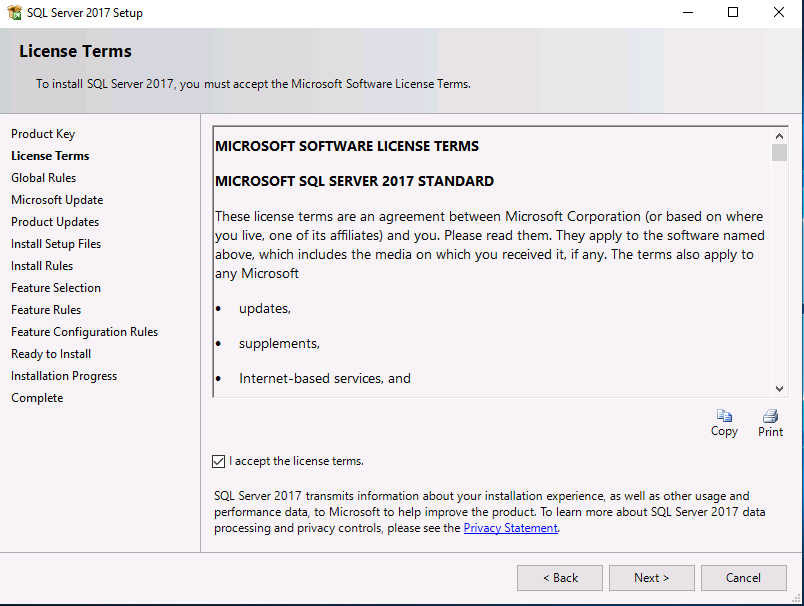
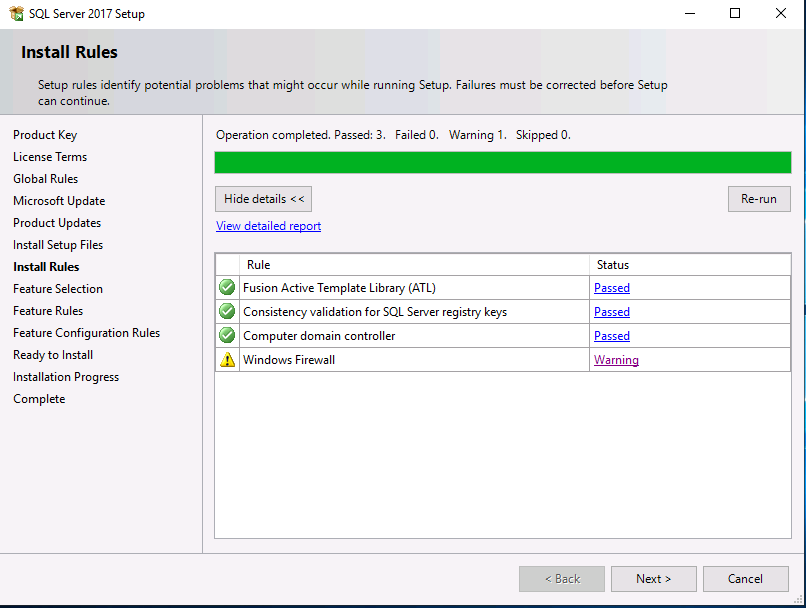
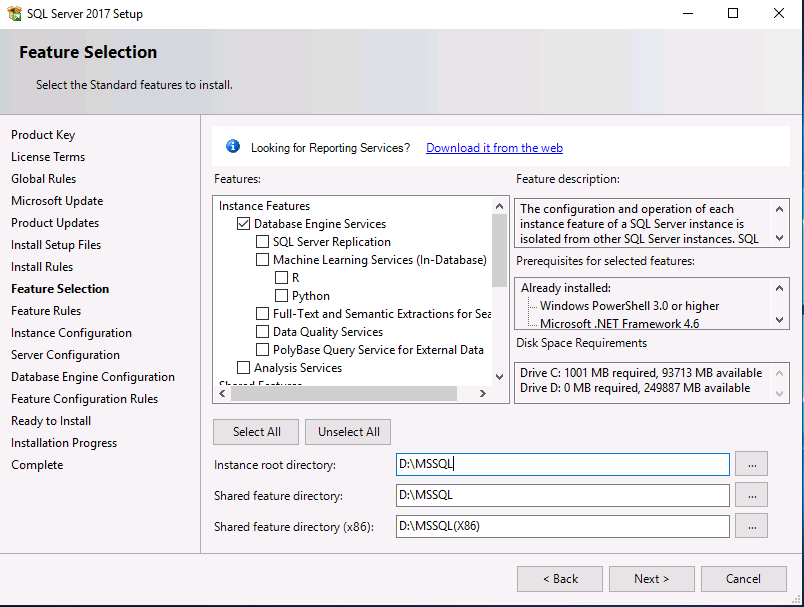
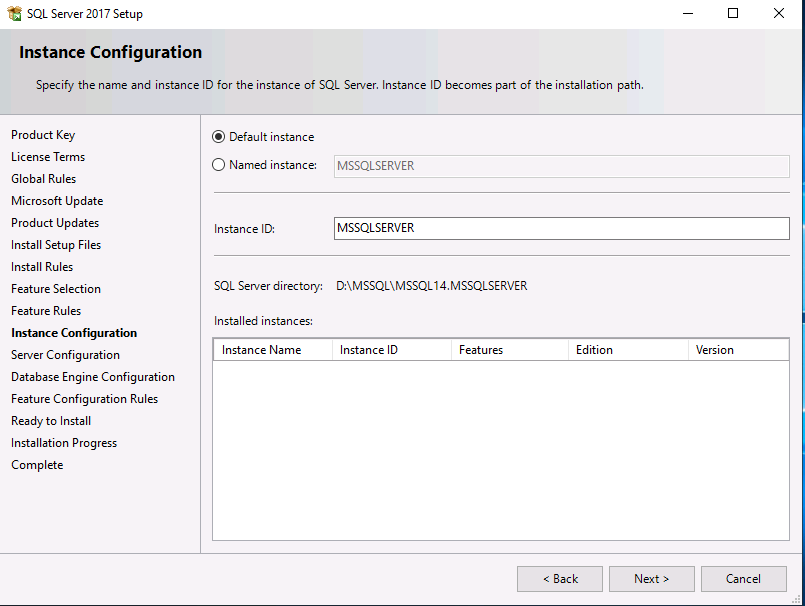
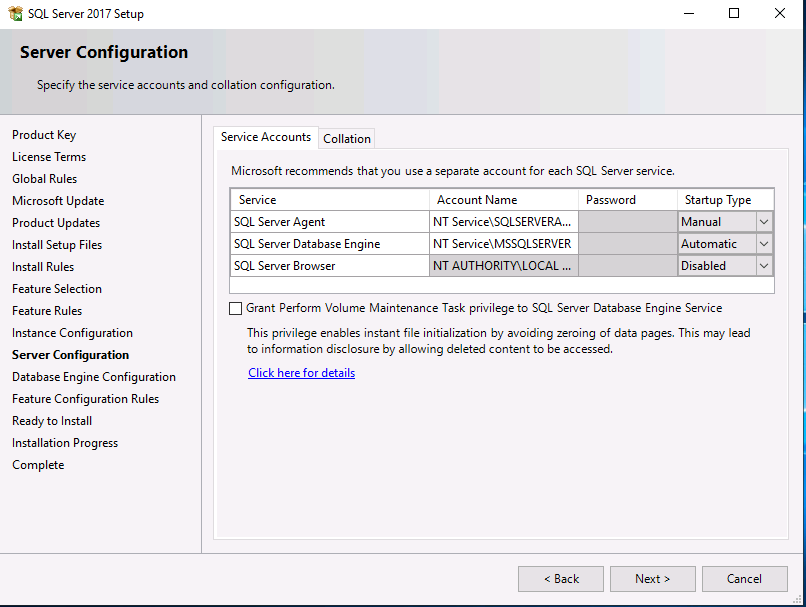
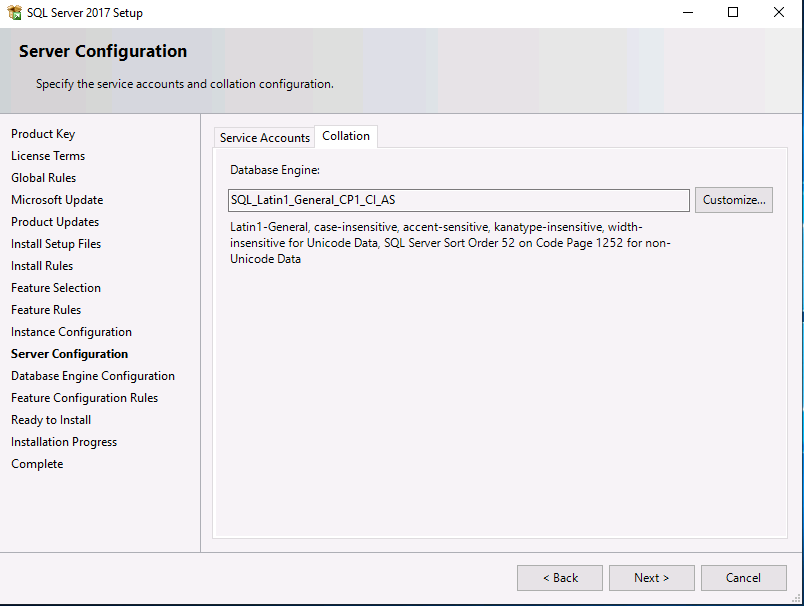
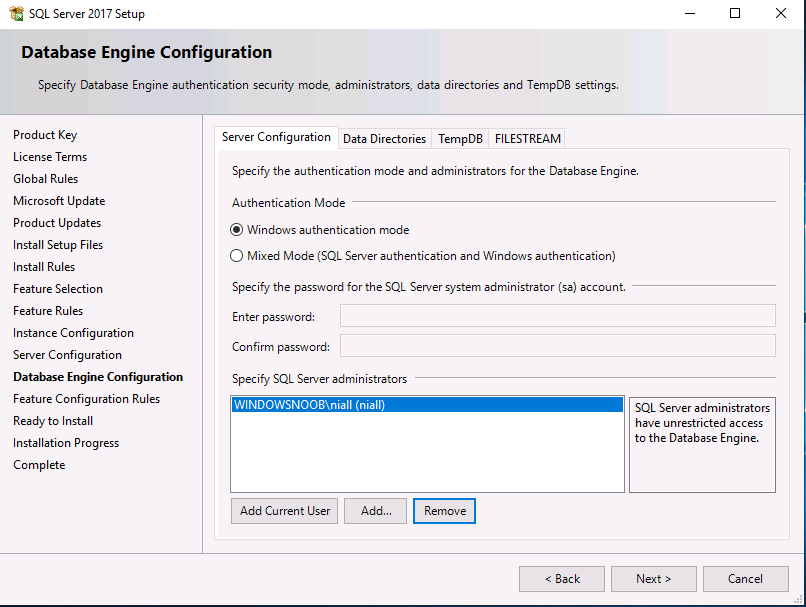
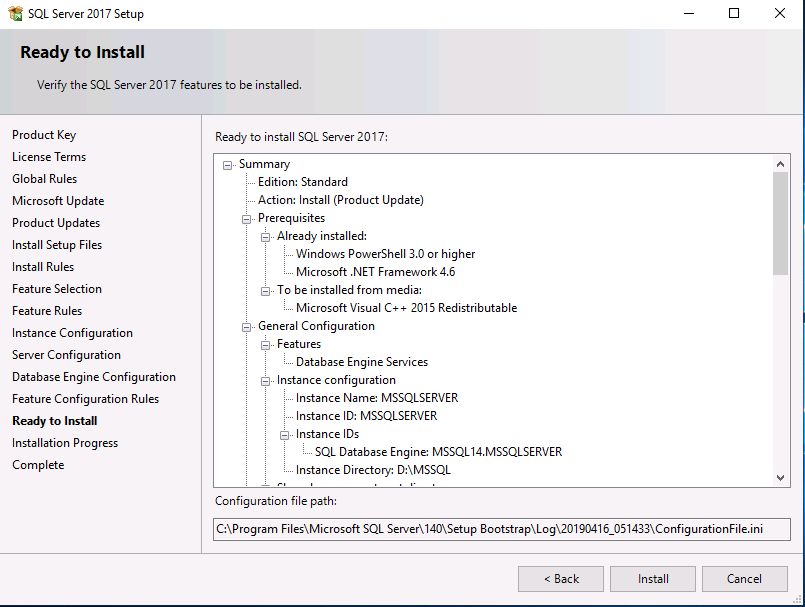
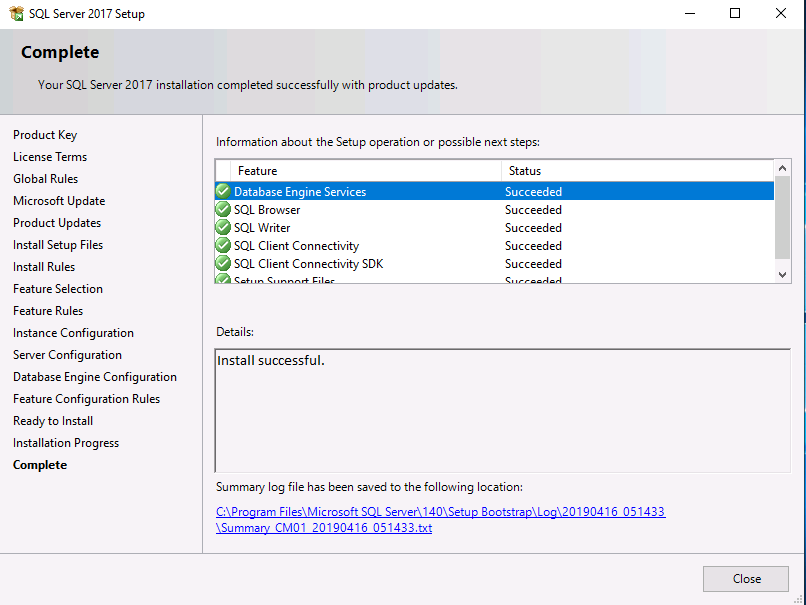
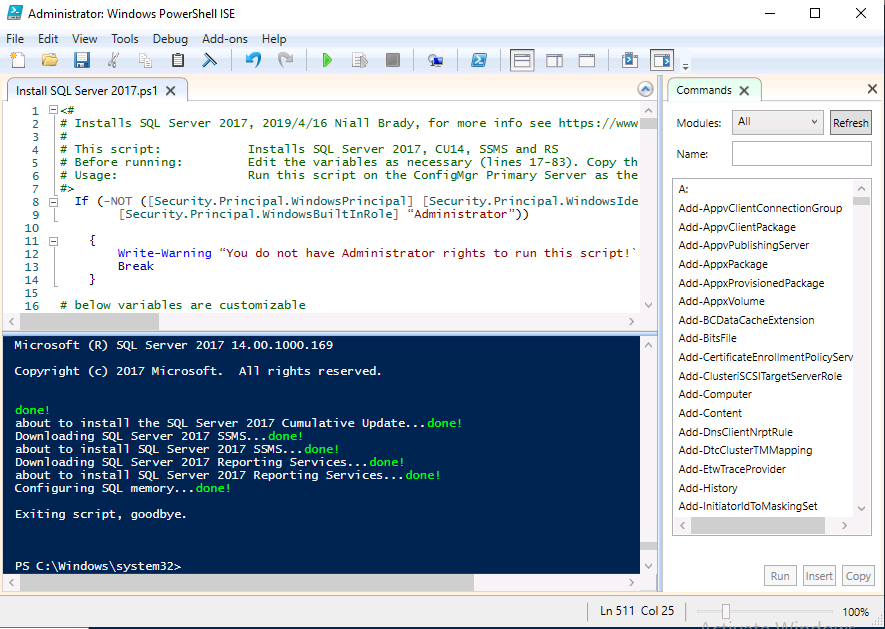
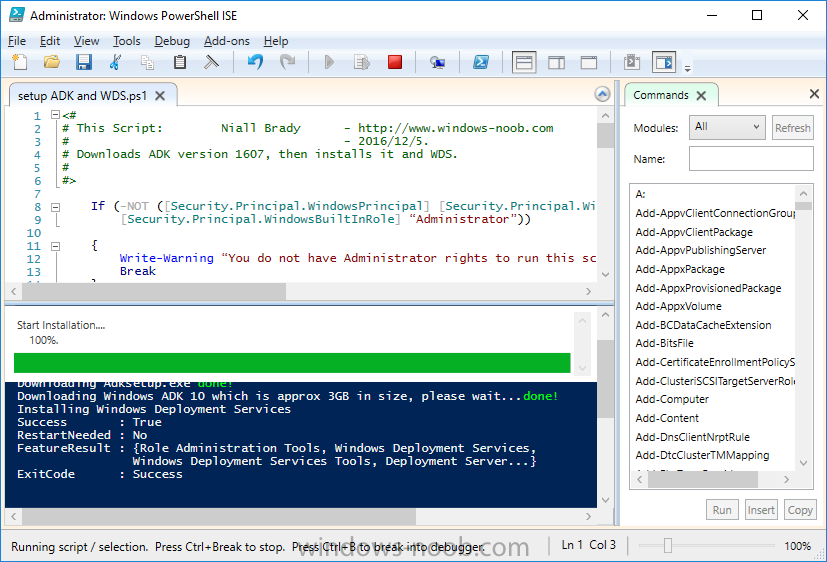
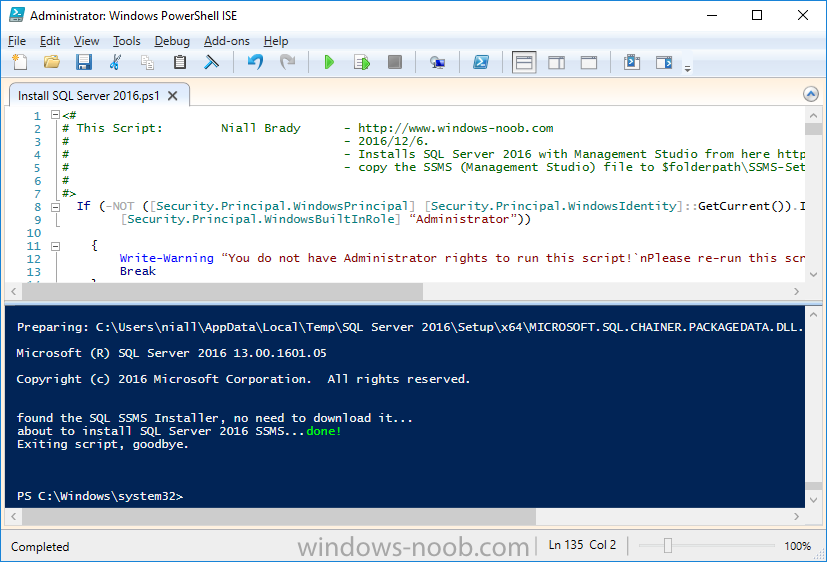
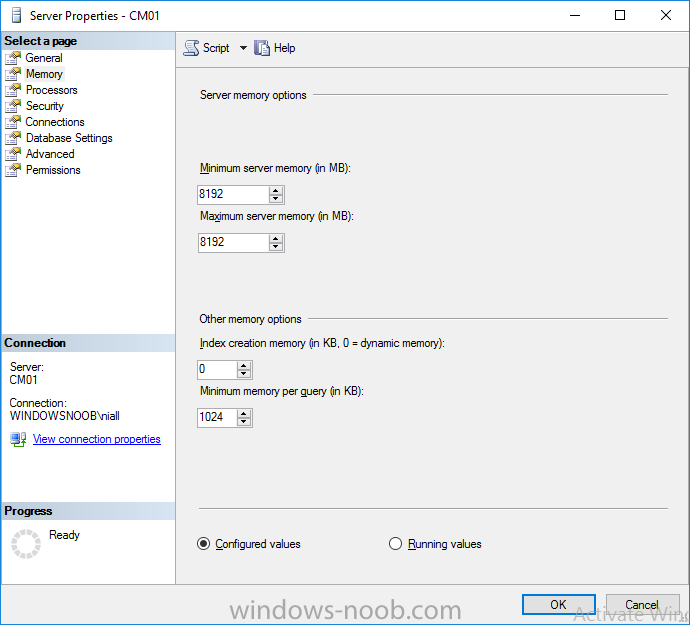
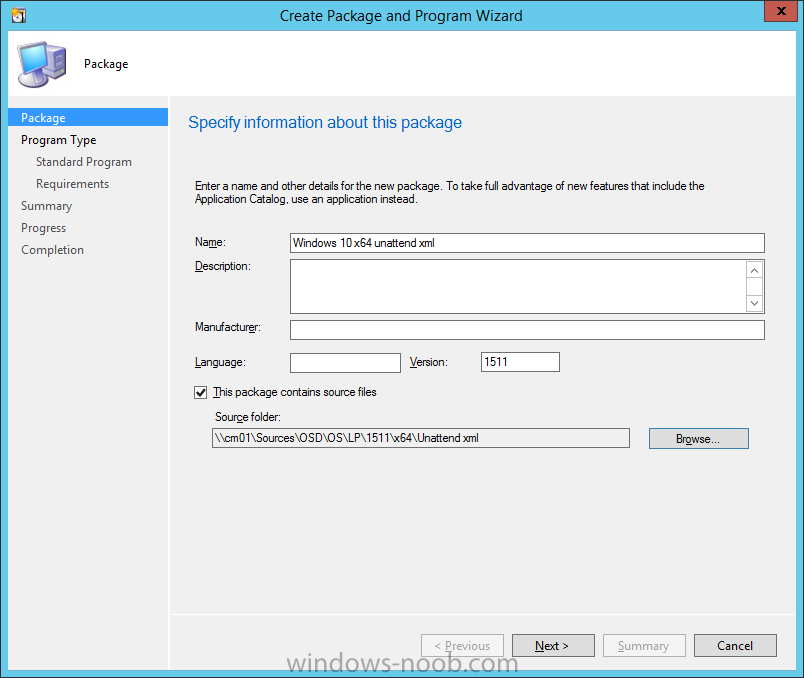
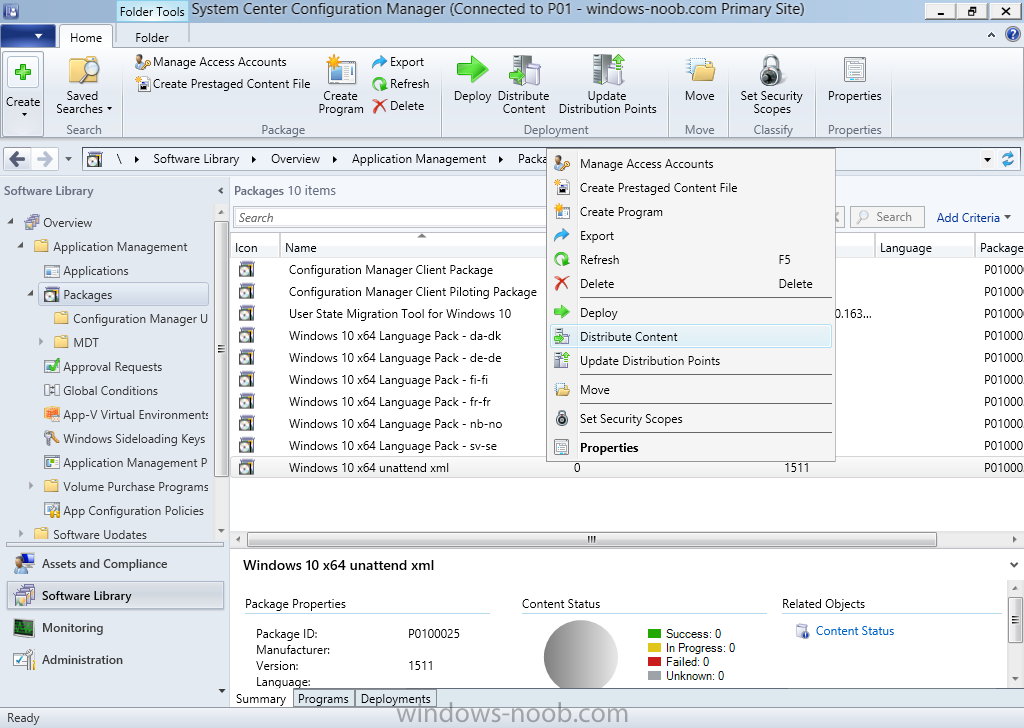
Introduction This multi-part guide will show you how to install the latest baseline version of Configuration Manager from Microsoft. The latest available baseline version is System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1902 as of April the 10th 2019. I blogged how to upgrade to 1902 here. This guide is aimed a new installations of SCCM. Baseline media is used to install new ConfigMgr sites or to upgrade from supported versions, for more information about baseline media please see my blog post here. Note: The SCCM 1902 Current Branch media is not yet available on MSDN or VLSC. When the new baseline media is released I'll update this note. This series is broken down into the following parts:- Part 1 - Get the lab ready, configure ADDS Part 2 - Join CM01 to Domain, add users, create the Systems Management container, delegate permission Part 3 - Role and Feature installation, installation of WDS and ADK Part 4 - Configure and install SQL Server 2017 (This part) Part 5 - Configure and install SCCM 1902 Current Branch Part 6 - Post configuration You can use this multi-part guide to get a hierarchy up and running on Windows Server 2019 using SQL Server 2017. The concept behind this is to guide you through all the steps necessary to get a working Configuration Manager Primary site installed (for lab use) using manual methods or automated using PowerShell. This gives you the power to automate the bits that you want to automate, while allowing you to manually do other tasks when needed. You decide which path to take. PowerShell knowledge is desired and dare I say required if you are in any way serious about Configuration Manager. I will show you how to do most steps via two methods shown below, it's up to you to choose which method suits you best but I highly recommend automating everything that you can, using PowerShell. Method #1 - Do it manually Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell Downloads The scripts used in this part of the guide are available for download here. Unzip to C:\Scripts. The scripts are placed in the corresponding folder (Part 1, Part 2 etc) and sorted into which server you should run the script on (DC01 or CM01). Scripts.zip Step 1. Install SQL Server 2017 Note: Perform the following on the Configuration Manager server (CM01) as a Local Administrator, I'd suggest you logon as the username matching your name. Method #1 - Do it manually In this section you will install SQL Server 2017 CU14 which is the latest supported version of SQL Server that is compatible with SCCM 1902 Current Branch as of 2019/4/16. For details about which versions of SQL Server are supported with different site systems in ConfigMgr, please see this page. Before starting, please configure the firewall as described in https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=94001 to allow access to SQL Server through the firewall. You can do this by executing the following command as local administrator on the CM01 (ConfigMgr) server. netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLPort dir = in protocol = tcp action = allow localport = 1433 remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN After configuring the firewall, browse to the drive where the SQL Server 2017 media is, and run setup.exe. The SQL Server Installation Center wizard will appear. Click on Installation and then choose New SQL Server standalone installation or add features to an existing installation. Enter the Product Key or use the evaluation version if that's what you want to use. Note: The product key will be automatically filled in for licensed media downloaded from Microsoft Volume Licensing Service Center. Accept the EULA Make your Microsoft Update choices and review your Install rules, as long as you've opened the correct port for SQL you'll be ok and can safely ignore the Warning about the Firewall. select the SQL server instance features you need (at least Database Engine Services) and if necessary change the drive letter where you intend to install it And configure the Instance Configuration or just leave it as default Verify the Service Accounts settings and for Collation (click on the Collation tab in Server Configuration), make sure the collation is set to SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS For Database Engine Configuration, click on Add Current User After configuring Data Directories, TempDB and Filestream settings you are ready to install Click on Install to start the installation of SQL Server 2017, and once it's completed, click Close. Next download and install the following: SQL Server 2017 Cumulative Update 14. SQL Server 2017 SSMS here. SQL Server 2017 Reporting Services. Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell Note: Make sure your SQL Server 2017 media is in the drive specified in the script or edit the script to point to the new location of the media. The script set's the installation path pointing at D:\MSSQL if you want to install SQL somewhere else please change the variables as appropriate. To install SQL Server 2017 use the Install SQL Server 2017.ps1 script. The script will create a ConfigurationFile.ini used to automate the installation of SQL Server 2017, and after it's installed the script will download the SSMS executable (Management Studio) and install it. Then it will download Reporting Services and install it. If either of the EXE's are in the download folder, it will skip the download and just install. SQL Server no longer comes with the Management Studio or Reporting Services built in, and they are offered as separate downloads, don't worry though, my PowerShell script takes care of that for you. 1. Extract the scripts to C:\Scripts on CM01 and load the Install SQL Server 2017.ps1 script located in C:\Scripts\Part 4\CM01 2. Edit the variables [lines 17-81] as desired before running. 3. Logon as the user specified in line 20. 4. Start Windows PowerShell ISE as Administrator and run the script by clicking on the green triangle. Done ! That's it for this part, please join me in Part 5 where we Configure and Install System Center Configuration Manager 1902.2 points
-
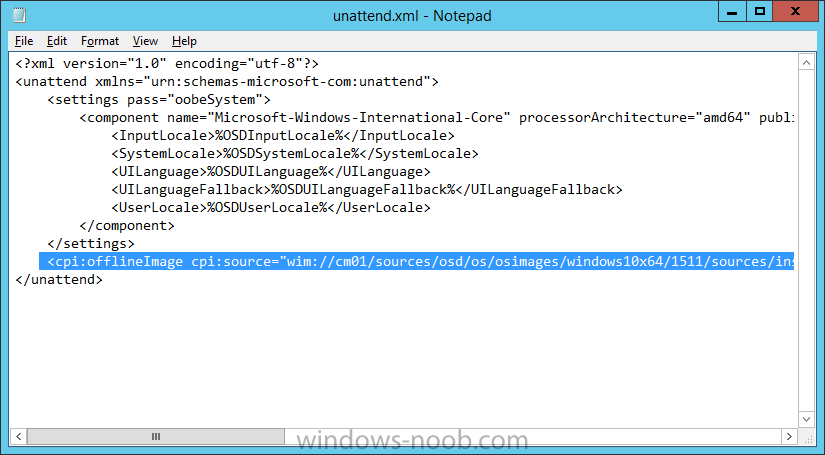
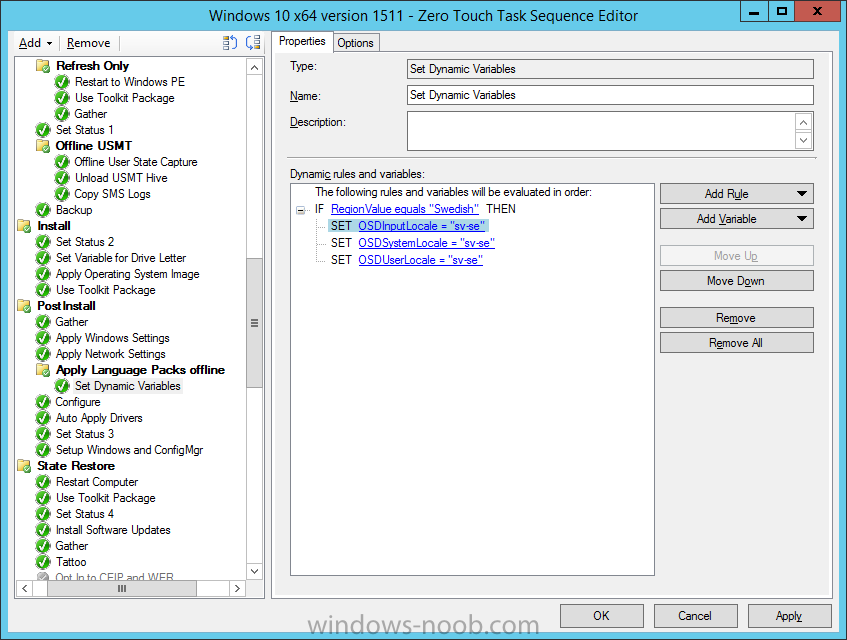
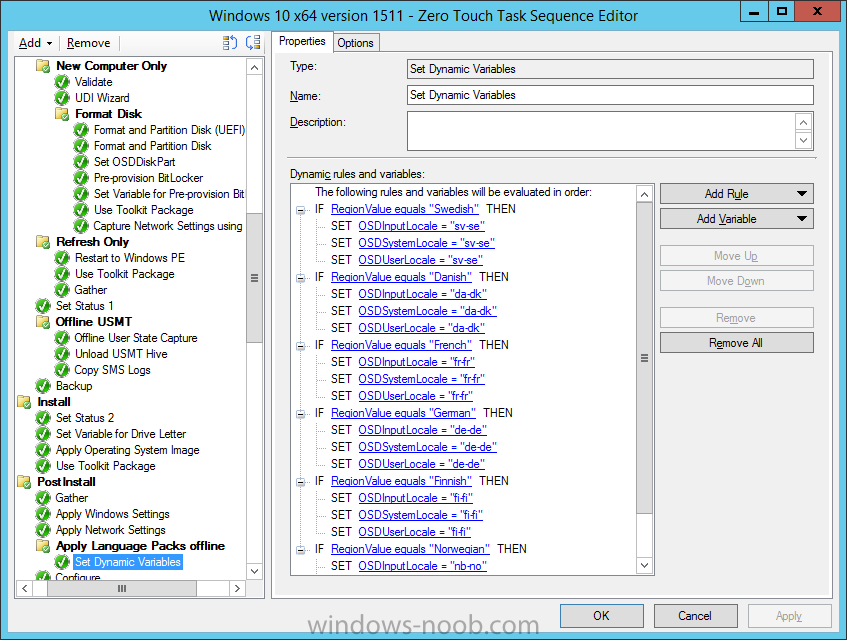
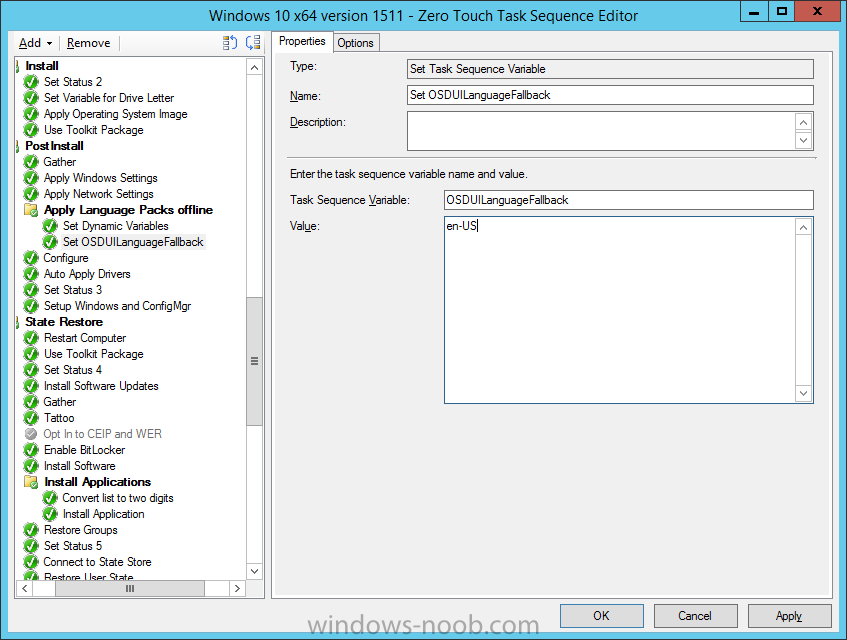
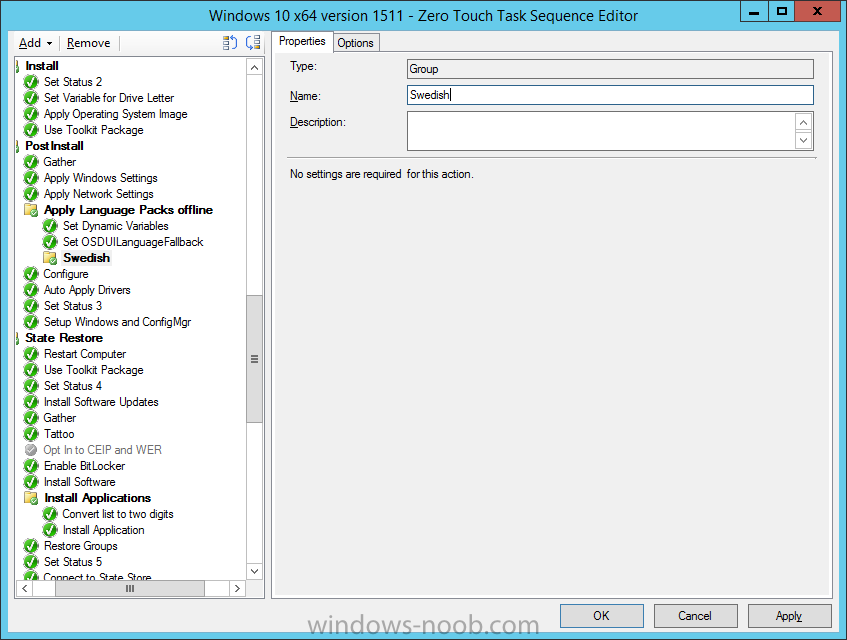
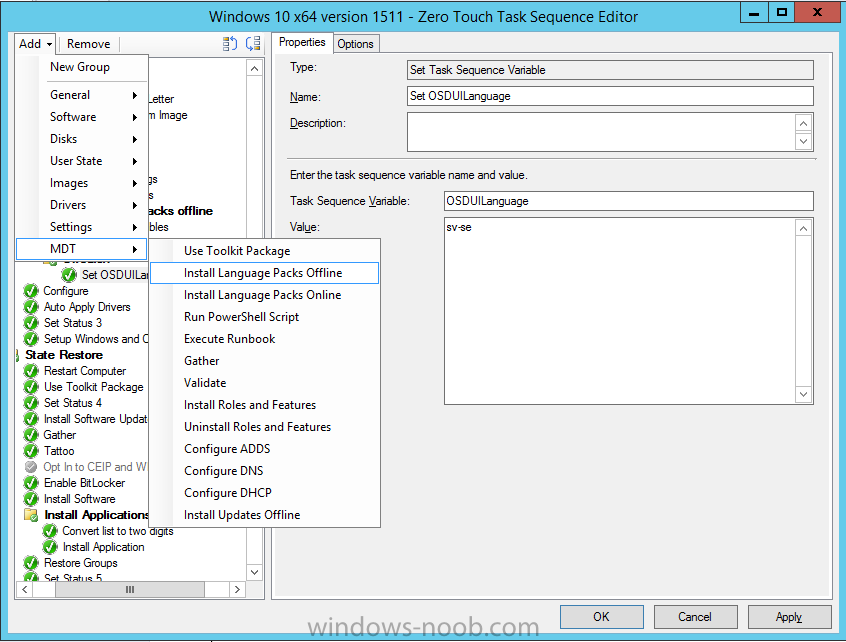
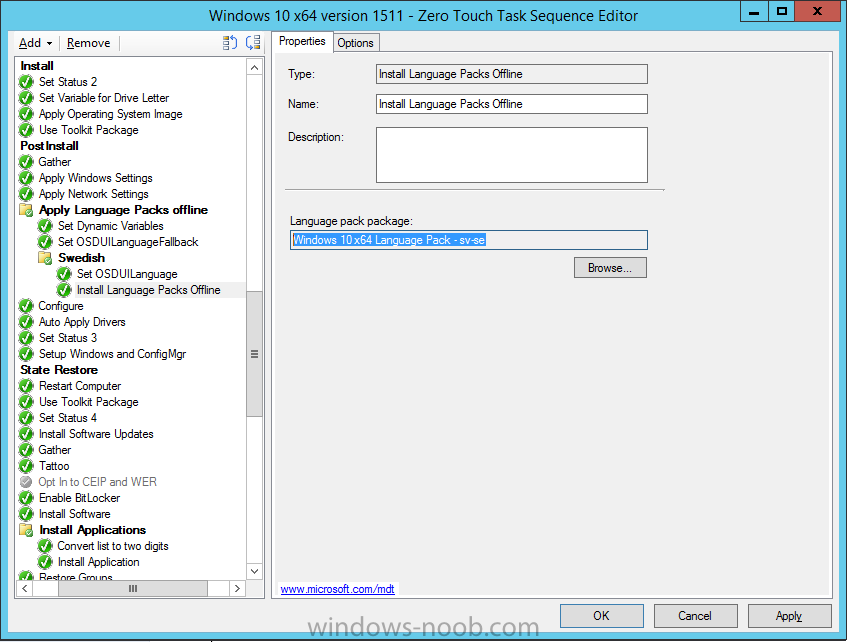
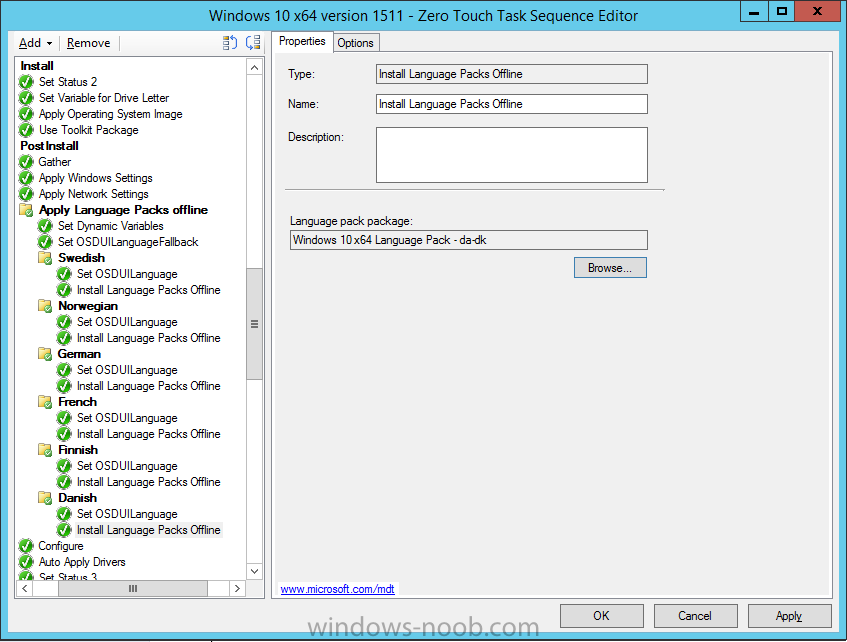
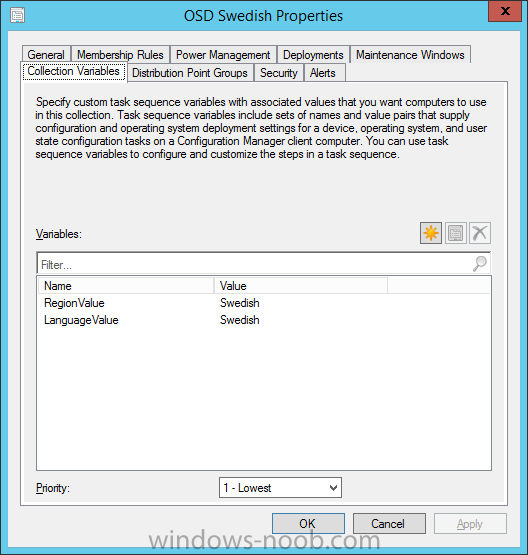
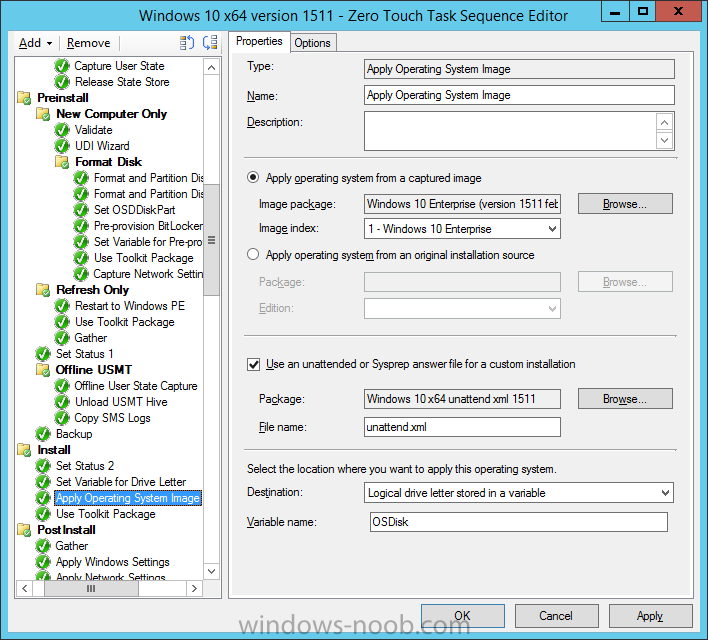
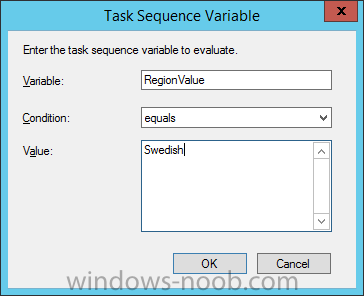
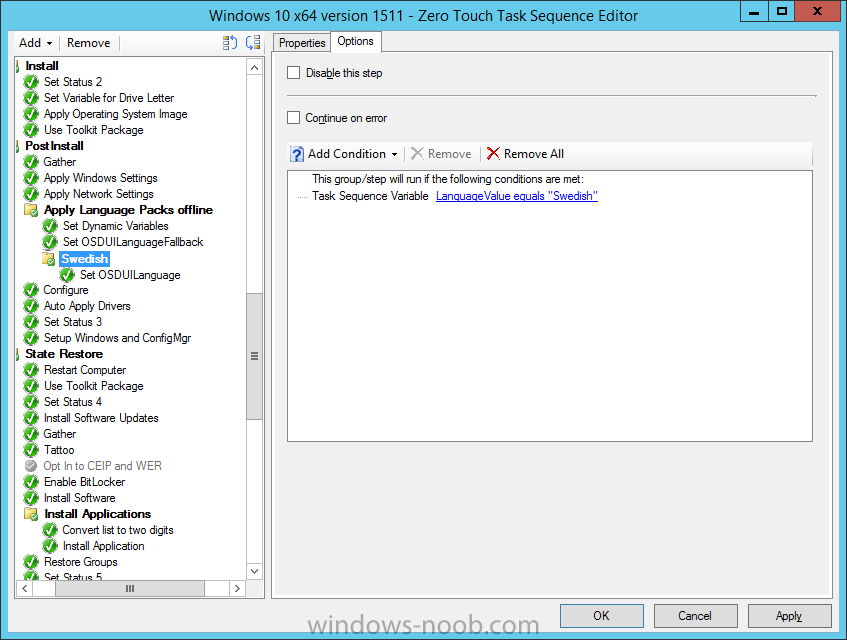
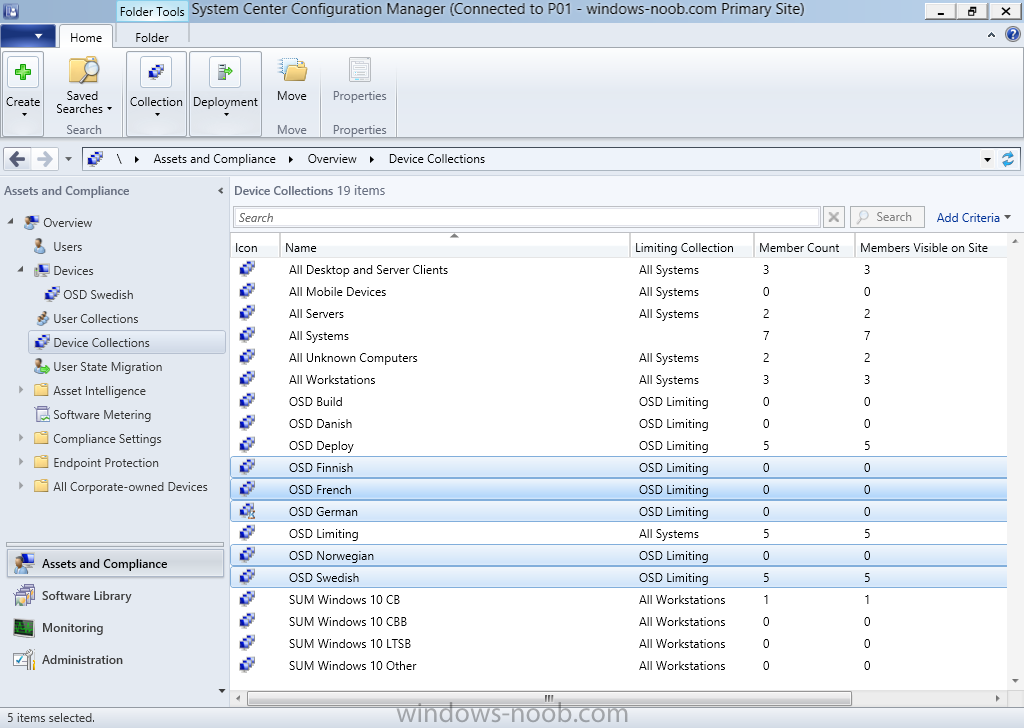
Hi, I reviewed the Task Sequence (for which thanks a million!) and I believe the reason for 'error 87:parameter is not correct' in two of the steps you disabled for the time being is the wrong dism parameter: DISM.exe /image:%OSDisk%\ /Set-UILanguage:%OSDUILanguage% that should be-> DISM.exe /image:%OSDisk%\ /Set-UILang:%OSDUILanguage% Similarly Set-UILanguageFallback should be changed to Set-UILangFallback. I did not have enough time to test that one myself yet but according to DISM documentation Set-UILang is the parameter name that exists.2 points
-
I was able to Solve my authenticate issue. While running the site install Powershell script, I had to give the group names as the Pre-Windows 2000 as they differed slightly.2 points
-
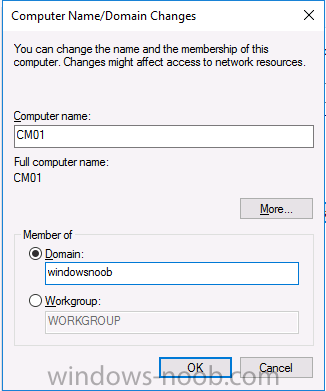
