-
Posts
9257 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
371
Everything posted by anyweb
-
if you've already extended the schema for ConfigMgr then you are good to go. to verify you can delete everything in the system mangement container using adsiedit and restart the sms_executive component, it should repopulate the system management container, if not it's not working or delegated correctly
-
yes you can, those workgroup machines can be Azure AD joined (and enrolled into MDM with Intune) or they can be simply workgroup machines enrolled into MDM or they can be workgroup machines that use MAM-WE
-
what does your smspxe.log tell you ? attach it here
-
On Microsoft's blog, they announced that RS3 (Redstone 3) aka Fall Creators Update is coming October 17th 2017. "Create and play this holiday with the Windows 10 Fall Creators Update coming Oct. 17" It offers the following new features Windows Inking Windows Inking keeps getting better, letting you ink directly onto PDF’s, making it easier and faster to comment and share with others, improving on what you could do with pen and paper alone. Smart Ink applies artificial intelligence to inking automatically making the squares you draw more perfect, or turning boxes into a table for you with no extra work. And you know how sometimes you can’t find your keys, wallet, and phone, sometimes it’s hard to find your pen to do the inking. Windows Find my Pen fixes that in the Fall Creators Update. Photos and Videos We have reimagined our Photos Application to deliver remixed experiences for telling your stories with photos, videos, music, 3D, and even inking. OneDrive Files On-Demand You can save all of your creations in OneDrive Files On-Demand, accessing your cloud files like any of your other files on your PC, without using up your local storage space. Gaming The fuel that often inspires creativity is play. With the Fall Creators Update, we’ve updated Game Mode, which allows your games to use the full processing power of your device as if it was an Xbox game console, right from a new button on the Game bar. And to take advantage of this power, we have a fantastic lineup of Xbox Play Anywhere games coming including, Cuphead, Forza Motorsport 7, Super Lucky’s Tale and Middle-earth: Shadow of War. And, if you love these Xbox play anywhere games, coming on November 7 you can play them on the most powerful console on the planet, Xbox One X. Security While you create and play, our goal is to keep you safe and secure. With the Fall Creators Update, Windows Defender is smarter and defends better than ever before. With behind the scenes cloud intelligence that enables new defenses against ransomware and exploits. I can’t talk about security without talking about Windows 10 S. Introduced last May, Windows 10 S is specifically designed for simplicity and security, with significant breakthroughs in battery life and performance. It’s off to a great start, with some of our highest customer satisfaction results yet. This is the core of Fall Creators Update, it’s all about unleashing your creativity and having some fun while at the same time keeping you safe and secure. Accessibility I also want to share some exciting new technology that speaks to our mission at Microsoft to create products which are inclusive by design. With the Fall Creators Update, we are making Windows more accessible for those with Lou Gehrig’s disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disease that impacts the brain’s ability to control your muscles. The one muscle it doesn’t impact, are the eyes. A new feature Eye Control implements incredible eye tracking technology that lets you type, and operate a mouse just using your eyes, this is life changing technology for those with Lou Gehrig’s disease. This is real advancement in accessibility that we are introducing to the world with the Fall Creators Update. Windows Mixed Reality Lastly, with the Fall Creators Update, we are enabling you to immerse yourself in a new reality, the world of Windows Mixed Reality. By combining our physical and digital worlds, we believe mixed reality is the next step in the evolution of human computing. For the first time, we are talking about a mixed reality system that fully immerses you in the experience not limited to a mobile device screen size. One that is easy to setup, not requiring you to mount cameras around the room, just put