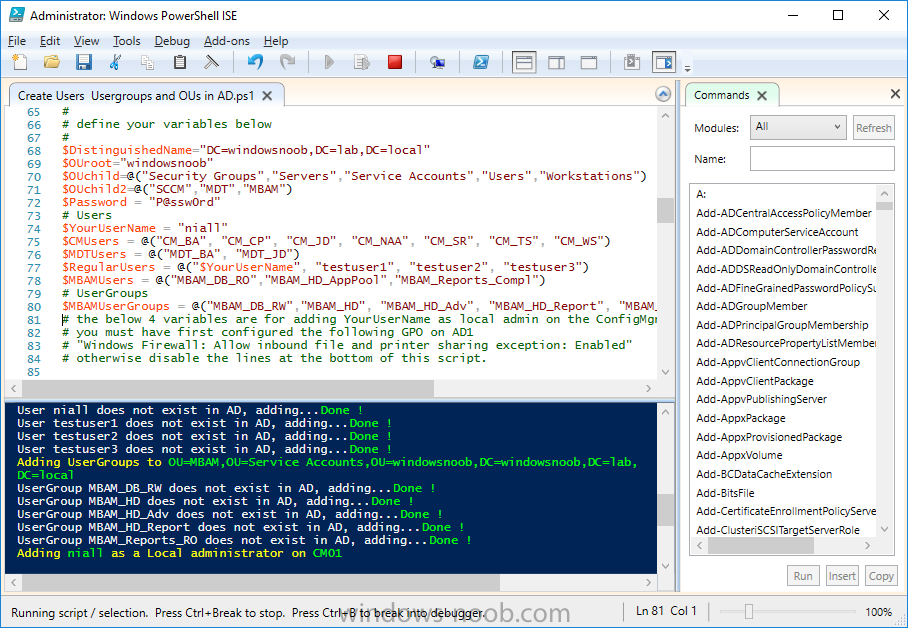
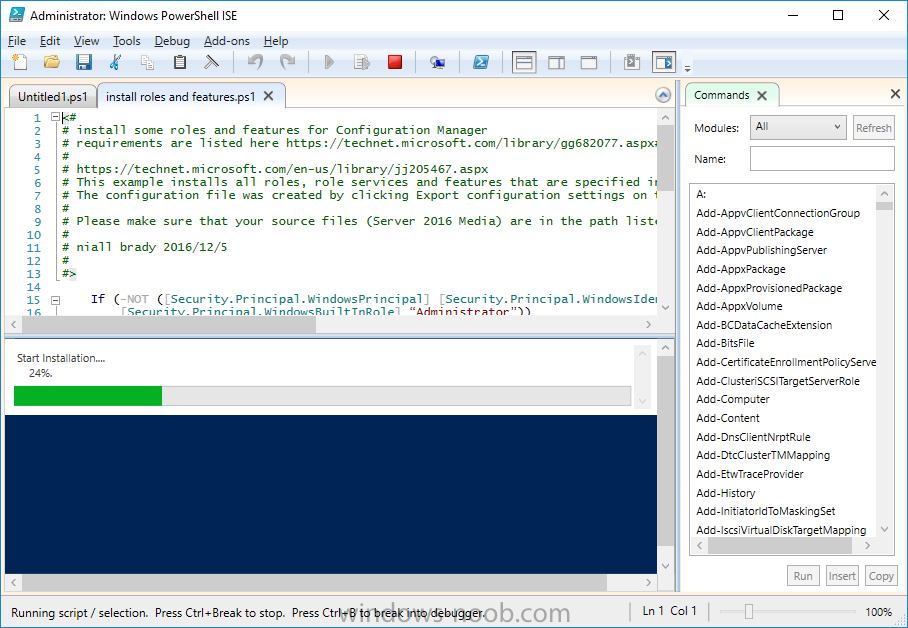
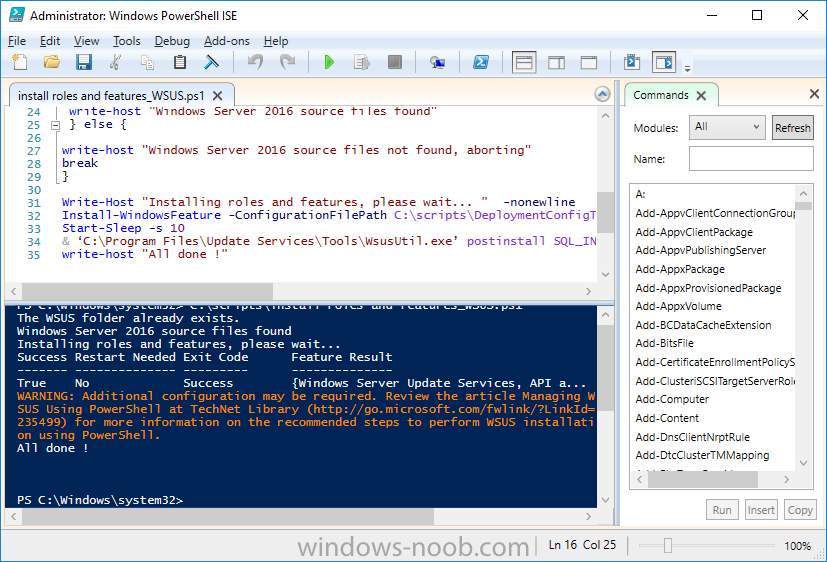
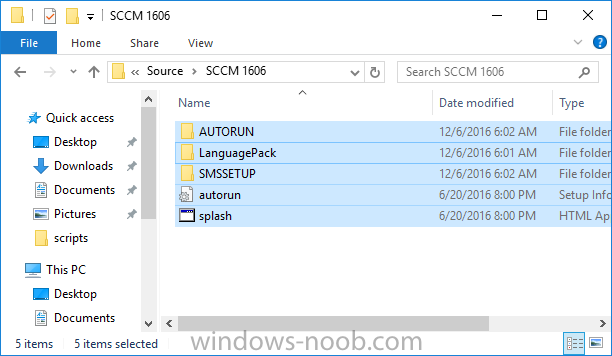
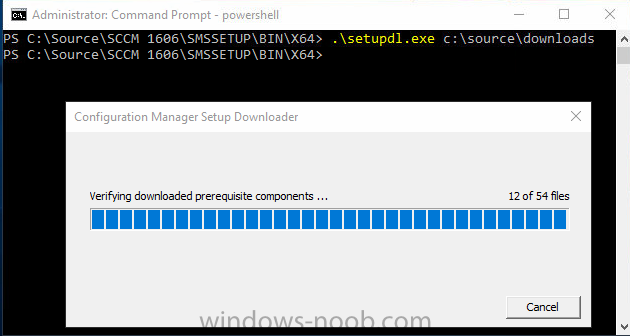
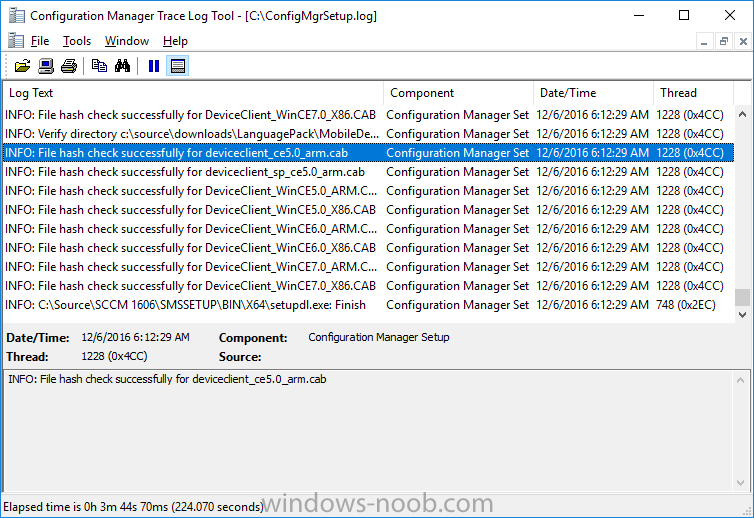
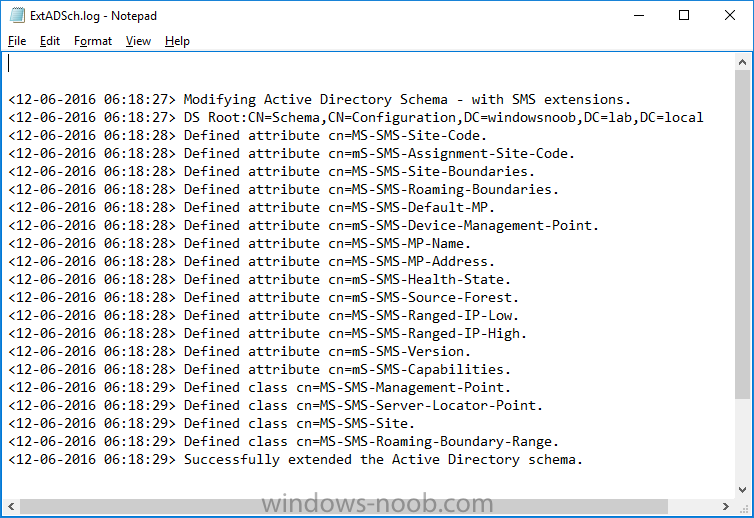
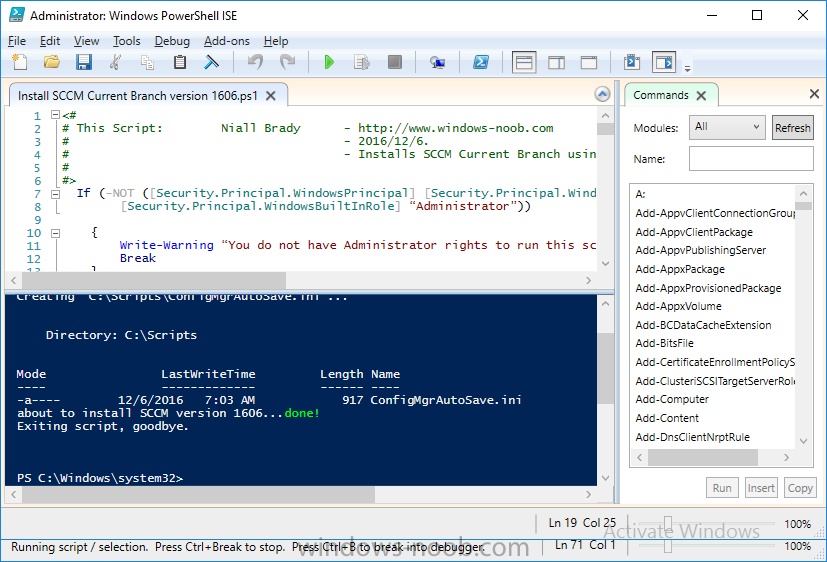
Update: please see this updated guide for SCCM 1802 CB, with SQL Server 2017. Introduction In a previous guide I showed you how to install System Center Configuration Manager version 1511 (Current Branch) on Windows Server 2012R2. Times are changing fast in this cloud-first mobile-first world, and as a result the System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) releases are being released rapidly. In addition to these releases are new Windows Server and SQL Server releases. Now that these new releases are all supported to run together, this guide will show you how to quickly install System Center Configuration Manager version 1606 (Current Branch) on Windows Server 2016 using SQL Server 2016, and then upgrade it to System Center Configuration Manager version 1610 (Current Branch). We use System Center Configuration Manager version 1606 (Current Branch) in this guide as it is the latest baseline version available on Microsoft's Volume License Service Center site (as of time of writing, December 2016). Some PowerShell knowledge is desired. I will show you how to do most actions manually as well as automated. Assumptions In this guide I assume you have already installed two workgroup joined servers running Windows Server 2016 (choose Windows Server 2016 Standard (Desktop Experience)) as listed below, and that you've configured the network settings. I also assume you have some knowledge of PowerShell, if you don't, start learning it now ! Server name: AD01 Server status: Workgroup joined IPv4 Address: 192.168.4.1 Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway: 192.168.4.199 DNS: 192.168.4.1 Server name: CM01 Server status: Domain joined IPv4 Address: 192.168.4.2 Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway: 192.168.4.199 DNS: 192.168.4.1 Server name: Smoothwall Server roles: A Linux firewall for sharing internet into these virtual machines, in hyperv you can add two legacy nics to achieve this. Scripts used in this guide The scripts used in this guide are available at the bottom of the guide in the Downloads section, download them before beginning and extract them to C:\scripts on your destination server(s). Step 1. Configure Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) Note: Perform the following on the AD01 as Local Administrator on the workgroup joined server. To setup Active Directory Domain Services you could manually click your way through the appropriate wizard in Server Manager or automate it using PowerShell. For your benefit I'll show you both methods below, all you have to do is choose which one suits you. Method #1 - Do it manually 1. To manually setup ADDS, in the start screen search for Server Manager 2. Click on Add roles and features, for Installation Type choose Role-based or Feature-based installation 3. For Server Selection choose the local server (AD01) 4. For Server Roles select Active Directory Domain Services and DNS Server, answer yes to install any required components. 5. Continue the the wizard and click Install, then click Close to complete the wizard. 6. After it's finished, perform the Post Deployment Configuration by clicking on Promote this server to a domain controller select the Add a new forest option, give it a root domain name such as windowsnoob.lab.local and click through the wizard, when prompted for the password use P@ssw0rd. Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell To configure ADDS automatically, use the ConfigureADDS.ps1 PowerShell script. 1. Copy the script to C:\scripts. 2. Edit the variables as desired before running. 3. Start Windows PowerShell ISE as Administrator and run the script by clicking on the green triangle. Step 2. Join CM01 to the domain Note: Perform the following on the CM01 as Local Administrator on the workgroup joined server. Method #1 - Do it manually To join the domain manually, bring up the computer properties. Click on Change settings beside the computer name, click Change and enter the appropriate domain join details, reboot when done. Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell To join the domain automatically, use the joindomain.ps1 PowerShell script. 1. Copy the script to C:\scripts. 2. Edit the variables as desired before running. 3. Start Windows PowerShell ISE as Administrator and run the script by clicking on the green triangle. Step 3. Create users Note: Perform the following on the Active Directory Domain Controller server (AD01) as Local Administrator You can do this step manually or automated using the supplied PowerShell script. Method #1 - Do it manually To create users manually, add the following users in AD using Active Directory Users and Computers: * <your user name>, a domain user, this user will become a local administrator on CM01 * Testuser, a domain user * CM_BA, used for building ConfigMgr created images * CM_JD, used for joining computers to the domain * CM_SR used for reporting services. * CM_CP, a domain user used when installing the Configuration Manager Client for Client Push. * CM_NAA, a domain user, (Network Access Account) used during OSD Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell To create users automatically, use the Create Users Usergroups and OUs in AD.ps1 PowerShell script. Tip: You need to edit the script and adjust the variables to your liking, for example if you want to change the default password. You may also want to rem out the MDT and MBAM user/groups that are created and change some of the user names within the script. To rem out a line place a # in front of it. 1. Copy the script to C:\scripts. 2. Edit the variables [lines 68-80] as desired before running. 3. Start Windows PowerShell ISE as Administrator and run the script by clicking on the green triangle. After running the PowerShell script in Windows PowerShell ISE you'll see something like the following. Step 4. Create the System Management Container Note: Perform the following on the Active Directory Domain Controller server (AD01) as Local Administrator For details of why you are doing this see https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg712264.aspx. Method #1 - Do it manually Open ADSI Edit, click on Action, Connect To and click Ok, Double Click on Default Naming Context and the DC= that appears below it. Click on the + and scroll down to CN=System. Right Click on CN=System and choose New, Object, choose Container from the options, click Next and enter System Management as the value as shown below Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell To create the System Management container automatically, use the Create System Management container.ps1 PowerShell script. Step 5. Delegate Permission Note: Perform the following on the Active Directory Domain Controller server (AD01) as Local Administrator Method #1 - Do it manually Open Active Directory Users and Computers. Click on view, select Advanced Features. Select the System Management Container, and right click it, choose All Tasks and Delegate Control. When the Welcome to Delegation of Control Wizard appears click next, then click Add. click on Object Types, select Computers. Type in your Configuration Manager server name (CM01) and click on Check Names, it should resolve. Click Ok, then Next. Choose Create a Custom Task to Delegate, click next, make sure This folder, existing objects in this folder and creation of new objects in this folder is selected. Click next, select the 3 permissions General, Property-Specific and Creation-deletion of specific child objects are selected then place a check mark in Full Control. Tip: Repeat the above process for each site server that you install in a Hierarchy. Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell To delegate permissions to the System Management container automatically, use the Delegate Permissions.ps1 PowerShell script on CM01. That's right, on the ConfigMgr server. Step 6. Install Roles and Features on CM01 Note: Perform the following on the Configuration Manager server (CM01) as a Local Administrator To support various features in System Center Configuration Manager, the setup wizard requires some Server Roles and Features pre-installed. On CM01, login as the username you added to the Local Administrators group and navigate to C:\scripts. The XML files within the Scripts Used in This Guide.zip were created using the Export Configuration File option in Server Manager after manually installing roles and features and the accompanying PowerShell script simply installs it. Note: Make sure your Server 2016 media is in the drive specified in the script or edit the script to point to the location of the media. Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell To install the roles and features needed, start Windows Powershell ISE as Administrator and run the install roles and features.ps1 script. Step 7. Download and install Windows ADK 10 version 1607 Note: Perform the following on the Configuration Manager server (CM01) as a Local Administrator The ConfigMgr prerequisite checker will check for various things, including ADK components such as USMT and Windows Preinstallation Environment (amongst others), therefore you need to install Windows ADK on your server. To do so, either download ADKsetup from here and manually install it or run the setup ADK and WDS.ps1 PowerShell script to download and install the correct components for you. This script not only downloads the components needed, it's also installs ADK 10 and then installs Windows Deployment Services. The setup ADK and WDS.ps1 PowerShell script is available in the Scripts Used in this Guide zip file. Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell To download and then install Windows ADK 10 with the components needed, start Windows Powershell ISE as Administrator and run the setup ADK and WDS.ps1 script. Step 8. Install SQL Server 2016 Note: Perform the following on the Configuration Manager server (CM01) as a Local Administrator The following script will create a ConfigurationFile.ini used to automate the installation of SQL Server 2016, and after it's installed the script will download the SSMS exe (Management Studio) and install it. SQL Server no longer comes with the Management Studio and it's offered as a separate download, don't worry though, my PowerShell script takes care of that for you. Note: Make sure your SQL Server 2016 media is in the drive specified in the script or edit the script to point to the location of the media. Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell To install SQL Server2016 use the Install SQL Server 2016.ps1 script. 1. Copy the script to C:\scripts. 2. Edit the variables [lines 17-75] as desired before running. 3. Start Windows PowerShell ISE as Administrator and run the script by clicking on the green triangle. Step 9. SQL Memory Configuration Note: Perform the following on the Configuration Manager server (CM01) as a Local Administrator Depending on your memory configuration and server setup, you may also want to configure SQL memory limits as per the following guidance prior to installing ConfigMgr otherwise you'll get warnings in the Prerequisite checker when it runs the Server Readiness checks. Configuration Manager requires SQL Server to reserve a minimum of 8 gigabytes (GB) of memory for the central administration site and primary site and a minimum of 4 gigabytes (GB) for the secondary site. This memory is reserved by using the Minimum server memory setting under Server Memory Options and is configured by using SQL Server Management Studio. For more information about how to set a fixed amount of memory, see here. If your SQL Server is configured for unlimited memory usage, you should configure SQL Server memory to have a maximum limit. Method #1 - Do it manually Open Management Studio, select CM01, right click, choose Properties, select memory and configure the values as appropriate for your environment. Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell Use the following PowerShell in ISE on the server that you installed SQL Server 2016 on, thanks go to SkatterBrainz for the code snippet, you might want to adjust the $SqlMemMin and $SqlMemMax variables to suit your environment. $SqlMemMin = 8192 $SqlMemMax = 8192 [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('Microsoft.VisualBasic') | Out-Null [System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadWithPartialName('Microsoft.SqlServer.SMO') | Out-Null $SQLMemory = New-Object ('Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server') ("(local)") $SQLMemory.Configuration.MinServerMemory.ConfigValue = $SQLMemMin $SQLMemory.Configuration.MaxServerMemory.ConfigValue = $SQLMemMax $SQLMemory.Configuration.Alter() Step 10. Restart the Server Note: Perform the following on the Configuration Manager server (CM01) as a Local Administrator Open an administrative command prompt and issue the following command: shutdown /r Step 11. Install the WSUS role Note: Perform the following on the Configuration Manager server (CM01) as a Local Administrator Now that SQL server is installed, we can utilize that for the WSUS database. To install WSUS and configure it to use the SQL servers database instead of the Windows Internal Database, do as follows: Method #1 - Do it manually <Coming soon> Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell Browse to the location where you extracted the scripts, C:\scripts. Start Windows PowerShell ISE as administrator, open the Install roles and features_WSUS.ps1 script, edit the $servername variable and replace CM01 with the ServerName your are installing ConfigMgr on (SQL server). Make sure to have your Windows Server 2016 SXS media in the path referred to by $Sourcefiles. Step 12. Download and extract the ConfigMgr content Note: Perform the following on the Configuration Manager server (CM01) as a Local Administrator To install System Center Configuration Manager version 1606 you'll need to download the content. You can download it from Microsoft's Volume license site for use in production or from MSDN for use in a lab. The VLSC download can be found be searching for Config and then selecting System Center Config Mgr (current branch and LTSB 1606) as shown below. Method #1 - Do it manually For the purposes of this guide I used the 1606 release from VLSC. This iso is named SW_DVD5_Sys_Ctr_ConfigMgrClt_ML_1606_MultiLang_ConfMgr_SCEP_MLF_X21-16461.ISO and is 1.20GB in size. Once downloaded, I mounted the ISO in Windows File Explorer and copied the contents to C:\Source\SCCM 1606 on CM01. Step 13. Download the ConfigMgr Prerequisites Note: Perform the following on the Configuration Manager server (CM01) as a Local Administrator You can download the prerequisites during ConfigMgr setup or in advance. As you'll probably want to install more than one copy of ConfigMgr (one lab, one production) it's nice to have the prerequisites downloaded in advance. To do that, open a PowerShell prompt with administrative permissions and navigate to the following folder: C:\Source\SCCM 1606\smssetup\bin\X64 Run the following line .\SetupDL.exe C:\Source\Downloads Tip: Browse to C:\source\SCCM 1606\SMSSETUP\TOOLS and double click on CMTrace.exe, answer Yes to the default logging question. Then, using Windows File Explorer, browse to C:\ and double click on ConfigMgrSetup.log which will open the log file in CMTrace. This will allow you to view any errors or problems with the download of the prerequisites in real time. Step 14. Extend the Schema Note: Perform the following on the Domain controller server (AD01) as Administrator. You do not have to extend the Active Directory schema if it was already extended for Configuration Manager previously. 1. Using Windows File Explorer on the Active Directory Domain Controller, browse to \\<server>\c$\Source\SCCM 1606\SMSSETUP\BIN\X64 where <server> is your ConfigMgr server 2. locate extadsch.exe, right click and choose Run As Administrator. 