the headset on your head, plug it into your PC and get started, leaving your hands free to interact with the mixed world. It’s available from a wide range of partners around the world, like Acer, ASUS, Dell, HP, and Lenovo with headsets starting as low as $299. I am thrilled to announce that Windows Mixed Reality headsets will start to become available on October 17 when the Fall Creators Update ships. And if you find yourself without a headset, we will also deliver mixed reality experiences through the PC. With Mixed Reality Viewer, you can see 3D objects – either from the Remix3D.com community or your own creation from Paint 3D – mixed into your actual surroundings through your PC’s camera – and snapped and shared – for powerful ways to tell your story.
-

Boot Media - Now fails at network settings
anyweb replied to LOKI's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
try this script it will help -
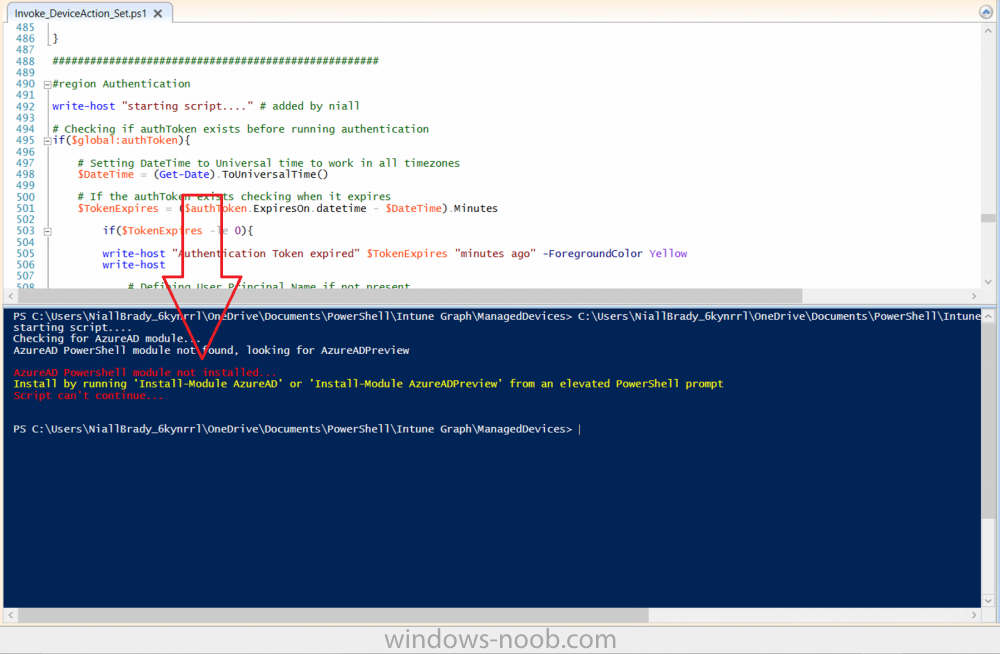
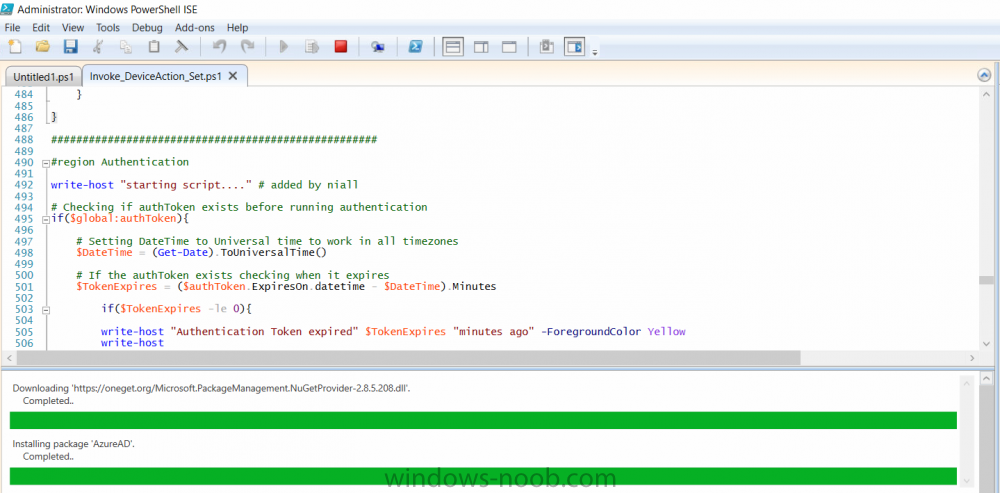
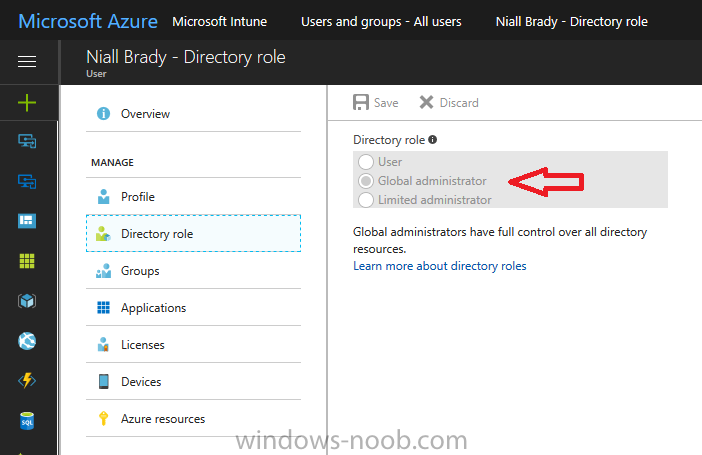
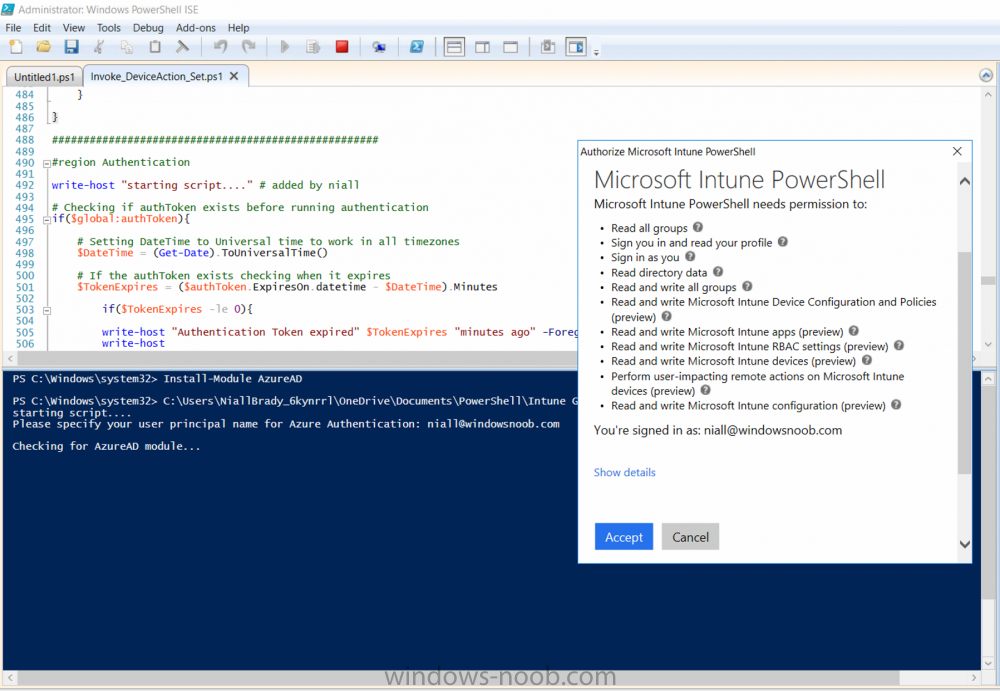
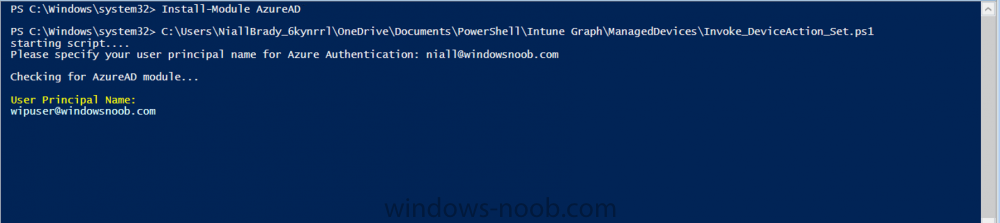
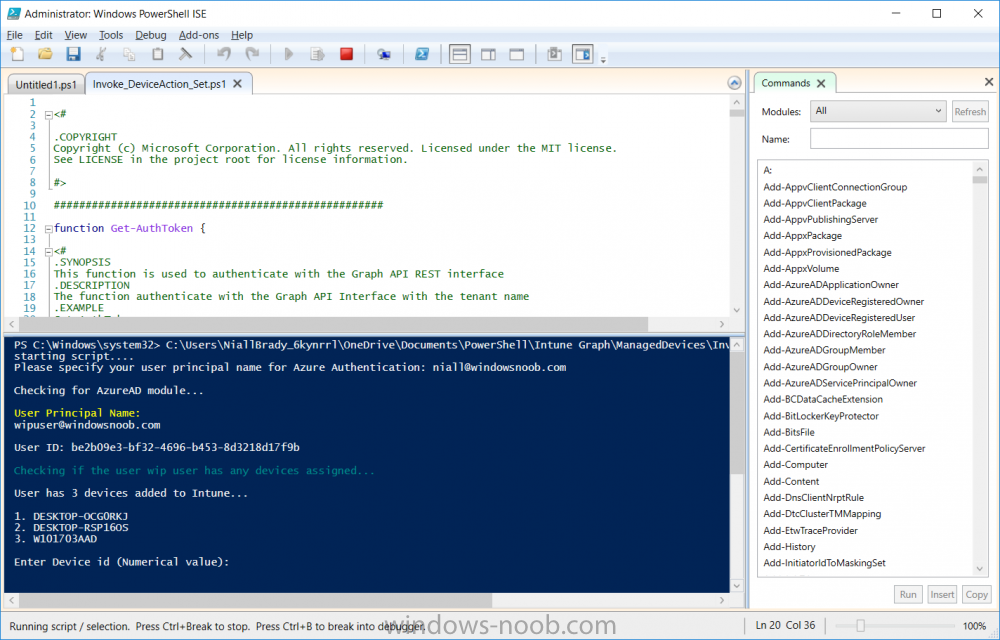
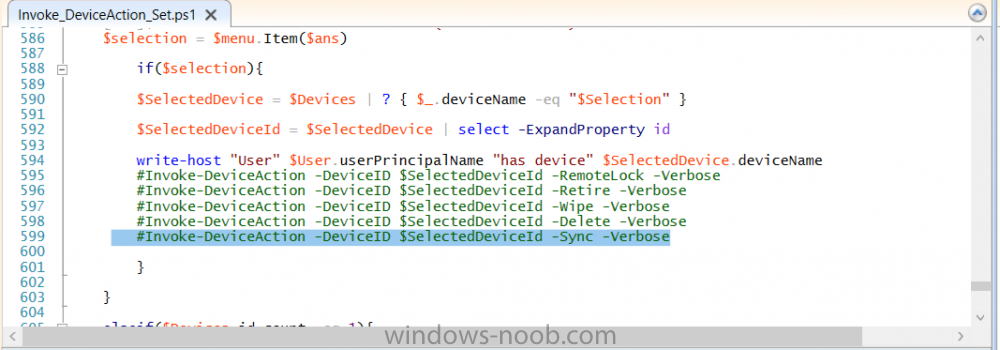
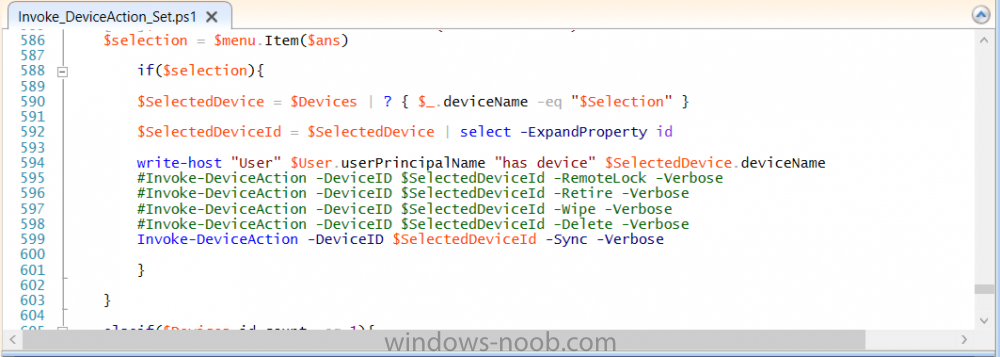
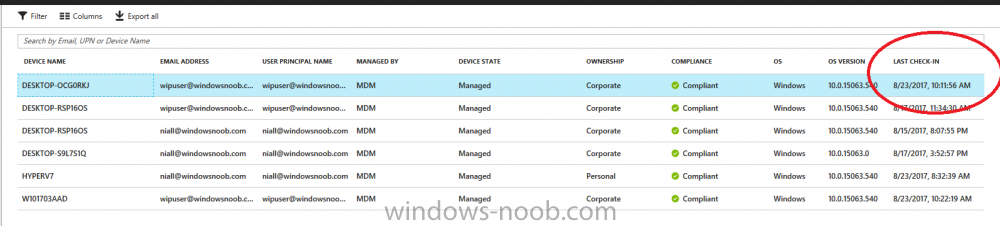
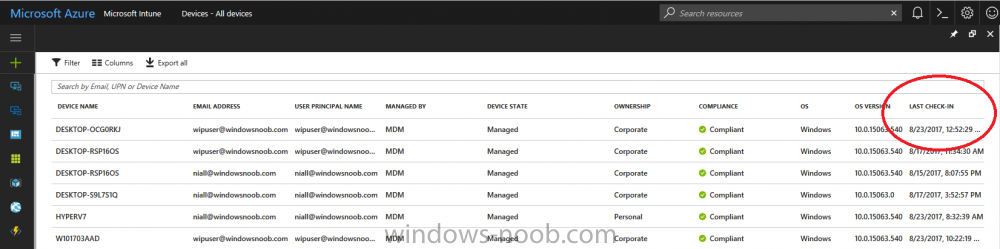
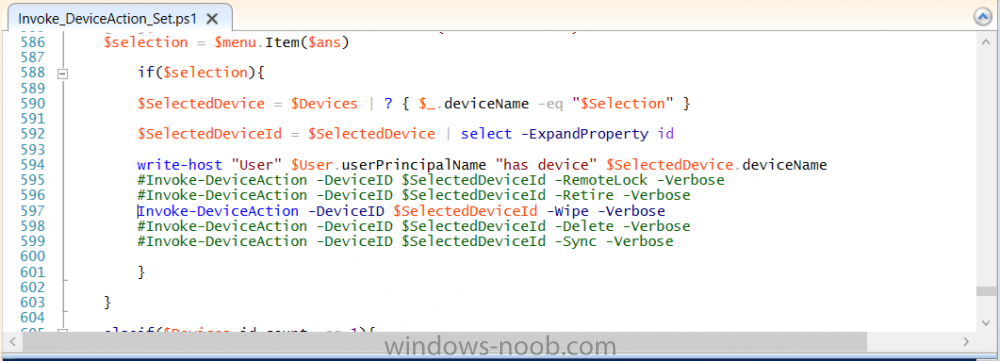
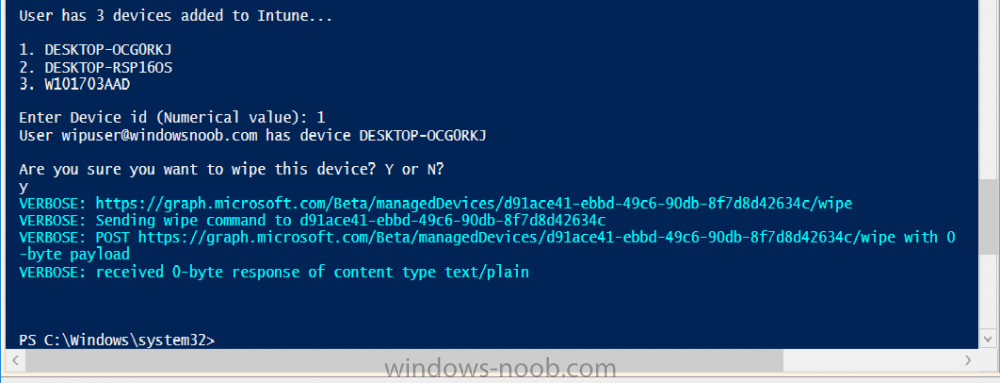
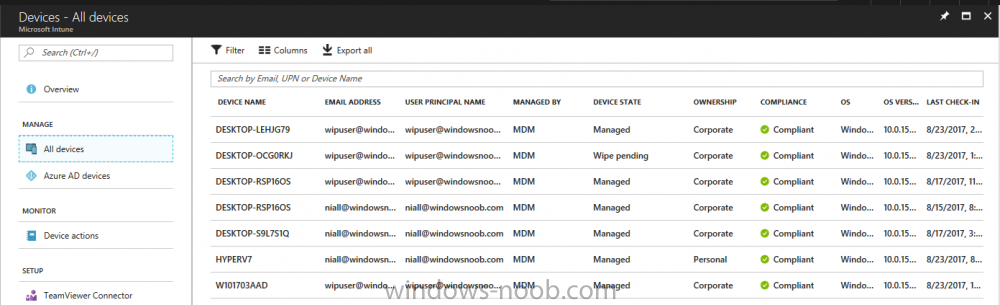
Introduction According to Microsoft, Microsoft Graph is: …your entry to automate things in the cloud via the Microsoft Graph API. This API gives you access to AzureAD, Excel, Intune, Outlook, OneDrive, OneNote, SharePoint, and more. Microsoft Graph is a RESTful web API that enables you to access Microsoft Cloud service resources. After you register your app and get authentication tokens for a user or service, you can make requests to the Microsoft Graph API. This API uses the following HTTP methods: Get Post Patch Put Delete For example, here is a Post action to RemoteLock a device: POST https://graph.microsoft.com/Beta/managedDevices/fd3e81ec-a7d0-4f35-af7c-1478213f56c7/remoteLock If you’d like to play with it right now then you can also check out Graph Explorer, which is a web based (web browser) gui for controlling Graph and it’s available here. OK that’s already a bit complicated for some people, so what does this mean in real terms for a Microsoft Intune admin that wants to automate things using PowerShell. In this guide I’ll show you step-by-step how to get up and running with Graph for Intune and how to begin automating actions using PowerShell. This is not for the feint hearted but I encourage you to take the time and effort to try this for yourself, you’ll be glad you did ! Note: In this guide I assume that you already have a Microsoft test Intune tenant setup and configured and that you have some PowerShell knowledge. At the time of writing (August 2017), Graph for Intune is still in Beta and is subject to change. Use of these APIs in production applications is not supported by Microsoft. Step 1. Download the sample PowerShell scripts Before you get started, you’ll need to download the PowerShell sample scripts. You can download the Graph PowerShell Intune samples from Github at the following address: https://github.com/microsoftgraph/powershell-intune-samples Make sure you have the latest scripts If you have the latest scripts, then skip this section. The scripts are updated from time to time, so if you downloaded them in the past, go to Github again and download the latest copy of the scripts, chances are that the scripts have been updated and that can mean bugs are fixed or behavior has changed. For example The following script Invoke_DeviceActionSet.ps1 had this content in June 2017 in the ManagedDevices section param ( [switch]$RemoteLock, [switch]$ResetPasscode, [switch]$Wipe, [switch]$Retire, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true,HelpMessage=”DeviceId (guid) for the Device you want to take action on must be specified:”)] $DeviceID ) The same script in August 2017 has been updated to include more ability param ( [switch]$RemoteLock, [switch]$ResetPasscode, [switch]$Wipe, [switch]$Retire, [switch]$Delete, [switch]$Sync, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true,HelpMessage=”DeviceId (guid) for the Device you want to take action on must be specified:”)] $DeviceID ) In addition there can be behavior changes within the script, for example in the below section (from June 2017) it invokes a RemoteLock action by default write-host “User” $User.userPrincipalName “has device” $Device.deviceName Invoke-DeviceAction -DeviceID $Device.id -RemoteLock -Verbose #Invoke-DeviceAction -DeviceID $Device.id -Retire -Verbose #Invoke-DeviceAction -DeviceID $Device.id -Wipe -Verbose The same script in August 2017 does not do any action by default, you’d need to un- comment the appropriate line if you want it to perform a specific action or just edit the script to your liking. write-host “User” $User.userPrincipalName “has device” $SelectedDevice.deviceName #Invoke-DeviceAction -DeviceID $SelectedDeviceId -RemoteLock -Verbose #Invoke-DeviceAction -DeviceID $SelectedDeviceId -Retire -Verbose #Invoke-DeviceAction -DeviceID $SelectedDeviceId -Wipe -Verbose #Invoke-DeviceAction -DeviceID $SelectedDeviceId -Delete -Verbose #Invoke-DeviceAction -DeviceID $SelectedDeviceId -Sync -Verbose What’s in the script samples ? The script samples are neatly organized into 15 different sections listed below: AppleEnrollment Applications AppProtectionPolicy Authentication CheckStatus CompanyPortalBranding CompliancePolicy DeviceConfiguration EnrollmentRestrictions ManagedDevices Paging RBAC RemoteActionAudit TermsAndConditions UserPolicyReport Within each section you’ll find one or more sample PowerShell scripts and there is a readme.md file included in each section which gives more details about what functions are contained in the scripts and what the scripts actually do. Step 2. Install the AzureAD PowerShell module The first time you attempt to run one of the scripts, a function within the script will check for the AzureAD PowerShell module and if not found it will prompt the user to install the module and it will then exit from the script. To avoid this, start PowerShell ISE as administrator, then issue the following command: Install-Module AzureAD After entering that command, you’ll get one or more popups asking if it’s OK to download and install NuGet, answer yes to all. and then it will start installing the module. You are now ready to test the scripts. Step 3. AzureAD admin versus target user When you run one of the sample scripts (for the first time, after installing the AzureAD module) you’ll get prompted for AzureAd credentials to access Intune resources, these are the credentials that you’d normally use to do administrative work in the Intune service in Azure. In this example you’ll use the Invoke_DeviceAction_set.ps1 script in the ManagedDevices section, open that script using PowerShell ISE as administrator. Click on the green triangle to Run the script. As you can see it prompts for the user principal name for Azure authentication. For this blogpost, I’m connecting to Azure using a user that has a Directory role of a Global Administrator. Tip: You can verify the directory role a user has in Intune, by selecting Users and groups – all users, user, Directory role. Global administrators have full control over all directory resources, if that’s not what you want you can customize the permissions using Limited Administrator and selecting the various options available. After entering the AzureAD user principal name, you’ll see a popup requesting permission to access various Intune resources, click Accept. The currently available actions in the Invoke_DeviceAction_Set.ps1 script are • RemoteLock • Retire • Wipe • Delete • Sync To use any of those actions on a device you’ll need to identify a target user (and their associated devices). To do this, enter the user principle name of that target user when prompted. This user is a regular user in Intune and not a Limited or Global Administrator. Step 4. Perform a Sync action Once entered, you’ll see any devices registered to that user, in this example, the specified user has 3 devices assigned. Press a number matching the device and… nothing will happen, the script exits. This is ok as the behavior of the script is modified to perform this way, let’s make a change so that instead of simply exiting, that it will perform a device Sync action. Locate line 599 in the script which contains this text and remove the hash in front of that line. Save the file. Before running the script again, verify the last sync time of the device you want to test automation against. You can verify