3. A command prompt window will appear briefly as the schema is extended, check in C:\ for a log file called ExtADSch.log it should look similar to this Step 15. Install SCCM Current Branch (version 1606) Note: Perform the following on the ConfigMgr server (CM01) as Administrator. If you are NOT using eval (as in my example) then you need to add this section to the configuration.ini file [SABranchOptions] SAActive=1 CurrentBranch=1 Method #1 - Do it manually <Coming soon> Method #2 - Automate it with PowerShell You will need to edit the Install SCCM Current Branch version 1606.ps1 script and replace the variables inside with those that work in your environment. For example, to change the ProductId open the script in Windows ISE, locate the line that reads $ProductID= and either enter your ConfigMgr Product Key or use the evaluation version of ConfigMgr by entering the word EVAL. 1. Copy the script to C:\scripts. 2. Edit the variables [lines 16-17 & lines 32-57] as desired before running. 3. Start Windows PowerShell ISE as Administrator and run the script by clicking on the green triangle. Once the script completes successfully, System Center Configuration Manager Current Branch (version 1606) is installed. Note: Currently there is a bug when using System Center Configuration Manager 1606 (Current Branch) and Windows ADK 1607 when used with Windows Server 2016 and SQL Server 2016, in that the boot images will not be created. The error shown in ConfigMgrSetup.log will be "ERROR: Failed to call method ExportDefaultBootImage. Error 0x80041013". If you experience this issue add your voice to Microsoft Connect ID 3116118. The solution at this point is to continue onto the next step and use Upgrades and Servicing to upgrade to System Center Configuration Manager 1610 (Current Branch). After completing that upgrade, the ADK 1607 boot images will be correctly added to ConfigMgr. Step 16. Upgrade to SCCM Current Branch (version 1610) Note: Perform the following on the ConfigMgr server (CM01) as Administrator. Method #1 - Do it manually As the upgrade process is a whole blog post by itself, please follow my guide here. Summary In this guide you used a lot of PowerShell to automate most of Installing System Center Configuration Manager Current Branch (version 1606), including installing and configuring SQL Server 2016 on Windows Server 2016. You then upgraded to version 1610 using Updates and Servicing. Related Reading Configuration Manager and the Windows ADK for Windows 10, version 1607 here. Documentation for System Center Configuration Manager here. What's new in version 1610 of System Center Configuration Manager here. Recommended hardware for System Center Configuration Manager here. Supported operating systems for sites and clients for System Center Configuration Manager here. Support for SQL Server versions for System Center Configuration Manager here. Use a command line to install System Center Configuration Manager sites here. Supported operating systems for System Center Configuration Manager site system servers here. Install-WindowsFeature here. Downloads You can download a Microsoft Word copy of this guide here dated 2016/12/6 How can I install System Center Configuration Manager version 1606 (Current Branch) on Windows Server 2016 with SQL 2016.zip You can download the PowerShell scripts used above here Scripts Used In This Guide.zip2 points
-
If anyone gets an access denied error at the last step (certutil -crl), then please reboot your Issuing CA server once and then issue the command again. I had this issue and apparently several other users had this too per various forums.2 points
-
In March 2017 I blogged a method to allow you to forcefully upgrade your Windows 7 or Windows 10 computers to the latest version of Windows 10 using a popup (HTA) that gives the user some form of control (5 deferrals). Note: if you want to see how many days of support are left for Windows 7 extended support click here. This was very popular and spawned different versions of the same original concept by other MVP’s and the community at large. I always wanted to update mine, but never had time, however what I have done is incorporate bug-fixes and features, and rewritten the original VBS wrapper code to PowerShell. In the next version I’ll replace the HTA with a PowerShell gui. So how about listing the features of this solution. Designed to run as required Runs before the task sequence starts Shows the user a popup with options Can run on Windows 7 or Windows 10 Allows deferrals After deferrals run out, starts a 4 hour timer If the user ignores the popup, subtracts one deferral after 8 hours Checks for Power Checks for hard disc free space Checks for Supported Model Checks for VPN Is easy to Brand with your company details Has several checks to ensure it won’t run by accident So that’s enough of the features, here’s a look at what it will look like to the end user running either Windows 10 or Windows 7. Time to upgrade In the above screenshot, the user sees the popup daily at a time that you decide eg: 11am. The user has a number of choices: Upgrade now by clicking on the box ‘my files are backed up’, and then selecting Upgrade now Upgrade later by clicking on Defer Cancel, by clicking on the X in the top corner, this will remove one deferral. Note that this verifies how many deferrals are left and if there are none left, will start the task sequence Do nothing. The popup will auto close after 8 hours and remove one deferral. Kill it with Task Manager, this will remove one deferral. If the user runs out of deferrals the 4 hour timer will start. If the user still does nothing, when the 4 hours runs out the task sequence will begin. They can of course click the checkbox and select Upgrade now to start it at any time. Branding So how can you add your branding to it ? start with the banner.png. Open it in MSPaint and replace the windowsnoob logo with your own, try and keep it to 500×65 pixels otherwise you’ll need to edit the Upgrade.HTA code also. Next, open the wrapper.ps1 in PowerShell ISE. Edit CompanyName in line 15 to suit your Company Name. Save the changes, next, open upgrade.hta in Notepad ++. Edit CompanyName in line 50 to suit your company name. edit line 395, and put your company name in Troubleshooting The popup creates 3 log files in C:\ProgramData shown below Windows10RequiredUpgradeHTA.log Windows10RequiredUpgradeWrapper.log Windows10RequiredUpgradeStart-Upgrade.log The process creates registry keys (and deletes them upon successful closure of the HTA before starting the task sequence). For more details about how to set this up in your environment, please see the following blogpost. I’ve updated that blogpost to include the new files and the PowerShell wrapper.ps1. Note: To download the files included, you need to be a registered member of windows-noob.com cheers niall2 points
-
Do follow steps 1) delete c:\windows\system32\GroupPolicy\Machine\Registry.pol 2) Gpudate /force 3)initiate Machine policy , software update and evaluation.2 points
-
As a matter of interest are there any parts of the sccm install process you have not been able to powershell? I ask as around this time last year I was in a position of knowing I needed to rebuild my entire domain as we were going through a company rename but didnt yet have the new name. Ended up building a few dozen domain environments through powershell+powercli (vmware environment) including a lot of the sccm stuff so that once i did have the name+domain name i was ready to get going pretty quickly. I accept I am no powershell expert but as it took me a long time to put together if there are any smaller parts of interest I'm happy to share them, log of entire build attached. I made a lot of sacrifices in the scripts for the fact these scripts were all running remotely, e.g. i installed SQL as a scheduled task. Names/ip addresses tweaked for semi-anonymity. CleanedUpNames.Build.txt2 points
-
In the .HTA file I changed the following line: If DPI > 120 then DESIGN_DPI = 160 'dots per inch 'DESIGN_WIDTH = 450 'pixels 'DESIGN_HEIGHT = 365 'pixels DESIGN_WIDTH = dw 'pixels DESIGN_HEIGHT = dh 'pixels to If DPI > 120 then DESIGN_DPI = 96 'dots per inch <<--- 'DESIGN_WIDTH = 450 'pixels 'DESIGN_HEIGHT = 365 'pixels DESIGN_WIDTH = dw 'pixels DESIGN_HEIGHT = dh 'pixels This seems to have solved my scaling problems. You still need to adjust the Window size from above, reference: Call ReSizeWindow (425,335,500,535) in the code above the ReSizeWindow function. When the DPI is <120 the formula uses the design width and height 500,535 respectively. However when the DPI is >120 it will use the numbers 425,335 and then factor accordingly. To get mine to work I had to reduce those numbers somewhat but it now almost displaces the same as on a system with DPI set to 96.2 points
-
sorry just read the rest of your thread... as a work around, you can advertise the task to your desktop collection, but have the task respond ONLY to PXE and MEDIA, have it set to AVAILABLE and put a password on your boot media. MEDIA and PXE only, available setting and the password are all items to prevent current devices from getting reimaged by accident.2 points
-
Ok so finally figured this out. On the ScanAgent.log I was seeing a lot of "Sources are not current" messages. This led me to dig further and that the SUP MUST be in the default boundaries group, which I didn't know. It apparently is new to 1702?!?! Once I added the SUP to the default group clients started reporting in instantly! Hope this helps someone out there. Regards Kevin2 points
-
$location = Get-ItemProperty "HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SMS\Setup" | Select-Object -ExpandProperty "UI Installation Directory" Resolves to C:\Program Files\Microsoft Configuration Manager\AdminConsole. That is the correct registry key. However AdminConsole folder is not in the C:\Program Files\Microsoft Configuration Manager The Module is only in x86 folder. I changed the registry 'UI Installation Directory' to point to: C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Configuration Manager\AdminConsole and script is working after that change.2 points
-
Up and running again! Thanks to anyweb (and Microsoft) we are now running 1702 and so far everything looks good! A huuuge thank you for the help!2 points
-
Up and running again! Thanks to anyweb (and Microsoft) we are now running 1702 and so far everything looks good!2 points
-
I have upgraded Windows-Noob.com today to the latest and greatest version of the IPS Community Suite. We are now on version 4. Among all the other features, this should significantly improve your experience when accessing the site on mobile devices thanks to the responsive theme. If there are any issues that you notice, please post in the Suggestion box.2 points
-
What has to be done if you change the external web services url in regards to the proxy server / edge server, and the internal and external certificates.2 points
-
One thing i can't stand about forums is no one responding back to how they fixed their issue. I hope this helps someone down the road. I just got off the phone with support and this was their fix as well. They said it's a client side issue with certificates being corrupt. ERROR: Error. Status code 500 returned OSDSMPClient 7/25/2016 4:25:28 PM 5656 (0x1618) Received 1231 byte response. OSDSMPClient 7/25/2016 4:25:28 PM 5656 (0x1618) pReply != NULL, HRESULT=80004005 (e:\qfe\nts\sms\client\osdeployment\osdsmpclient\smpclient.cpp,2391) OSDSMPClient 7/25/2016 4:25:28 PM 5656 (0x1618) SMP Root share info response is empty OSDSMPClient 7/25/2016 4:25:28 PM 5656 (0x1618) ClientRequestToSMP::ClientRootShareRequestToSMP failed. error = (0x80004005). OSDSMPClient 7/25/2016 4:25:28 PM 5656 (0x1618) ExecuteRootShareInfoRequest(sRootShareList), HRESULT=80004005 (e:\qfe\nts\sms\client\osdeployment\osdsmpclient\smpclient.cpp,1717) OSDSMPClient 7/25/2016 4:25:28 PM 5656 (0x1618) ClientRequestToSMP::DoRequest failed. error = (0x80004005). OSDSMPClient 7/25/2016 4:25:28 PM 5656 (0x1618) Request to SMP 'http://myservername.domain.com'failed with error (Code 0x80004005). Trying next SMP. OSDSMPClient 7/25/2016 4:25:28 PM 5656 (0x1618) Sleeping for 60 seconds before next attempt to locate an SMP. OSDSMPClient 7/25/2016 4:25:28 PM 5656 (0x1618) Retry number 2 OSDSMPClient 7/25/2016 4:26:28 PM 5656 (0x1618) Microsoft's response ++ It looks like there is certificate issues while performing the restoration task. ++ Please run following command under PowerShell (As Admin ) · Remove-Item -Path ‘HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\SMS\Certificates\*’ -force; · restart-service ccmexec Sunshine2 points
-
2 points
-
Any guides how to deploy Lync 2013 to one AD Domain/Forest with multiple sites? HA is in mind... What servers need to be deployed to sites and how to do the configuration?2 points
-
Hei sorry for not answering sooner. If you just install Lync 2010 standard then all u need is dc (as in domain) + 1 server to install Lync itself (standard). If u want high availability then Enterprise version is the way to go. With enterprise you can create pools of frontend servers for instance (with dns triks thouse pools work as load balancing). Also some spoilers from the next version: http://www.zdnet.com...ore-7000001415/ ---> Consolidation of roles; no separate server role needed for monitoring and archiving. Also if memory serves u cant select your own (remote) sql when using Standard (this could be lie as i dont remember no longer).2 points
-
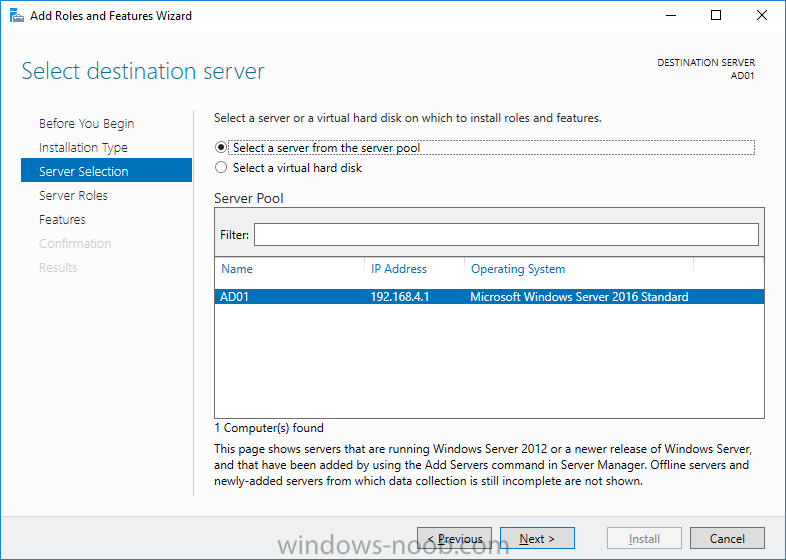
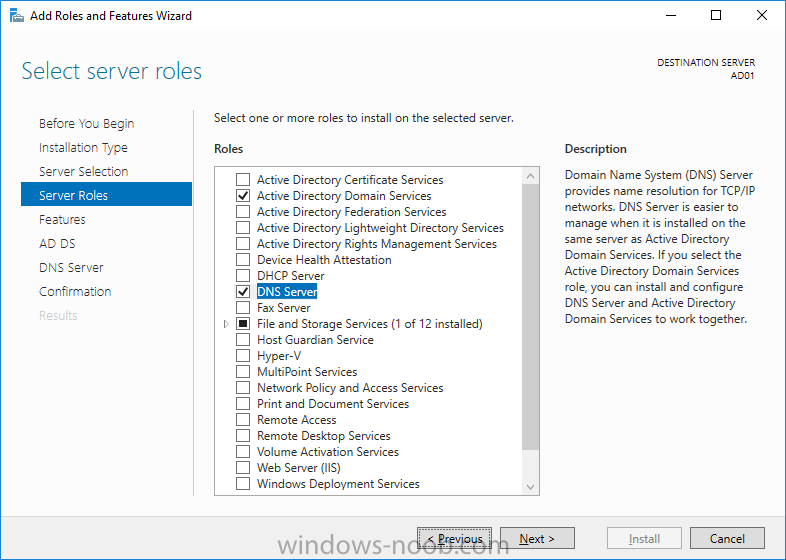
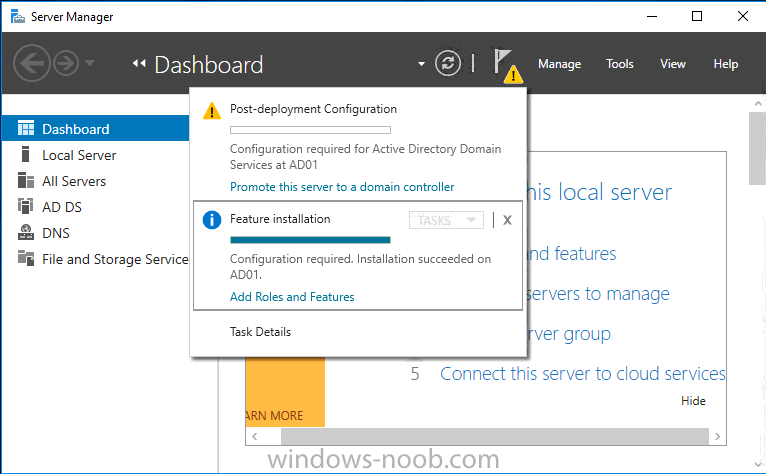
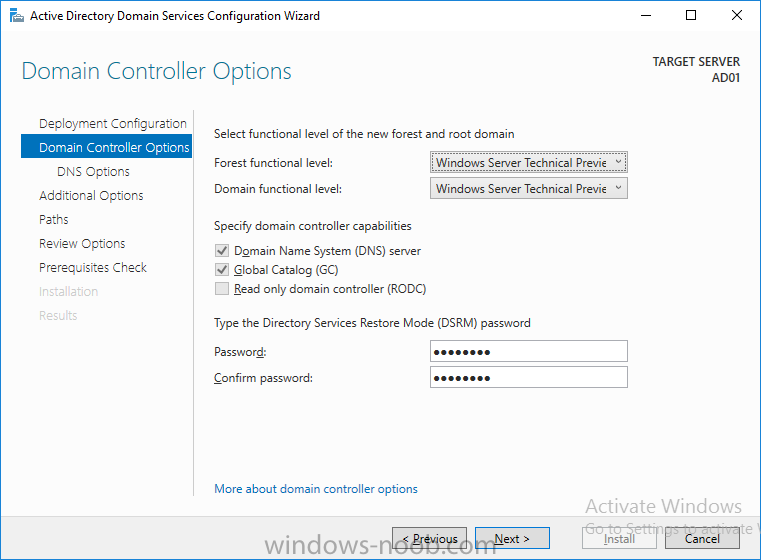
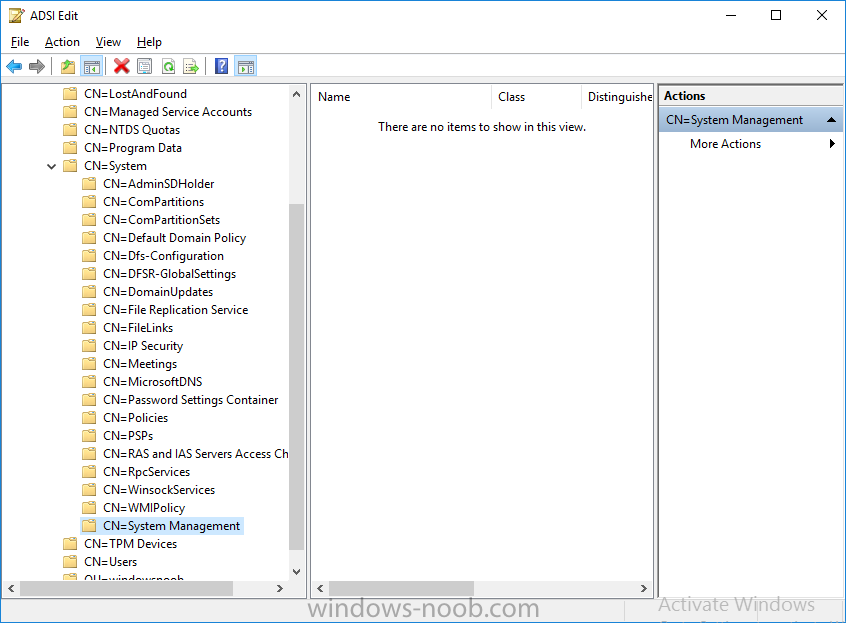
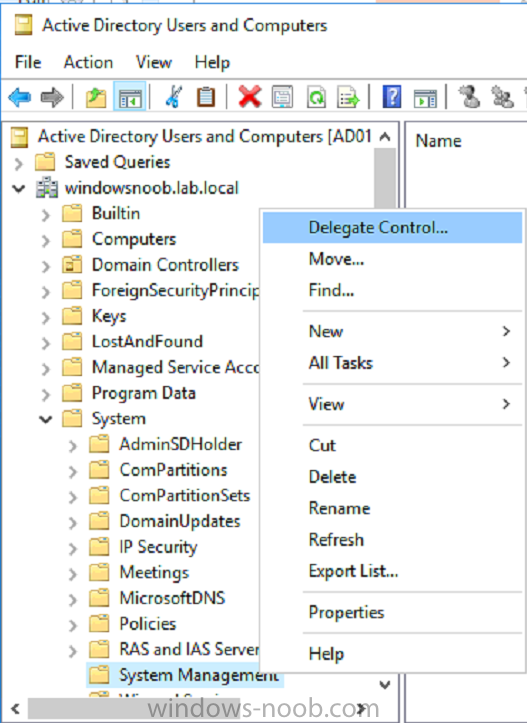
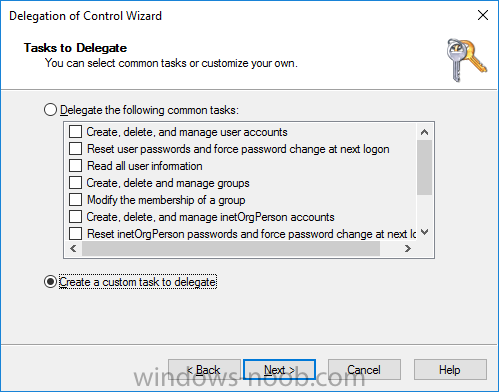
This list of guides is all about System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager. If you want to learn about SCCM 2012 this is how you can do it ! I've put together this list together to help people like you learn about Configuration Manager 2012 R2 and to help people learn about how they can integrate Microsoft Intune with Configuration Manager 2012 R2 to manage their iOS, Android and Windows Phone mobile devices. If you are looking for some of my other guides then please check below: Microsoft Intune (standalone) in Azure step by step guides are here Microsoft Intune (hybrid) guides look here (over 61,103 views as of July 2017) System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch and Technical Preview) here (96,953 views, May 2018) Configuration Manager 2007 guides then look here (over 948388 views as of July 2017) Microsoft Deployment Toolkit guides are here SMS 2003 guides are here (over 10423 views as of July 2017) Note: Some of my guides are also available for download, please see below links download the Microsoft Intune Mobile Device Management guides here. download the Standalone Primary guides in PDF and WORD format here. Step-by-Step Guides CM12 in a Lab - PXE boot failure after upgrading to System Center 2012 Configuration Manager Service Pack 1 CM12 in a Lab - How can I deploy Windows 8 X64 to the Microsoft Surface Pro using Configuration Manager 2012 SP1 ? CM12 in a Lab - How can I deploy System Center 2012 Endpoint Protection Definition Updates from a UNC file share CM12 in a Lab - How can I determine what Antimalware Policy is applied to my SCEP 2012 SP1 client ? CM12 in a Lab - when running /testdbupgrade for System Center 2012 Configuration Manager SP1 you get an error: SQL Native client 11 is not installed CM12 in a Lab - How can I backup System Center 2012 Configuration Manager ? CM12 in a Lab - SQL Server 2012 SP1 support in System Center 2012 Configuration Manager SP1 CM12 in a Lab - The CM12 BitLocker FrontEnd HTA - video CM12 in a Lab - The CM12 BitLocker FrontEnd HTA CM12 in a Lab - Where can I download additional clients for System Center 2012 Configuration Manager SP1 ? CM12 in a Lab - How can I sequence applications using App-V version 5 for Configuration