last sync time by selecting All Devices, find the device in question and look at the Last check-in time column. Run the script again and notice the difference, now you are prompted if you want to sync the device. Go back into Intune and verify the Last Check-in time. It will have changed for that device. Success ! You’ve accomplished your first automation using PowerShell in Intune. Step 5. Perform a device Wipe Note: A Wipe will reset a device and remove all apps and data on the device, both Personal and Company owned data. Next, let’s try another action and one that would be very useful to Automate, that is the ability to remove data on a device. In PowerShell ISE, place a # infront of the Sync line again, and remove the # from the Wipe line. Save the changes. Run the script again, notice that you are prompted if you want to to wipe the device this time. and look what happens next ! and in the Intune service in Azure you can see this (Wipe Pending) Note: Just because you can see actions in a script does not necessarily mean that those actions will apply to your scenario, and they may infact generate an error, an example of that is the RemoteLock functionality which is not supported on Windows 10 desktop. Step 5. Perform a device Retire Note: a Retire action will un-enroll a device from Intune, and remove company data, meaning it is un-managed. All personal apps, data, photos on the device will remain untouched. In the screenshot below, you can see the Company Portal app installed on an Iphone. And below you can see the Retire action on that same iPhone. In this GIF you can see the line used for the Retire action, and then the fact that the iphone shows up as a device for the user. After running the action it no longer appears in the device list for that user as it has been removed from device management and is no longer enrolled. Summary In this blog post you learned a bit about Microsoft Graph, and how you can use it to automate the management of Intune using PowerShell. Awesome, really awesome. Recommended reading Sign up for Intune trial https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/free-trial-sign-up Get Intune PowerShell samples for Intune https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/enterprisemobility/2017/05/15/get-intune-powershell-samples-for-microsoft-graph-api/ Download the scripts https://github.com/microsoftgraph/powershell-intune-samples Working with Azure Active directory Graph API from PowerShell https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/paulomarques/2016/03/21/working-with-azure-active-directory-graph-api-from-powershell/
-
- graph
- powershell
-
(and 1 more)
Tagged with:
-
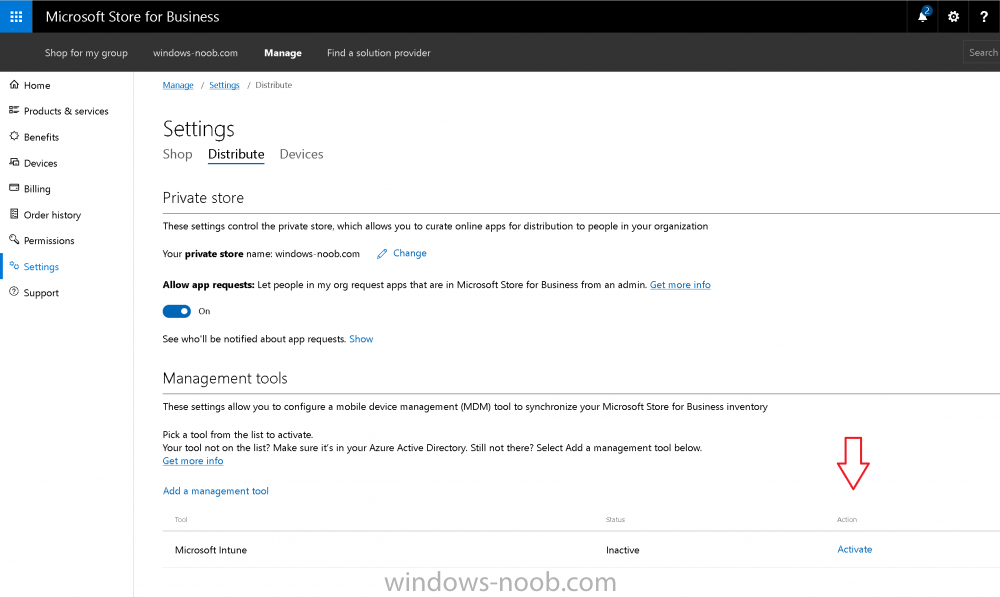
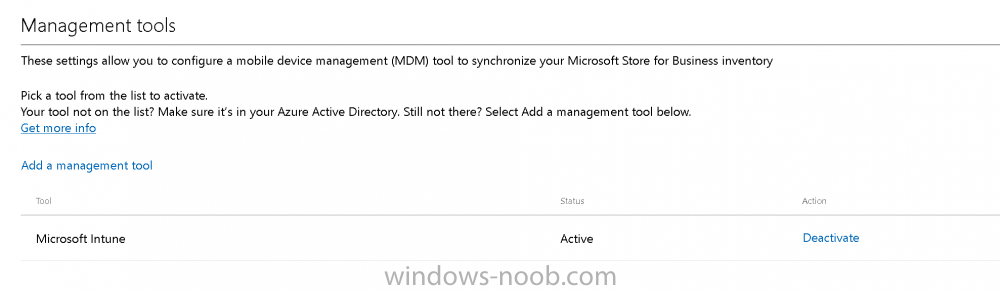
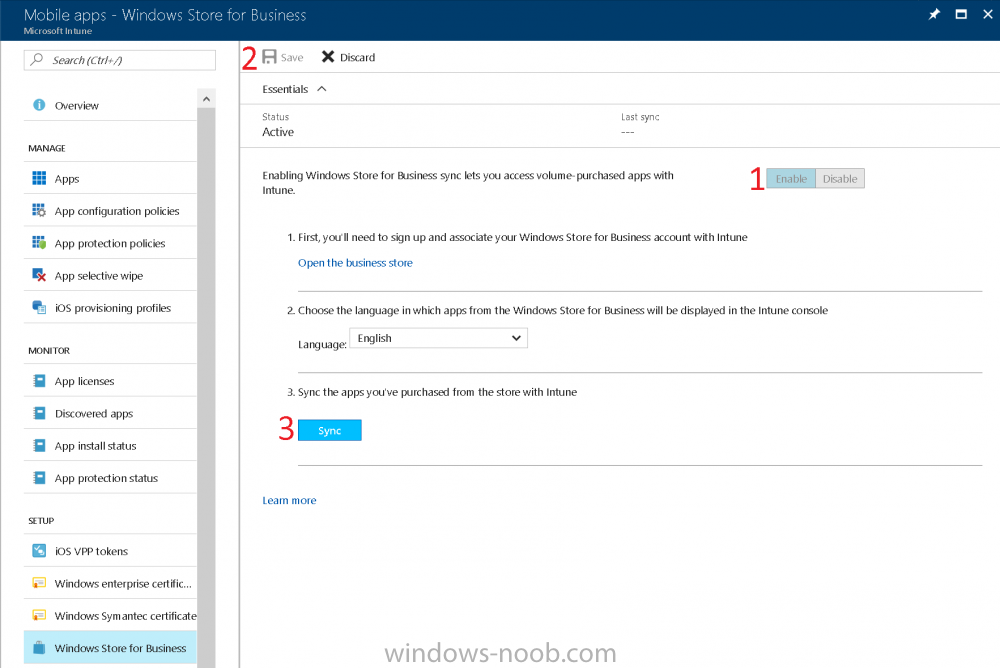
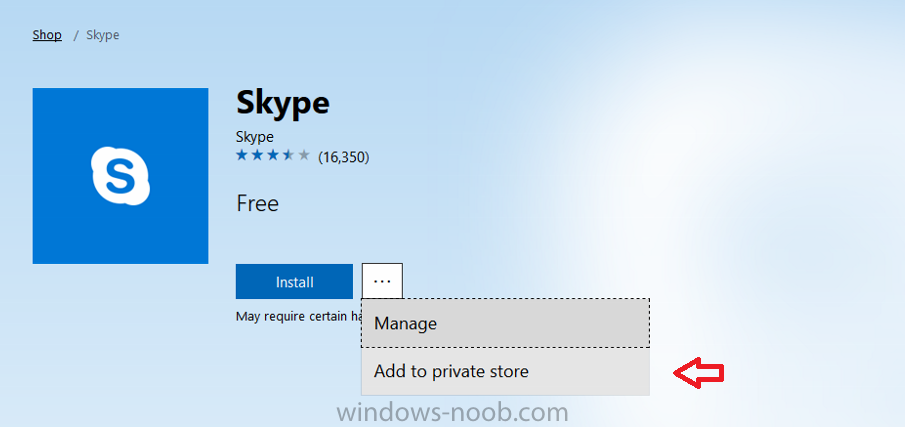
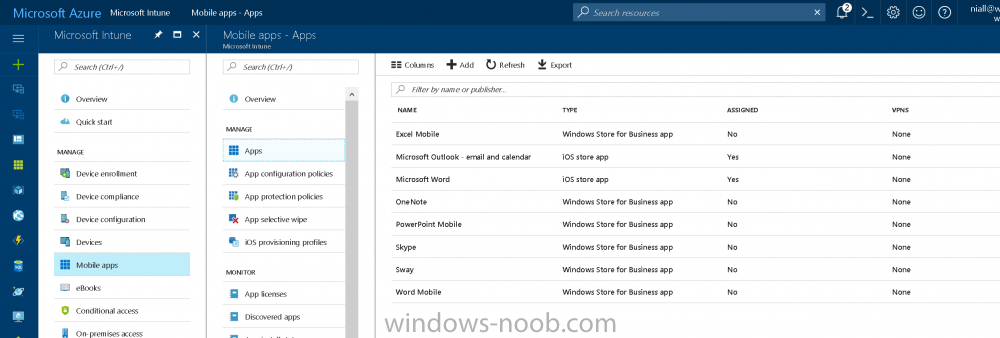
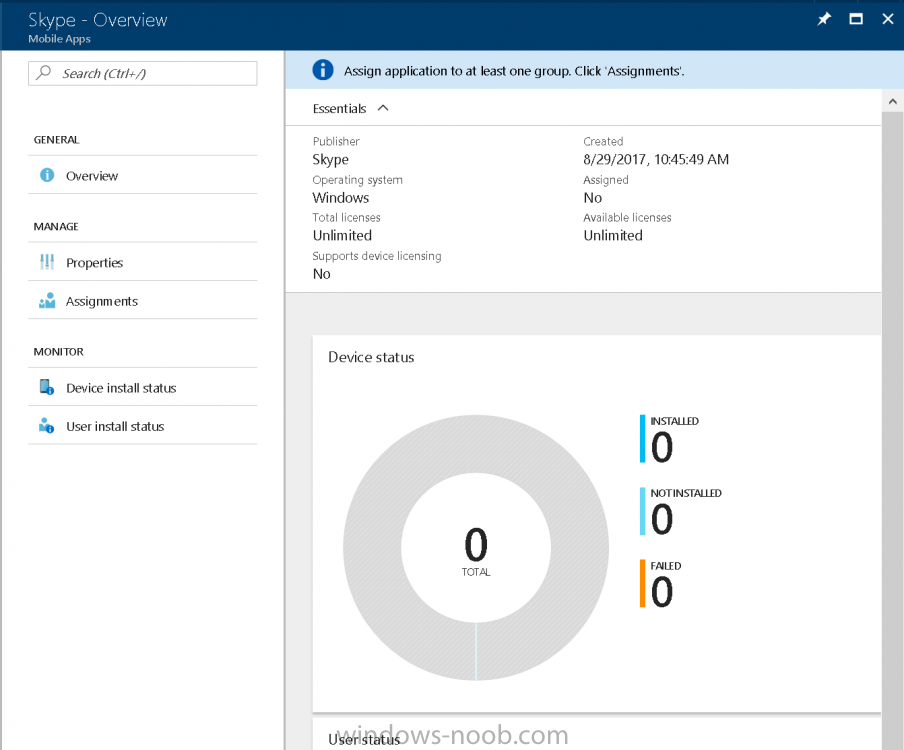
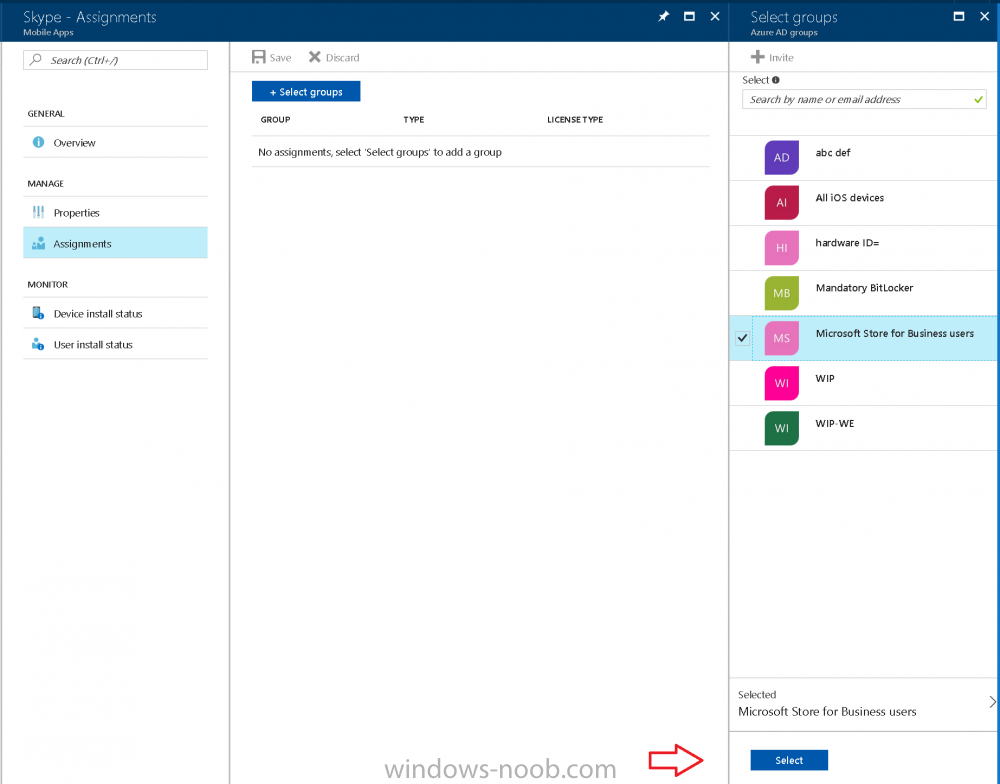
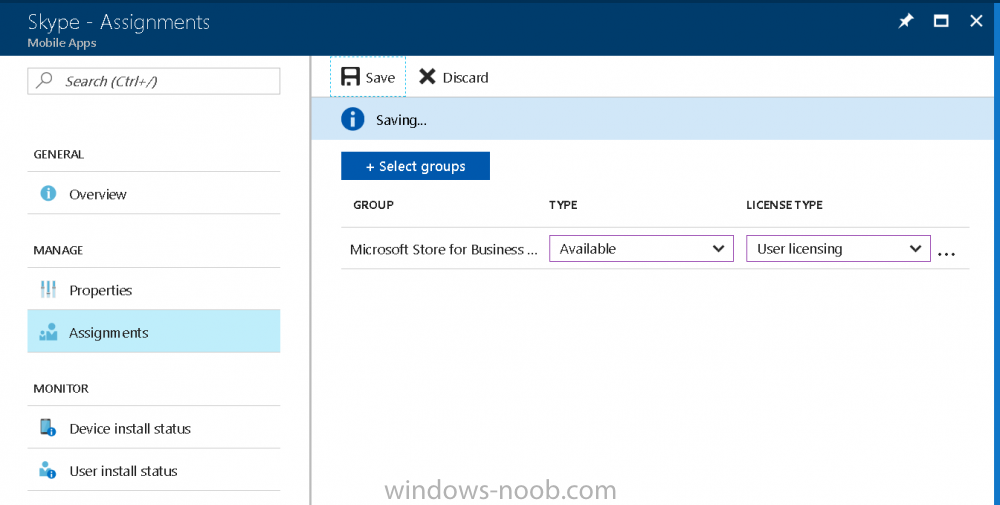
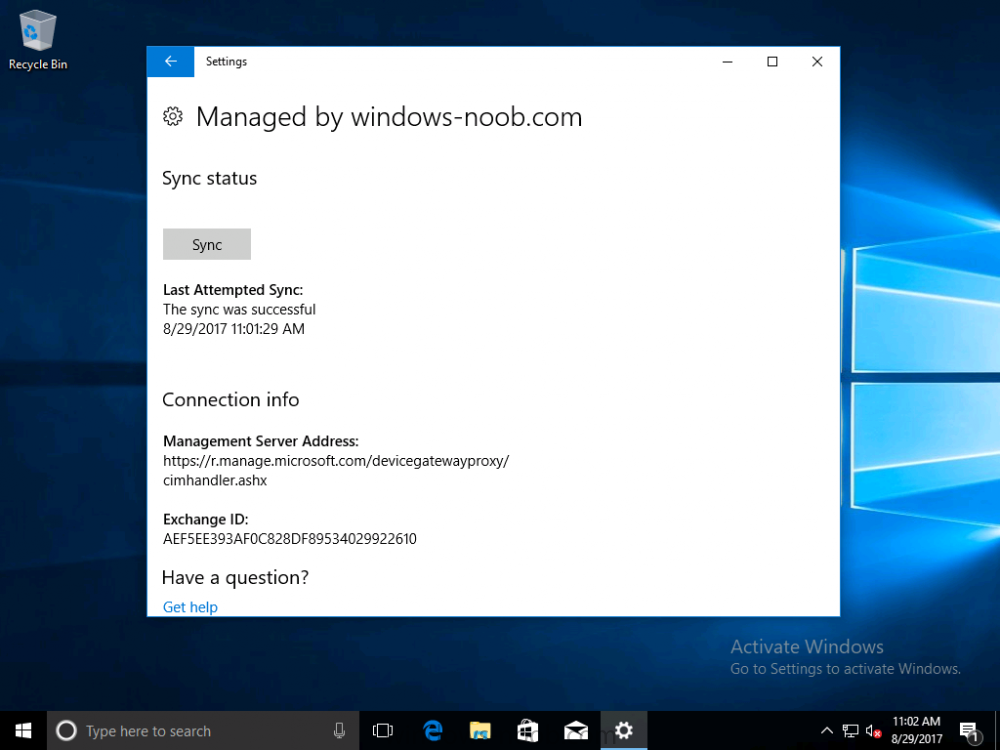
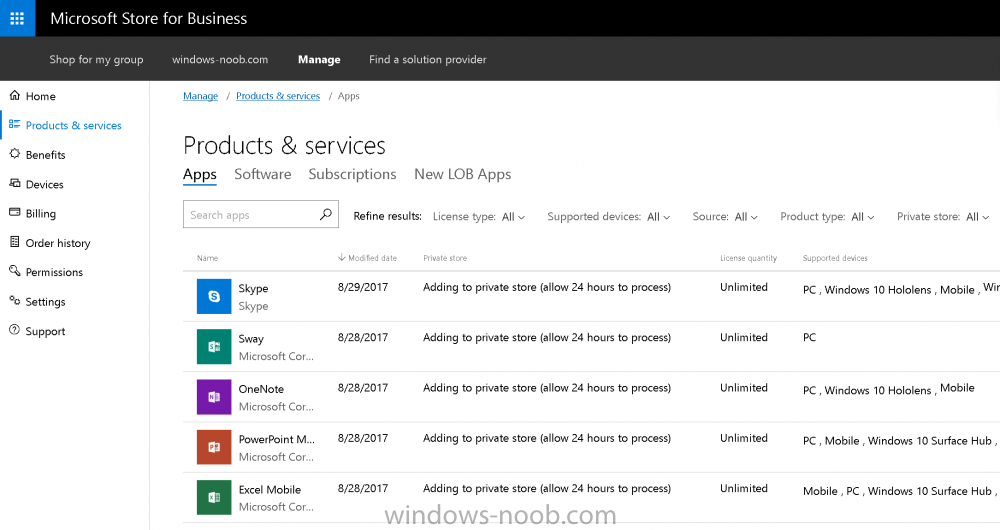
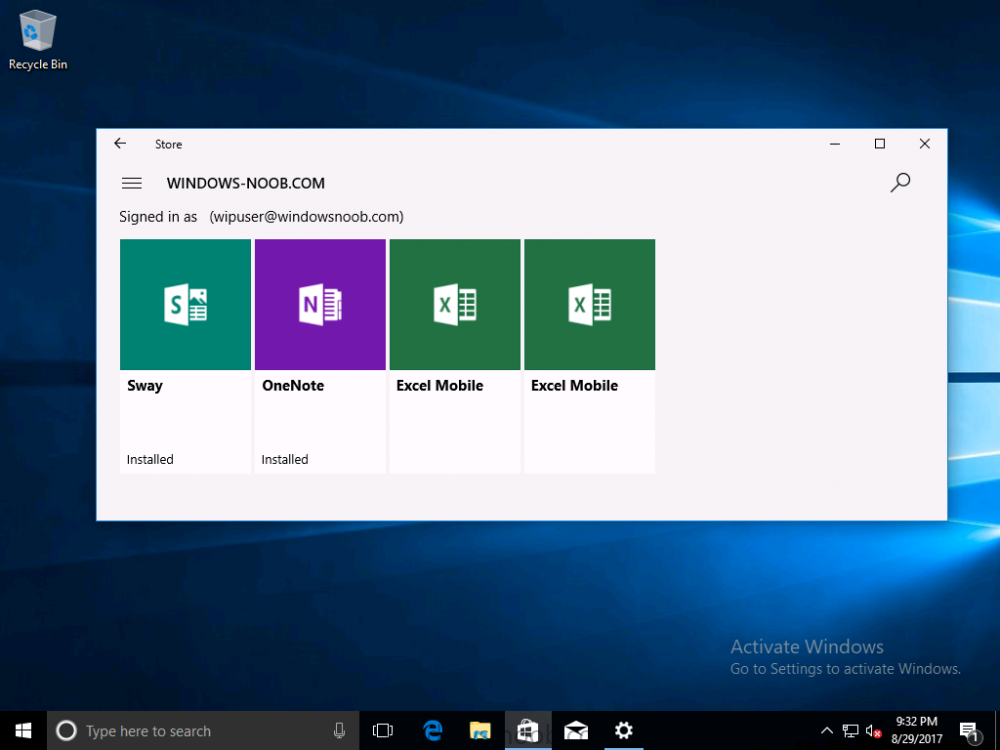
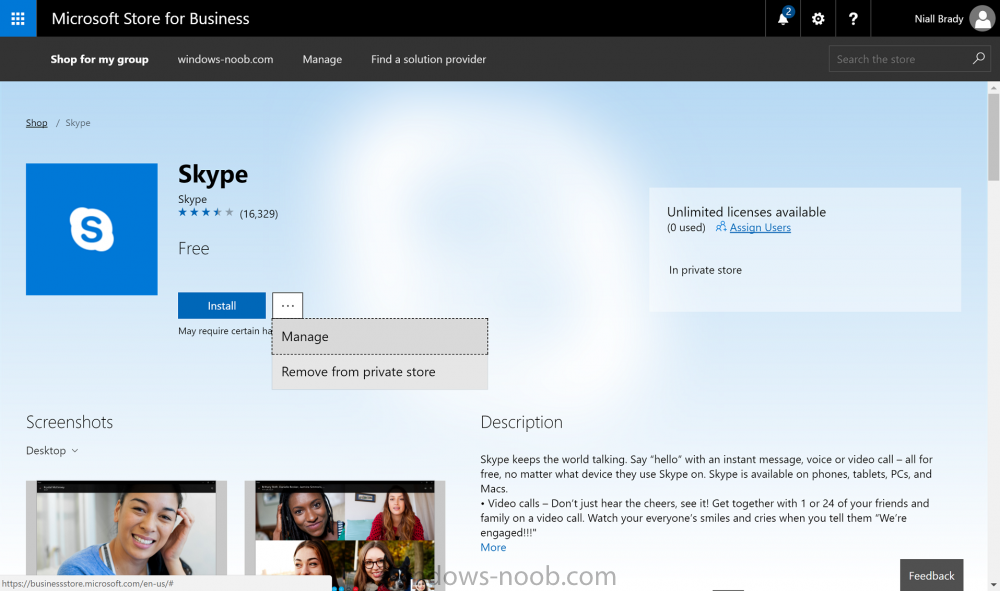
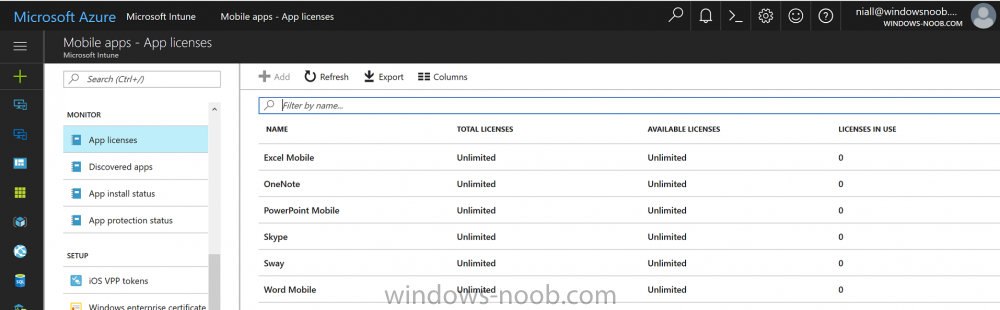
Introduction Windows users are used to seeing the familiar Windows Store icon on their Windows 10 devices, this gives them access to download free Windows store apps without credentials (for example the Microsoft Company Portal), or download paid apps using Microsoft live credentials. Microsoft Store for Business (formally known as Windows Store for Business) leverages the Windows Store concept and adds a new tab to that user experience to show apps to your users (that have been approved for use in your business) without the need for using an external Microsoft live account. Microsoft refers to the stores as follows: In this post I'll show you what you need to do to integrate MSFB into Intune in Azure and how to deploy MSFB apps to your users. Before you start though, be aware of the following: You must configure Intune as the mobile device management authority for your organization. You must have signed up for an account on the Microsoft Store for Business. Once you have associated a Business Store account with Intune, you cannot change to a different account in the future. Apps purchased from the store cannot be manually added to or deleted from Intune. They can only be synchronized