Manager 2012 SP1 CM12 in a Lab - How can I deploy a Hidden task sequence in Configuration Manager 2012 SP1 ? CM12 in a Lab - How can I pre-provision BitLocker in WinPE during Windows 8 deployments using Configuration Manager 2012 SP1 ? CM12 in a Lab - How can i disable “Connect to a wireless network” during Windows 8 OOBE ? CM12 in a Lab - How can I deploy Windows 8 in UEFI mode using Configuration Manager 2012 ? CM12 in a Lab - Why is my System Center 2012 Configuration Manager console in read-only mode ? CM12 in a Lab - How can I view hidden Endpoint Protection Reports in System Center 2012 Configuration Manager ? CM12 in a Lab - How can I upgrade System Center 2012 Configuration Manager ? CM12 in a Lab - How can I add a PXE enabled Distribution Point on Server 2008 X86 for System Center 2012 Configuration Manager ? CM12 in a Lab - How can I display my System Center 2012 Configuration Manager hierarchy in Bing Maps ? CM12 in a Lab - How can I enable Debug View in the Configuration Manager console? CM12 in a Lab - How can I easily prompt for a computer name in Configuration Manager 2012 CM12 in a Lab - Importing Computers using a file CM12 in a Lab - Two New Endpoint Protection Reports added, What are they and what do they look like CM12 in a Lab - How can I setup a Distribution Point on a Windows 7 PC in Configuration Manager 2012 ? CM12 in a Lab - How can I capture an image using Capture Media in Configuration Manager 2012 ? Hierarchy with CAS using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 1. Installation - CAS using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 2. Install the Primary server - P01 using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 3. Configuring Discovery and Boundaries using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 4. Adding roles and configuring custom Client Device Settings and custom Client User Settings using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 5. Adding WSUS, Adding the SUP role, deploying the Configuration Manager Client Agent using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 6. Adding the Endpoint Protection role, configure Alerts and custom Antimalware Policies using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 7. Build and Capture Windows 7 X64 SP1 using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 8. Deploying Applications using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 9. Deploying Monthly Updates using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 10. Monitoring our Monthly Updates Automatic Deployment Rule using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 11. Upgrading your hierarchy to Service Pack 1 using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 12. Connecting Powershell and building a reference image of Windows 8 with .NET 3.5 using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 13. Deploying Windows 8 X64 with custom Start screen using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 14. Using Compliance Settings2 points
-
In case anyone else encounters this, the issue is that using the run as feature in a task sequence that isn't OSD seems to require an account with interactive login. If it's an OSD task sequence, interactive login is not required. I had to call the credentials in the script and use a variable for the password to get around this.1 point
-
All site maintenance has been completed successfully. Thank you for your patience!1 point
-
Introduction At the start of this series of step by step guides you installed System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch), then you configured discovery methods. Next you configured boundaries to get an understanding of how automatic site assignment and content location works. After that you learned how to update ConfigMgr with new features and fixes using a new ability called Updates and Servicing and you learned how to configure ConfigMgr to use Updates and Servicing in one of these two modes: Online mode Offline mode To prepare your environment for Windows 10 servicing (this guide) you learned how to setup Software Updates using an automated method (via a PowerShell script) or manually using the ConfigMgr console. Next you used a PowerShell script to prepare some device collections, then you configured client settings for your enterprise and finally you'll deployed the ConfigMgr client agent using the software updates method which is the least intensive method of deploying the Configuration Manager client agent. As System Center Configuration Manager (current branch) is being delivered as a service now, version 1602 was made available (March 11th, 2016) and you used Updates and Servicing to do an in-place upgrade to that version as explained here. Next you learned about how to use the Upgrade task sequence to upgrade your Windows 7, Windows 8 (and 8.1) and even your Windows 10 devices to a later build of Windows 10. You then learned about the new Windows 10 servicing features which use Servicing Plans in ConfigMgr (Current Branch). Next you integrated MDT 2013 update 2. MDT integration with ConfigMgr is useful as it provides additional functionality for operating system deployment scenarios such as Offline Language Package installation or User Driven Integration (UDI). In this guide you'll learn how to deploy Language Packs offline for Windows 10. Step 1. Get the language packs Each release of Windows 10 comes with it's respective language packs, so a language pack released for Windows 10 x64 version 1507 (RTM) will not work with Windows 10 x64 version 1511 and vice versa. Therefore you should only download language packs that match the version of Windows 10 that you are deploying. In this guide, I use Windows 10 x64 version 1511, however I've verified all the steps here work fine with Windows 10 version 1607 as long as you use the correct language pack for the operating system. If you are using Windows 10 version 1607 use the following ISO: Windows 10 Language Pack, Version 1607 (Updated Jul 2016) (x86 and x64) - DVD (Multiple Languages) File Name: mu_windows_10_language_pack_version_1607_updated_jul_2016_x86_x64_dvd_9058649.iso If you are using Windows 10 version 1511 (as used in this guide) use the following ISO: Windows 10 Language Pack, Version 1511 (x86 and x64) - DVD (Multiple Languages) File Name: mu_windows_10_language_pack_version_1511_x86_x64_dvd_7224763.iso. Once downloaded, go ahead and mount the iso in Windows File Explorer. When you mount the iso you'll see two folders x64 x86 As you are deploying Windows 10 x64, browse the x64 folder and navigate to x64\languages. For Windows 10 version 1511, there are 111 language packs. Step 2. Create individual Language Pack packages From the 111 language packs shown above, select one language pack (for example Swedish or sv-SE) and copy it to it's own folder like so: Now that you've copied the language pack files, create a package within ConfigMgr as follows: In the ConfigMgr console select Software Library, then Applications, right click on Packages and choose Create Package. Fill in details about the actual package and include information about the operating system name and version, point the package source folder to the UNC path of the folder you created for that language pack Choose Do not create a program and continue through to the end of the wizard Note:- If you add multiple language packs in the same package then they will be deployed together. If you want to deploy different combinations of language packs, create multiple packages containing one language pack each. Repeat the above process for each language you intend to add support for in your environment, making sure that the folder containing the language pack is itself contained in a folder eg: Swedish\sv-se Note: If you are using Windows 10 version 1607, the language pack files are named differently, previously they were simply named lp.cab. Below you can see examples of the difference between the Windows 10 version 1511 Danish Language Pack and the Windows 10 version 1607 Danish Language Pack. Windows 