with the Microsoft Store for Business. Intune synchronizes only online licensed apps you have purchased from the Microsoft Store for Business. Devices must be joined to Active Directory Domain Services, or workplace-joined, to use this capability. Enrolled devices must be using the 1511 release of Windows 10 (or later), in this guide I'm using Windows 10 Enterprise version 1703. Step 1. Login to the business store Login to the Microsoft Store for Business by signing in using the same tenant account you use to sign into Intune. If it's your first time there, you'll have an EULA to read and accept, it will look something like this. Your tenant name will be listed in the Microsoft Store for Business. Step 2. Associate your Microsoft Store for Business account with Intune In the Microsoft Store for Business, click on Manage (to the right of your tenant name), and in the new page that opens, click on Settings, then click on Distribute. Under Management Tools, you'll see Microsoft Intune listed and to the right. To activate MSFB with Intune, click on the Activate action. After activation, it will appear like so with a status of Active. Step 3. Configure Synchronization In this step, login to https://portal.azure.com and click on the Intune service. In Intune, click on Mobile apps, select Windows Store for Business (even though this is Microsoft Store for Business), and then click on the Enable (1), next click on Save (2), finally click on the Sync (3) button. You will get a notification that the sync has started and that it will take some time. Step 4. Synchronize Apps In the Microsoft Store for Business, you need to select some apps to sync otherwise no Microsoft Store for Business apps will appear in Intune. To do this, in the search field on the right side of the Microsoft Store for Business web portal, enter the name of an app (for example Skype) and press enter. The Search for Skype results will appear. In the list of search results displayed, select your chosen app. Info about the application will be displayed. Click on the Get the app button. Next click on the … beside the app, and choose add to private store. You'll be informed that the app is being added to your private store and that it can take up to 24 hours. After adding apps, you can review them in the Products and Services link under Manage and their status will be listed. Note: Even though the website states "Adding to private store (allow 24 hours to process)" it can actually take longer for those apps to appear in your private store, but be patient they will. After the apps appear in your private store it will look something like this. You can select an app, and you now have options to Manage or Remove from Private store. And any licenses associated with your Private Store apps can be reviewed in the Intune service, under Mobile Apps, App Licenses. Step 5. Assign apps in Intune Now that you've synced some apps from Microsoft Store for Business into Intune, you are ready to deploy (assign) some apps to users. To do so, login to https://portal.azure.com and click on the Intune service. In Intune, click on Mobile apps, select Apps. After sync has completed you'll see some pre-populated Microsoft Store for Business apps in addition to the apps you selected in the store. You can see these apps denoted with the Type field (Windows Store for Business app). Select your chosen app and that apps overview will be displayed. Click on Assignments to assign the app to a group of users then click on Select Groups and point it to a group of one or more users and then click on Select at the bottom of that blade. Next in the Group you selected, there are two drop down's as shown here, select your Assignment type (Available, Not applicable, Required, Uninstall) and License type (User licensing, device licensing) and click on Save. In this example you will make the Assignment type Available which gives the end user a choice in terms of installation, if you want to forcefully install it select Required. Step 6. Review the store on a Windows 10 device As a user that is in the Azure Group targeted with this assignment, login to a Windows 10 device. To ensure you have an up to date policy, trigger a sync with Intune via All Settings, Accounts, Access Work or School, Info, then Sync. Start the Windows Store by clicking on the Windows Store icon. Click on the hamburger icon and select your tenant (shown with a red arrow), note that the user you logged on to the Windows 10 device will be listed below that and you are not prompted for credentials in the Microsoft Store for Business. If your screen resolution is high, you won't see the hamburger icon but will instead see your tenant listed as a tab. And the apps you've made available are displayed, including their status (installed). Note: It may take up to 24 hours for your apps to appear (after you added them to the Private Store). Recommended reading https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/intune-classic/deploy-use/manage-apps-you-purchased-from-the-windows-store-for-business-with-microsoft-intune https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-store/distribute-apps-to-your-employees-windows-store-for-business
-
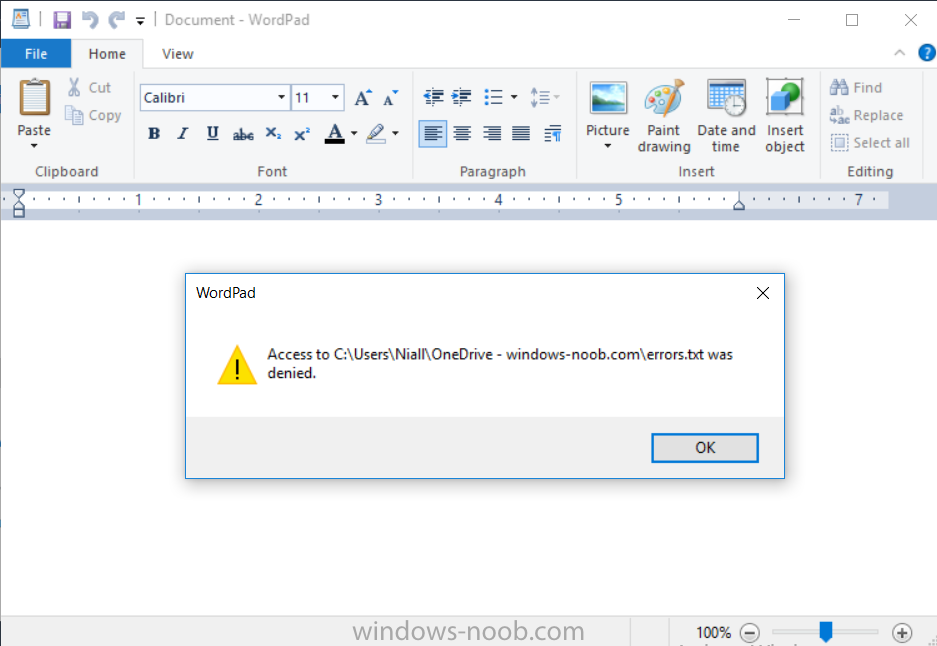
hi, thanks for the kind words, " To support Kerberos authentication, the TCP/IP network communication protocol must be enabled for the network connection of each SQL Server cluster node. Named pipes is not required, but can be used to troubleshoot Kerberos authentication issues. The network protocol settings are configured in SQL Server Configuration Manager, under SQL Server Network Configuration. " via https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/servers/deploy/configure/use-a-sql-server-cluster-for-the-site-database hope that helps, from cheers niall
-
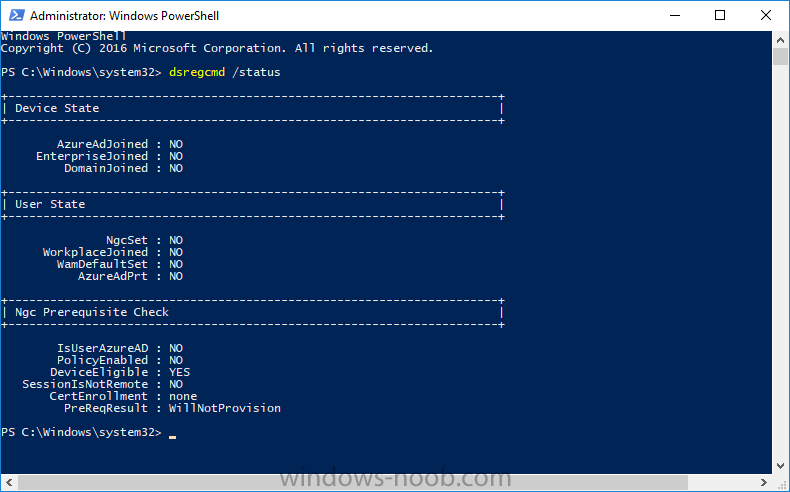
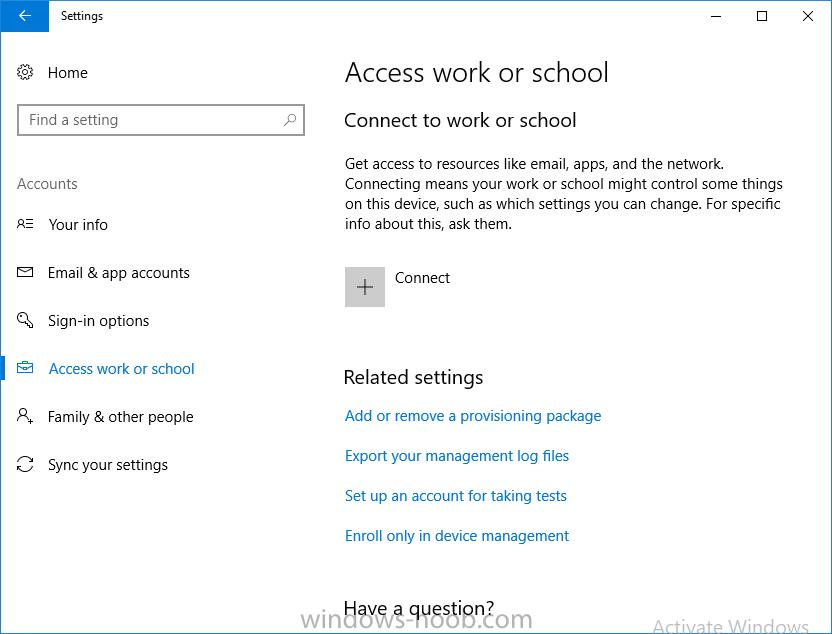
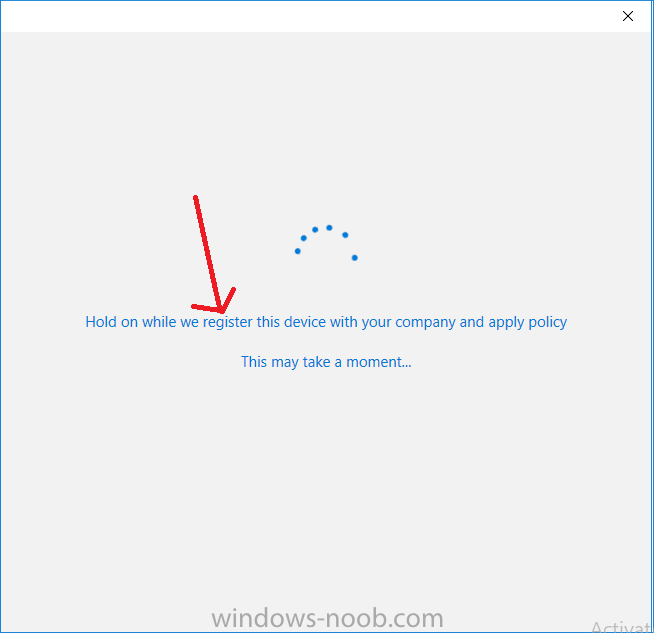
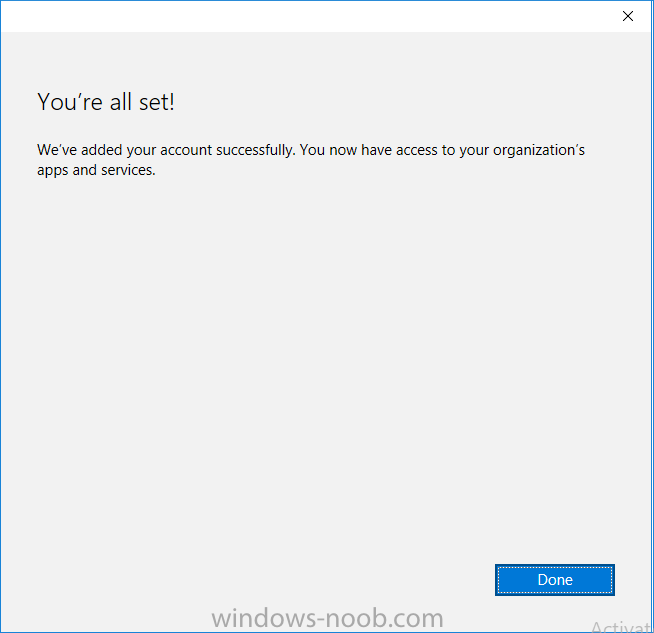
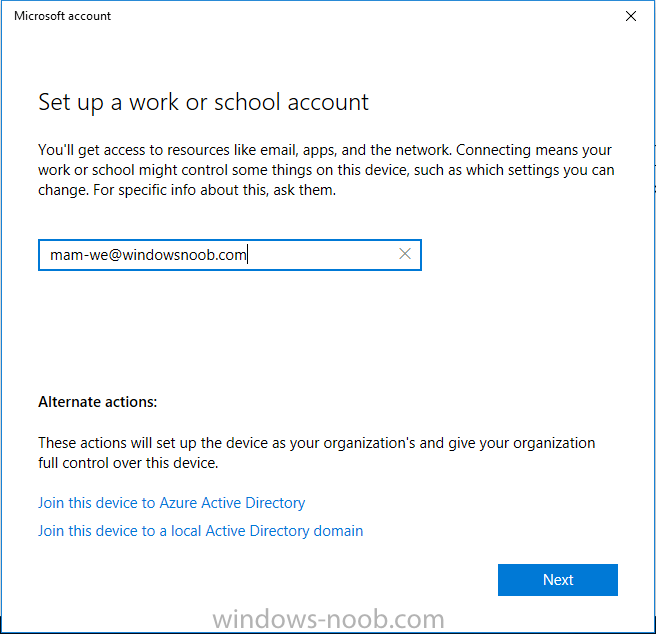
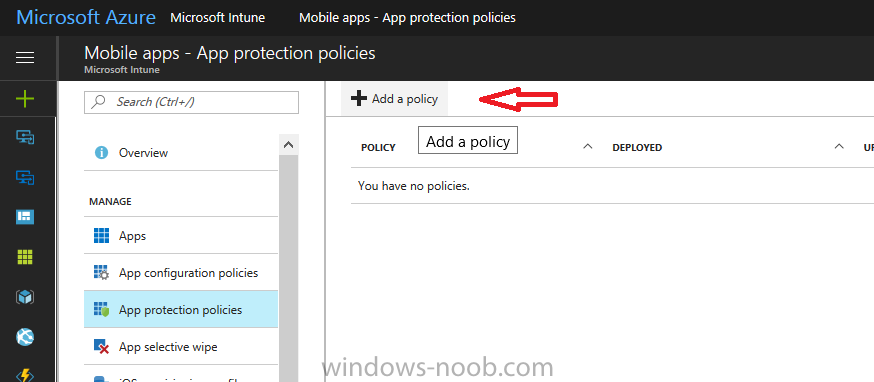
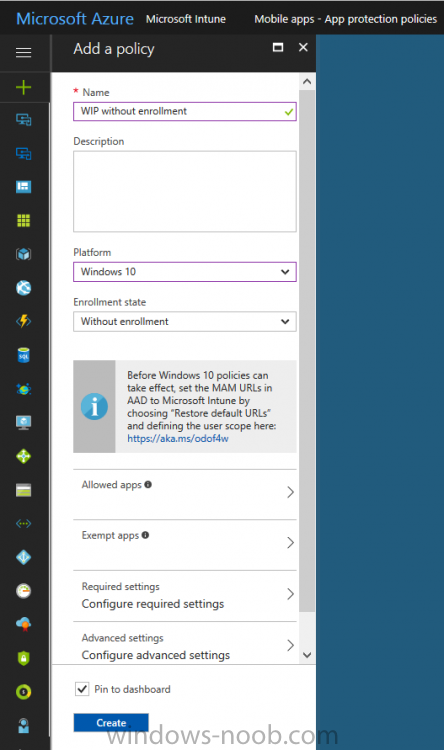
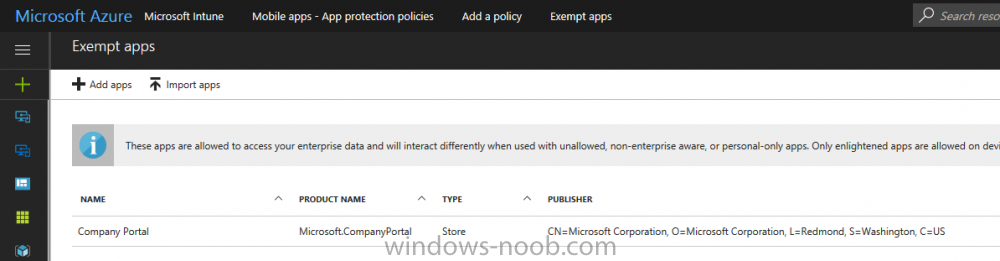
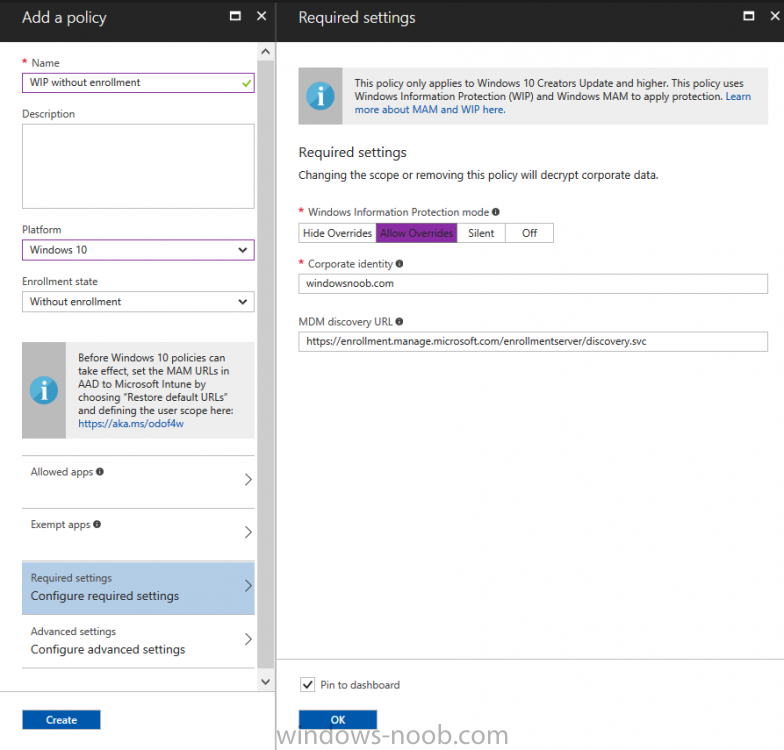
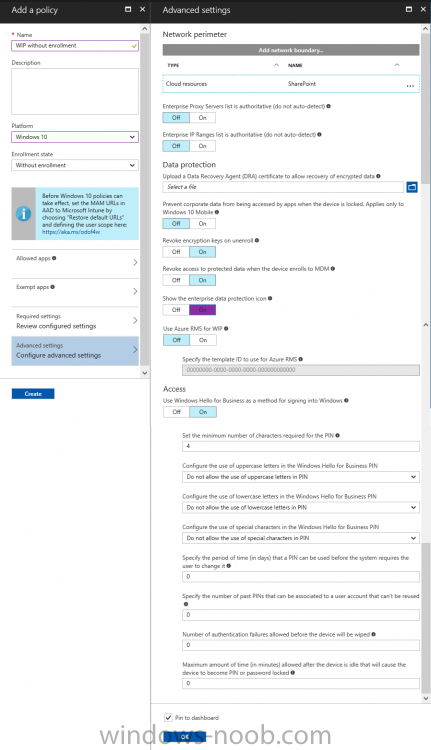
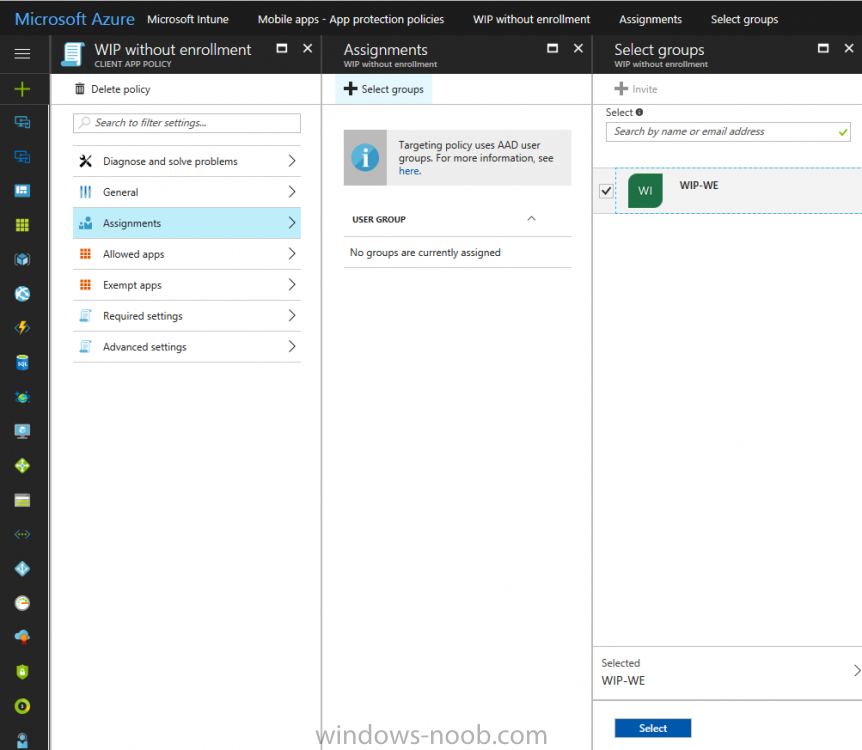
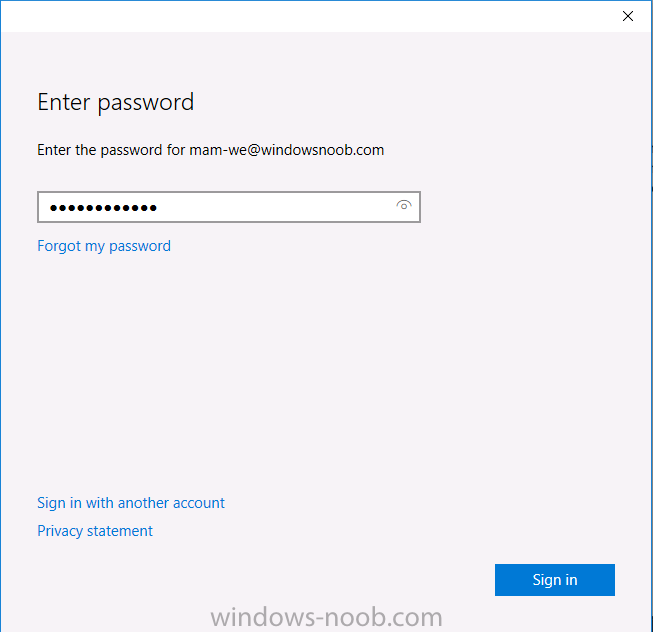
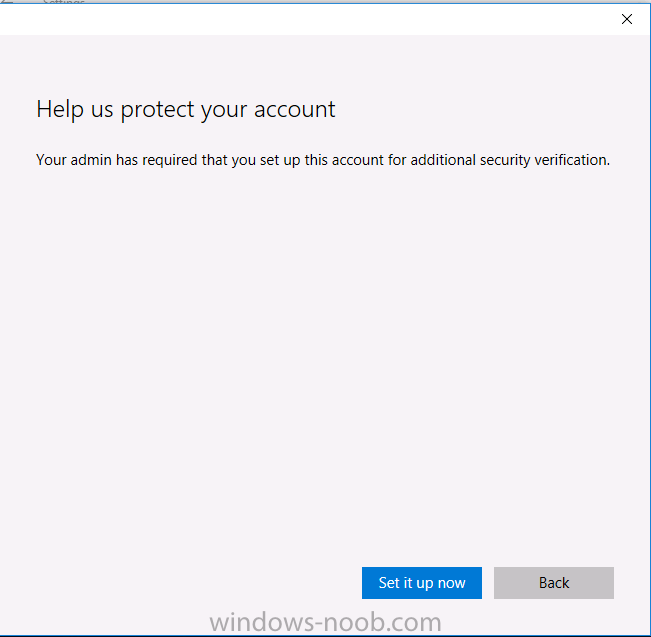
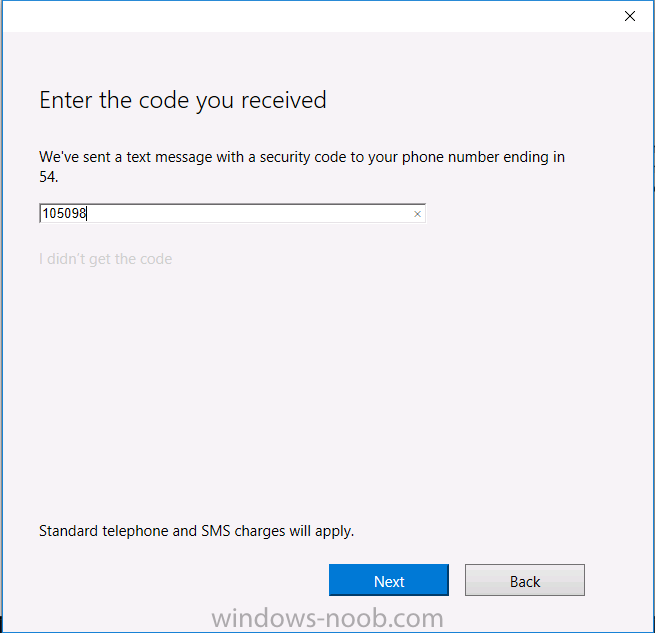
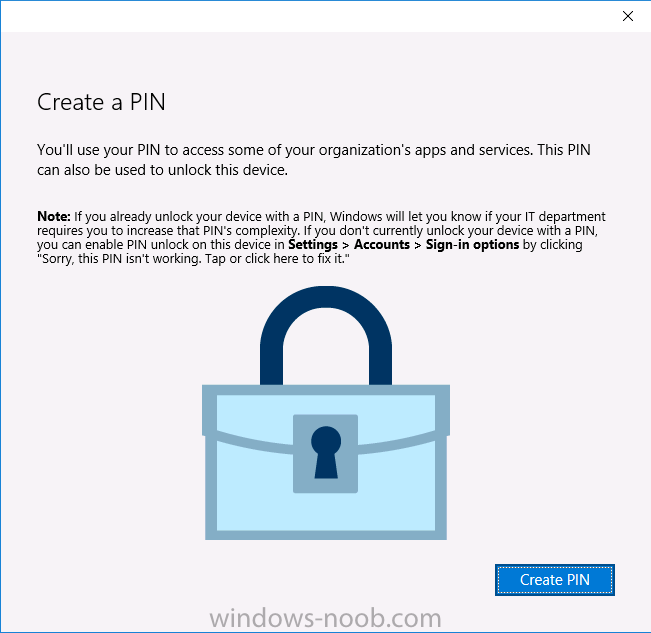
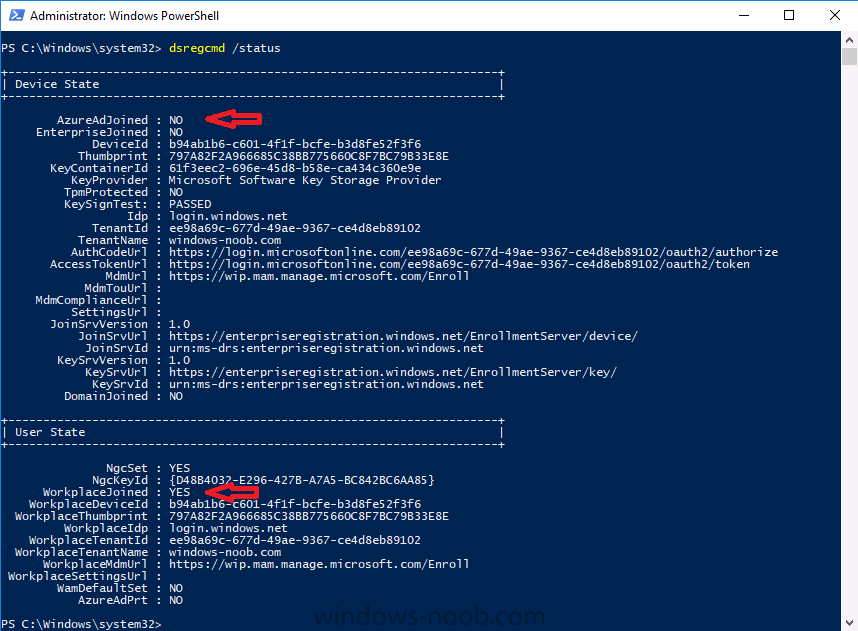
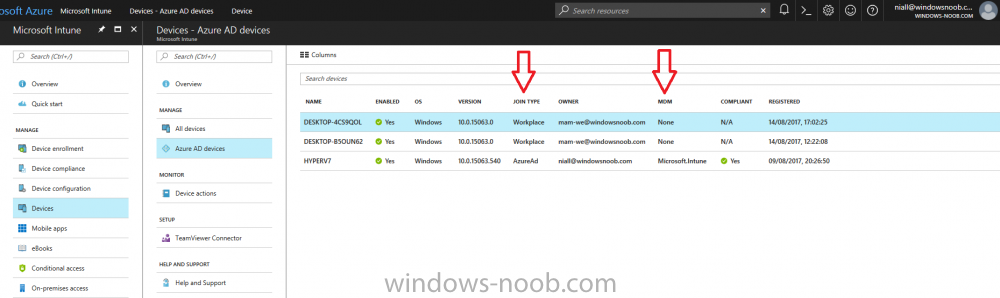
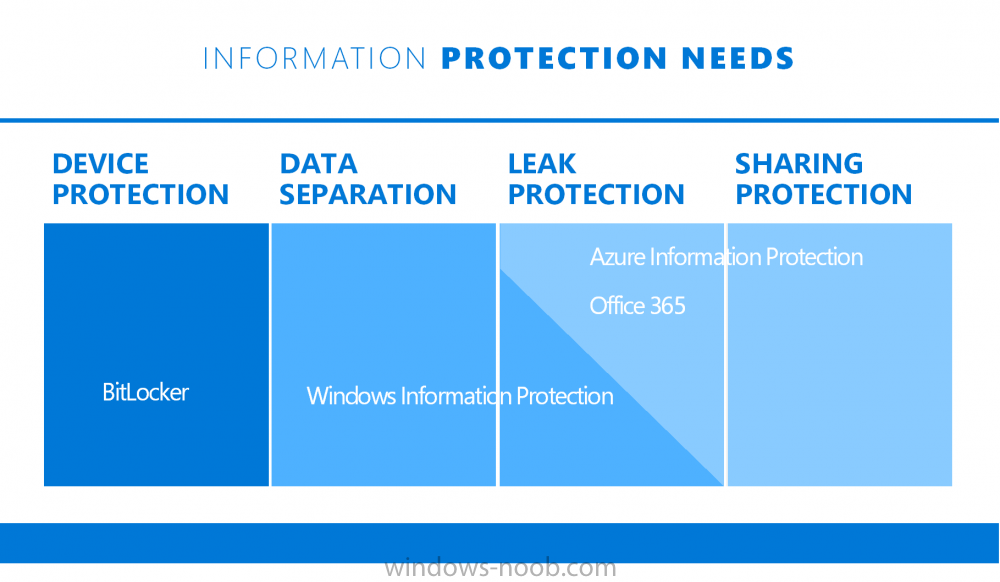
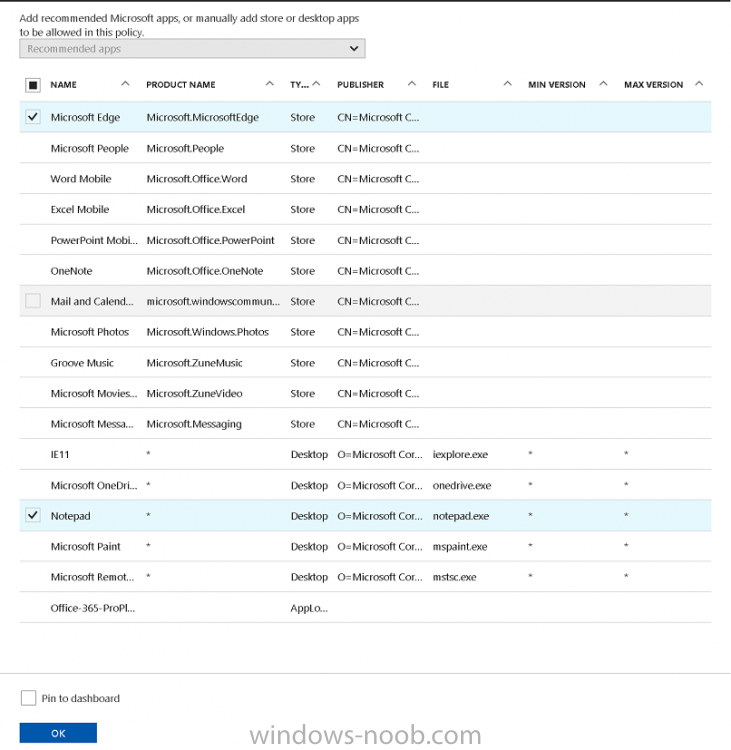
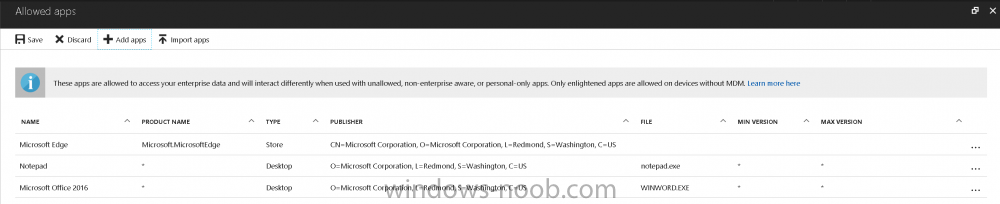
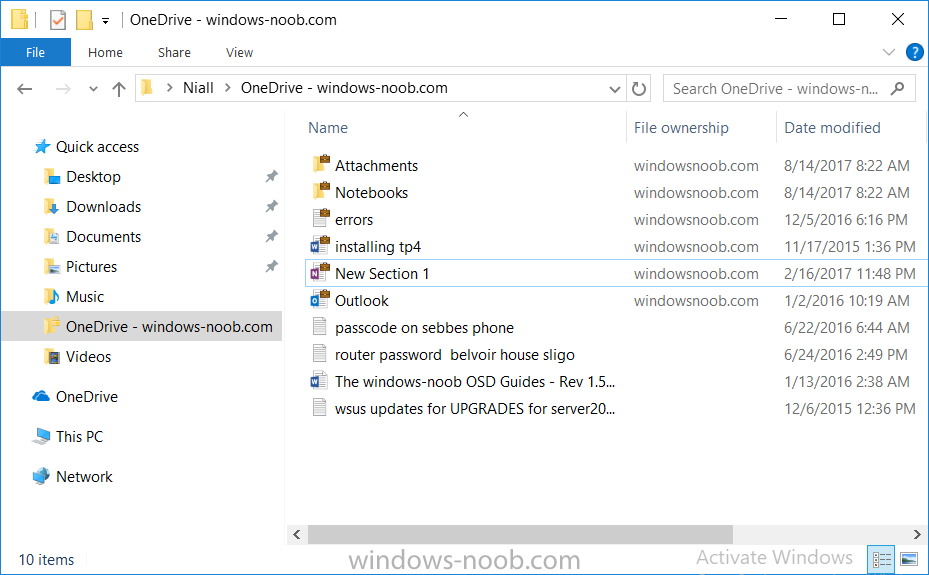
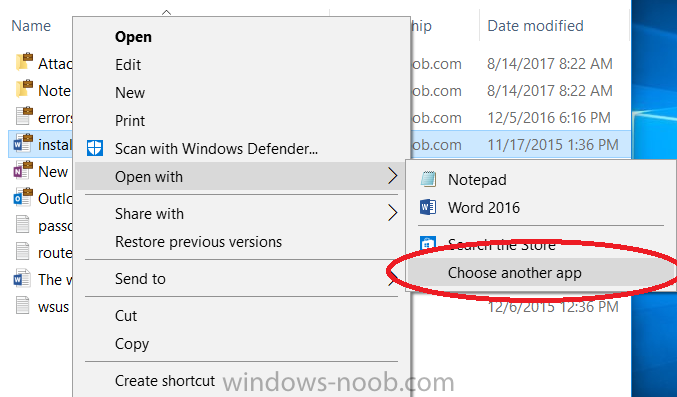
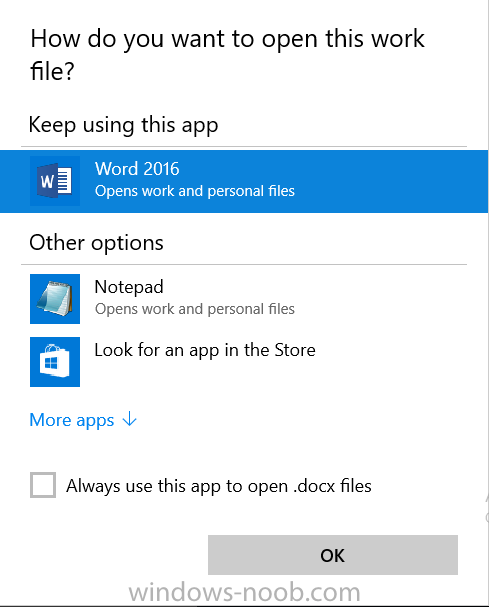
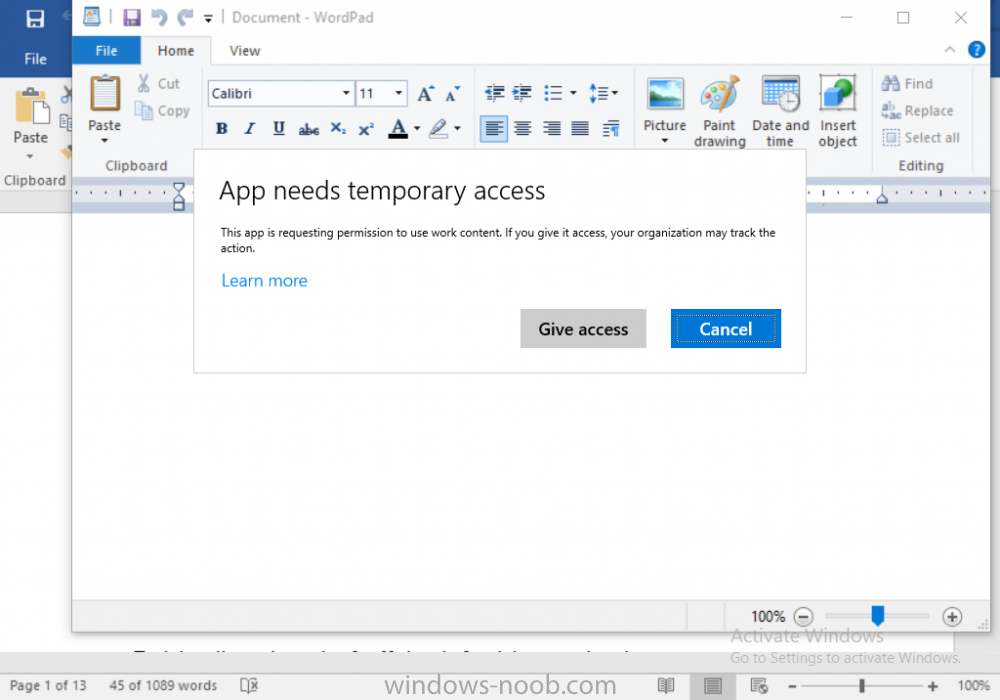
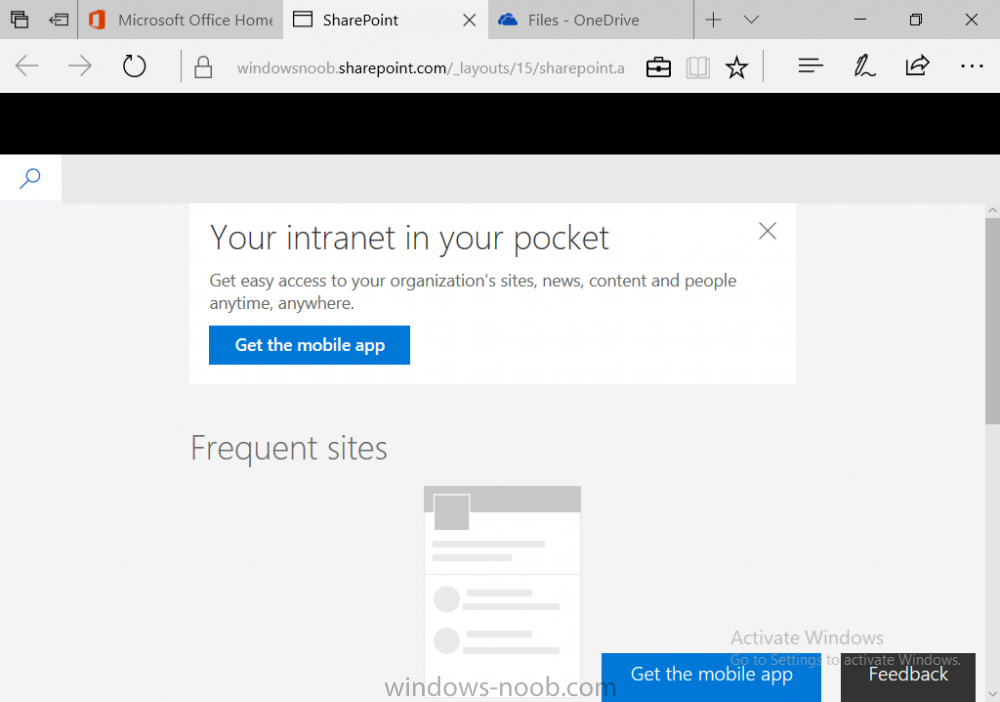
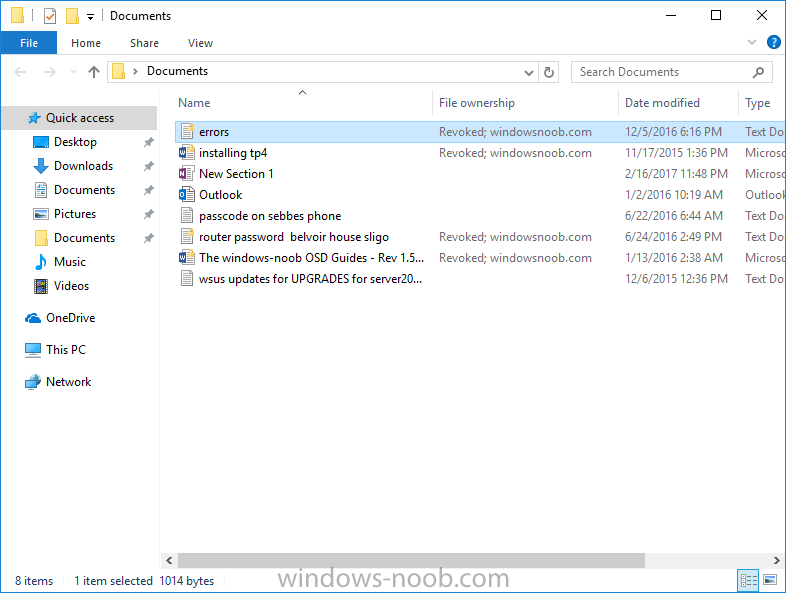
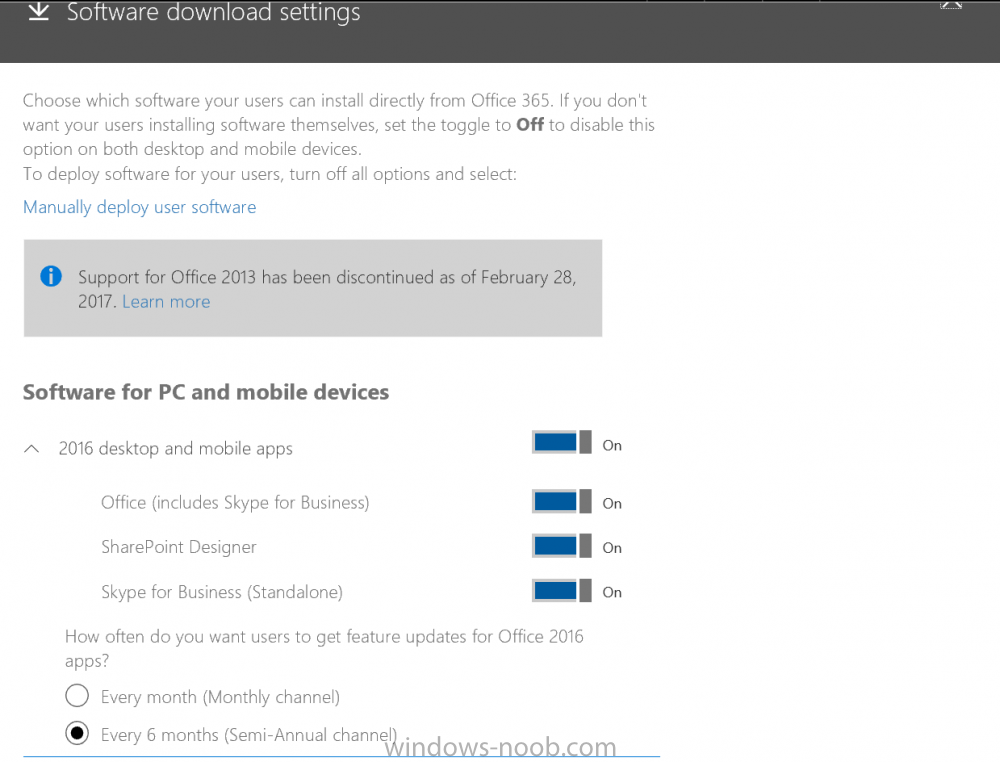
Introduction In a previous post you reviewed what Windows Information Protection (WIP) is and how you can configure Intune to use it, you then deployed a WIP policy to a group of users and verified the end result on a Azure AD joined (with Auto-MDM enrollment) Windows 10 version 1703 device. If you are still not familiar with WIP then I'd recommend you review this blog post from Microsoft, it covers it really well. The graphic below also gives you a nice indication of where WIP fit's in to your information protection needs and how it fits neatly into the Data Separation and Leak Protection space. In this post, you will see how WIP works on a Windows 10 version 1703 device that is Azure AD registered and not enrolled into MDM (MAM-WE). This is a typical Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) scenario. Create a WIP policy for Windows 10 devices without enrollment In a previous post you configured MAM in Azure, and now you will create a WIP policy for Windows 10 devices that are not enrolled into MDM, this will give you additional options to configure in the advanced section of the WIP Policy. To create the WIP Policy in the Microsoft Intune service in Azure, select Mobile Apps then click on App protection policies. Next click on Add a Policy. Give the policy a descriptive name, and optionally a description of what it does, in the Platform drop down select Windows 10 from the choices available. Next choose your enrollment option for Enrollment State, select Without Enrollment. Note, if you select the wrong enrollment option you cannot change it later, you'll have to recreate the policy with the correct enrollment option. Next, there are two sections in the Create Policy wizard related to Apps. Allowed apps - These are the apps that must adhere to the policy Exempt apps - These apps are exempt from the policy and can access