10 versions 1507 and 1511 In Windows 10 versions 1507 and 1511 the language pack file is called lp.cab Windows 10 version 1607 In Windows 10 version 1607, it has a long name such as Microsoft-Windows-Client-Language-Pack_x64_da-dk.cab Step 3. Distribute the language packs In order to install the language packs they need to be on a distribution point, so in the ConfigMgr console, select all the language packs you created in Step 2 and right click, choose Distribute Content. The Distribute Content Wizard appears and lists all the language packages you selected, click next select one or more distribution points by clicking on the Add drop down and select Distribution Points continue through that wizard until completion Step 4. Create an unattend.xml file In this step you will create a custom unattend.xml file which will contain variables to help with installing the language packs. To do that use Windows System Image Manager (WSIM) which is part of the Windows ADK 10. You could simply use an already made unattend.xml file and paste in the variables section shown below if you prefer. when WSIM starts you'll see the interface Click on File and select New Answer File, you'll be prompted to open a Windows Operating system image file. click on Yes and browse to the sources folder containing install.wim of the same version of Windows 10 that you downloaded language packs for, in this guide that's Windows 10 x64 version 1511 If it's the first time you've used WSIM on this image, you'll be prompted about creating a Windows catalog file, answer yes this process will take a few minutes, but once it is done you'll see the following Expand the Components node in the Windows image pane in the lower left pane, scroll down until you see x64_Microsoft-Windows-International-Core_10.0.10586.0_neutral right click on it and choose Add setting to Pass 7 oobeSystem Fill in the following variables in the corresponding settings fields in the Microsoft-Windows-International-Core Properties node %OSDInputLocale% %OSDSystemLocale% %OSDUILanguage% %OSDUILanguageFallback% %OSDUserLocale% To verify the changes, click on Tools, Validate Answer File and verify that there are no errors reported in the Messages pane. Finally save the Unattend.xml file by clicking on File, Save Answer File As and give it a suitable name such as unattend.xml. Close Windows System Image Manager. Note: Open the Unattend.xml file using Notepad and verify that the line containing <cpi:offlineImage cpi:source="wim: does not contain any %20, if it does, remove them and save the file. See this post for more details. Create a folder in your ConfigMgr sources path, and drop the unattend.xml file into it. Step 5. Create a unattend.xml package and distribute it In Software Library, Application Management, Packages, right click and choose Create Package, give the package a suitable name and point it to the folder that you copied the unattend.xml file into. do not create a program and continue through the wizard until completion. Right click the package and choose Distribute Content, and distribute it to your distribution points. Step 6. Edit a task sequence Edit a previously created MDT task sequence by right clicking it and choose Edit. Locate the Apply Operating System Image step and modify it so that it uses the unattend.xml file created above Create a New Group called Apply Language Packs offline in the PostInstall section after that Apply Windows Settings and Apply Network Settings Steps. This group must go before the Setup Windows and ConfigMgr steps otherwise the Install Language Pack offline steps will fail. Create a new Set Dynamic Variables step called Set regional options using Dynamic Variables, click on Add Rule and choose Task Sequence Variable from the options Fill in the following values: Variable: RegionValue Condition: Equals Value: Swedish Click OK then select Add Variable, and Custom Variable from the menu Fill in the following values: Variable: OSDInputLocale Value: sv-se click OK then add another Custom Variable Variable: OSDSystemLocale Value: sv-se click OK then add another Custom Variable Variable: OSDUserLocale Value: sv-se repeat the above process for each language pack you intend to support Create a new Set Task Sequence Variable step called Set OSDUILanguageFallback and fill in the following values: Task Sequence Variable: OSDUILanguageFallback Value: en-US Create a New Group with the name of the Language pack you are offering to install click on the Options tab of that group and add a task sequence variable LanguageValue = Swedish In that group, create a new Set Task Sequence Variable step called Set OSDUILanguage and fill in the following values: Task Sequence Variable: OSDUILanguage Value: sv-SE And next, add an MDT task sequence step called Install Language Packs Offline and select the corresponding language package, Windows 10 x64 Language Pack - sv-se Repeat the above process for each language that you intend to make available and Apply your changes when done. Step 7. Set variables on a collection To decide what language packages get installed on a computer you only need to set two variables RegionValue (for the keyboard layout) LanguageValue (for the language pack) You can set these variables on a computer, on a collection, via a HTA frontend (like this one) or whichever method suits you best, In this guide we'll set the variables via a collections properties. Create a device collection called OSD <language> and replace <language> with the name of the language pack you intend to install. Right click on the newly created collection and choose Collection Variables, add the two values below RegionValue=Swedish LanguageValue=Swedish Modify the Membership Rules of the Collection Properties to add any computers that you want installed with that language pack and regional settings Repeat this process and create a new Device Collection for each language you intend to support Step 8. Deploy the task sequence to the language specific collections Deploy the task sequence with a purpose of Available, and available to media and PXE to each of the collections you create for Language Pack usage. Step 9. Review the changes Start a new OSD deployment using the task sequence you just edited. after the task sequence starts you can open smsts.log in CMTrace and see the variables are set the install language packs offline step is in progress (and revealed in the smsts.log file) and after a while, all is done ! Troubleshooting Use the log files, in particular ztipatches.log which documents what happens when the process uses DISM to inject the changes Use at least 2 GB ram in your virtual machines otherwise the step will fail to install any language packs (may run out of ram). If regional settings (keyboard layout) are not being applied, make sure you added the unattend.xml file to your Apply Operating System Image step After the Install Language Pack Offline step the following will be created in C:\_SMSTaskSequence\ Packages<dir> ZTIPatches.tmp packageGroups.xml in the Packages directory you’ll have more sub-directories based on how many language packs’s you included, one language pack, one dir, 4 language packs in your Language Package, 4 dirs... You may also see a directory called C:\_SMSTaskSequence\SMSOSD\OSDLOGS and in there are three files including a log file called BDD_PKGMGR.LOG, analyze it if you are having issues deploying Language packs offline as it will reveal the success or failure of the DISM operations. You can press F8 in WinPE and browse to the locations below and use notepad to examine the changes to the unattend.xml file. Note: The unattend.xml file and/or C:\Windows\Panther\Unattend folder may not appear in your image until directly after the Apply Operating System Image step and the contents of that file depends on whether or not an unattend.xml file was specified in that step. Before the Setup Windows and ConfigMgr step is complete you can monitor C:\Windows\Panther\Unattend\unattend.xml to see what is happening in relation to your modifications taking place or not After the Setup Windows and ConfigMgr step is complete, you’ll see the following has been added to your C:\Windows\Panther\unattend.xml file. If it is not added or if there are no changes to the %OSD...