enterprise data freely. Note: Apps can be enlightened or unenlightened. Enlightened apps can differentiate between corporate and personal data, correctly determining which to protect, based on your policies. Unenlightened apps consider all data corporate and encrypt everything. For a list of Enlightened apps see here. Adding Allowed Apps Click on Allowed apps and then click on Add apps to add one or more apps that you want to adhere to the policy. There's a drop down with Recommended apps selected by default and those apps are listed below the drop down. Recommended apps: a pre-populated list of (mostly Microsoft Office) apps that allow admins easily import into policy. Store apps: Admin can add any app from the Windows store to policy. Windows desktop apps: Admin can add any traditional Windows desktop apps to the policy (e.g. exe, dll, etc.) If you want to add your own Store apps or Desktop apps manually then you'll need to select the appropriate option and fill in the blanks. To get information about how to generate the info needed for manually adding Store and Windows desktop apps see this post. To add Allowed apps, click on Add apps, then select Recommended apps and make your selection from those available. For the purposes of this guide select Microsoft Edge and Notepad from the list of apps available. Click OK on the Recommended apps page, then click on OK on the Add apps page, next you will add an additional desktop app such as Microsoft Word 2016, to do so use the following method. Click on Add apps, and from the drop down choose Desktop Apps. Fill in the following information in the blanks. Name: Microsoft Office 2016 Product Name: * Type: Desktop Publisher: O=Microsoft Corporation, L=Redmond, S=Washington, C=US File: winword.exe Min Version: * Max Version: * Note: if you get the Publisher information above wrong, for example a missing letter, or misplaced comma or a missing space, then the policy (for Microsoft Word) will fail to apply and it won't work. You can pick a built in desktop app like notepad and compare the publisher settings to your app. Here is a copy of the data used above: NAME PRODUCT NAME TYPE PUBLISHER FILE MIN VERSION MAX VERSION Microsoft Office 2016 * Desktop O=Microsoft Corporation, L=Redmond, S=Washington, C=US WINWORD.EXE * * And below is what it looks like after you've added it correct, compare the Notepad desktop app with the one you just added, the Publisher line must match exactly. Adding Exempt Apps Next click on Exempt apps, and add the Company Portal to allow the app to properly function. To do so, add the following Store app to the list of Exempt apps: Name: Company Portal Publisher: CN=Microsoft Corporation, O=Microsoft Corporation, L=Redmond, S=Washington, C=US Product Name: Microsoft.CompanyPortal as shown here Click OK when done. Next click on Required settings and configure the protection mode, in this example set it to Allow Overrides, remove Pin to Dashboard and click on OK. Note: Allow Overrides lets the user override the policy and share the data, logging the action to your audit log. The 4 available Windows Information Protection mode settings are listed below. Hide Overrides - WIP looks for inappropriate data sharing practices and stops the user from completing the action. This can include sharing info across non-corporate-protected apps, and sharing corporate data between other people and devices outside of your organization. Allow Overrides - WIP looks for inappropriate data sharing, warning users if they do something deemed potentially unsafe. However, this mode lets the user override the policy and share the data, logging the action to your audit log. Silent - WIP runs silently, logging inappropriate data sharing, without blocking anything that would’ve been prompted for employee interaction while in Allow Override mode. Unallowed actions, like apps inappropriately trying to access a network resource or WIP-protected data, are still stopped. Off (not recommended) - WIP is turned off and doesn't help to protect or audit your data. After you turn off WIP, an attempt is made to decrypt any WIP-tagged files on the locally attached drives. Be aware that your previous decryption and policy info isn’t automatically reapplied if you turn WIP protection back on. Configuring advanced settings Next click on Advanced settings, to configure advanced settings. Notice how you can configure Windows