% variables then something has failed and it's time to troubleshoot. Note: The above locations are during the WinPE phase. After the Setup Windows and ConfigMgr step is complete it will reboot your computer (unless you have a command prompt open in WinPE), and after that reboot, the unattend.xml file will have been removed (by the Setup Windows and ConfigMgr step). Summary Using MDT integrated task sequences gives you new abilities in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) such as the ability to install language packs offline. Related Reading How can I deploy Windows 10 with MDT 2013 Update 2 integrated with System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Why does Windows 10 setup prompt to choose a language when deploying language packs offline using System Center Configuration Manager ? Features On Demand V2 (Capabilities) Add Language Packs to Windows https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/hardware/commercialize/manufacture/desktop/add-language-packs-to-windows Downloads You can download a Microsoft Word copy of this guide here dated 2016/05/01 Installing language packs offline with MDT integrated task sequence in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch).zip Here is a copy of the unattend.xml file I created above unattend.xml1 point
-
Yeh whilst an option i just decided to go the destroy way so we have packages to remove all the unneeded software and as mentioned above modified the office install to attempt to remove office whilst also supressing error codes. PSAPPDEPLOY code is Execute-Process -Path "$dirFiles\setup.exe" -Parameters "/CONFIGURE remove.xml" -ContinueOnError $true -IgnoreExitCodes '*' and remove xml is below - not sure i need the remove all true whilst also calling out products but the reality sometimes doesnt match the documentation with Microsoft <?xml version="1.0"?> -<Configuration> <Display AcceptEULA="True" Level="None"/> <Property Value="TRUE" Name="FORCEAPPSHUTDOWN"/> -<Remove All="TRUE"> -<Product ID="O365ProPlusRetail"> <Language ID="en-us"/> </Product> -<Product ID="VisioProRetail"> <Language ID="en-us"/> </Product> -<Product ID="ProjectProRetail"> <Language ID="en-us"/> </Product> </Remove> </Configuration>1 point
-
1 point
-
If I am understanding you right then you are having issues if the computer account already exists? Sounds like your DomainJoin account does not have permissions to reuse and existing account. I would check the account permissions. http://blog.coretech.dk/mip/creating-a-joindomain-account-for-use-with-sccm-osd/1 point
-
1 point
-
I'm going to run through this guide again. There's a few inconsistencies. Each step has a different scripts.zip attached. I figured I would just download the part 5 which would include everything (6 wasn't out at the time). And I noticed when you run powershell to install WSUS calls for a XML file in part 2\cm01 folder that does not exist. The XML file is in part 4 folder. Small little things like this. Also install roles and features power shell is in part 4 and 5 folders.1 point
-
Unfortunately, the log file was clear, so I went ahead and uninstalled and reinstalled my MP, and all is working well. If it happens again though, that'll be the first file I check. Thanks @anyweb!1 point
-
We've had problems with Surface Pro 4 PXE too. Microsoft have confirmed it's a problem with the UEFI Network stack, and you need to have IPv6 enabled and routed to the PXE Server. If you just have IPv4 then it won't work. They are working on a firmware fix, which should be out in a few months.1 point
-
Hi all, Here are the new updates that fix the problem : Windows Server 2016 (KB4039396) Windows Server 2012 R2 (KB4039871) Windows Server 2012 (KB4039873) WSUS 3.0 SP2 (KB4039929) New update of August 28 (today). I installed it, and it works. Enjoy Bebop.1 point
-
We are moving from SCCM 2012 R2 + SQL 200R2 both on Windows Server 2008 R2, the new boxes are all Windows Server 2016, using SQL 2016. We are setting up a completly new primary site (albeit in a different 'resource' domain) we could have just joined the new and the old together and migrated everything however the old setup had so many inconsitancies and issues. We also decided to take a look at all the apps and make sure they were setup correctly- drop any old apps, introduce new/updated apps etc. in some cases i have exported apps, however you have to go change the content location, especailly if its in a different place, however thats simple. I've also taken the oppurtunity to redo all our device collections, mainly to help with the user admin/role based admin, as previously all the SCCM users were full admins so we are 'locking it down' this time around. Once we are done we will just drop the boundaries from the old site, add them to the new site and push the new client.1 point
-
Absolutely top work, I foresee problems to forcing users to upgrade and this deferring upgrades to suit the user is something that SCCM should have built in. I migrated from Zenworks to SCCM and for all its problems there's a few bits of functionality that I miss. This is definitely one. Thanks again.1 point
-
use the current version of MDT until the next release is released, as regards ADK 1703 don't use it with Server 2016 until it is fixed for the secure boot driver signing issue that occurs when you install it on Server 20161 point
-
That helped me as well, after SP1, CU1, the Software Summarization was set to run every hour, and had my SQL pegged. We went from 4 to 6 cores, same thing, bumped it to 8, same thing... If you're looking for where summarization is, right click on "All Software Updates" under Software Updates in Software Library, and you'll see summarization. It was set to every hour, so I changed that to 1 day, and it's much happier now.1 point
-
Double check that you have all the IIS-Pre Reqs installed! got the same problem when i left out ASAPI Filters and something else.1 point
-
On the SCCM Side, You can follow this guide to extend the schema For the rest, we have used SCCM and VMware clusters alot and find very few issues with them once you get teething issues out of the way, this includes things like vlan's/trunking etc. it can be a pain especially if your using the newer Nexus V1000 vSwitch for vSphere.. basic things i assume you'll sort out when thinking logically about it.... We separate our SCCM Central Servers from DP's as this is going to cause you alot of traffic, for our first deployment we have a couple of DP's sitting beside our SCCM Provider to handle this workload. its choice and licensing though... so go with what you feel your environment can handle... 170 WS's id say is achievable... we run between 200-500 a session during a deployment.... but just be aware its not a simple set and forget which is where alot of deployments come undone... you need to set them off and hang around for an hour or so... especially if multi casting as in our experience it seem to be still a tad on the flakey side... nothing worse than 80users showing up Monday morning without a PC to use.... I would suggest you stick with smaller groups over a few nights, ESPECIALLY if migrating from XP.... Is there any reason you couldn't script your pc naming? There's some more to go with all this but i suggest you pick a pilot target of 10-20 desktops and push it out on a Wednesday night so you have a couple of days to iron out the kinks.... and there will be kinks. For your driver issue, i'd be using SCCM if possible, and be building Driver Packs per http://www.windows-noob.com/forums/index.php?/topic/2428-how-to-create-a-driver-package/ .... read the whole post, checkout how to query WMI and install drivers that way if you have more concerns. Im not a huge fan of using just MDT and WDS to deploy, to much extra scripting required to get your basics setup..... this is just my experience and 2cents1 point