Hello for Business options in the policy. These Windows Hello for Business options can by targeted to a User group of your choosing (essentially the same User group that you assign the WIP policy to), which is useful if you don't like the default Windows Enrollment option for enabling Windows Hello for Business (which applies to All Users). Once you are done configuring it, click on OK and then Create to create the WIP policy. Deploying the policy Now that you've created your WIP policy, it needs to be deployed (assigned) to a group of users that you intend to target with this policy. To deploy the policy, select it and then click on Assignments. Next click on Select Groups to select a previously created Azure Group containing one or more users. After selecting a suitable user group, click on Select. The policy is now deployed. Registering a device in Azure AD (workplace join) Let's look at a Windows 10 device that is not joined to Active Directory or Azure AD, it is only work group joined (this is a typical state for BYOD devices). Using an Administrative PowerShell cmd prompt, issue the following command dsregcmd /status Output similar to the below should appear As you can see from the output, the Windows 10 device is not joined to AAD, not Domain Joined and also not Enterprise joined (some future option from Microsoft ?). AzureADJoined: No EnterpriseJoined: No DomainJoined: No To Azure AD register the device (workplace joined) do as follows: Click on All Settings, Accounts, Access work or school. Then click on Connect and enter your Intune user credentials, note that their are options to join Azure AD and an on premise Domain but you will not select either as this device will be AAD registered only. When prompted enter the password and click on Sign-in. you'll be informed about what is happening, note the 'while we register this device' text. If any additional authentication is configured (Windows Hello for Business), you'll be prompted to enter it. after the text message is sent to your phone... Click Next and then Setup a PIN click next and then Done to close the wizard. Note: The User name used to register the device is listed with a Windows icon beside it. At this point, once again issue the dsregcmd /status command in an Administrative PowerShell cmd prompt. From the output you can see that the device is NOT Azure AD Joined and it is Workplace Joined, which is another way of saying it is Azure AD registered. You can verify that the device is not MDM enrolled and that it is Workplace joined and Azure AD Registered by clicking on Azure AD devices in the Intune portal. Review WIP policy on a Windows 10 device So now that our Windows 10 device is Azure AD registered, let's verify how the WIP policy applies. To do so logon to the Windows 10 device used above. In the example below there are some documents, some are marked as Work (they have a suitcase icon on them and File Ownership is listed as the windowsnoob.com Enterprise.) and some are Personal. Right click on a protected Word document and choose Open With, next select Choose another App. if your policy is applied correctly you'll see the following (that Word 2016 can open both Work and Personal files), if not, sync the policy again and try again. Once the document is open in Word, copy some text and attempt to paste it into WordPad (which is not an allowed app.) If everything went well you'll be prompted to either Give Access or Cancel. Note: If you do not get the desired result, for example if the data simply pastes in, then you should verify the version of Office application you are using is up to date. For example, Office 365 may be on the Deferred Channel (now called Semi Annual Channel) meaning that it's version is 1701.(xxxx.xxxx) and that may mean that it cannot process the WIP policy correctly. Once you've updated Office 365 to the Current Channel (now known as Monthly) you'll get the desired result. Tip: You can review your software download settings for Office 365 by going to https://portal.office.com and, clicking on Software Download Settings on the main screen. In there, by default it will be set to the Semi Annual Channel which as of when I tested it in this guide, won't work correctly with WIP. In the screenshot below you can see that Office is configured for the Semi Annual Channel. As time goes on this will auto-correct itself, but if you see issues such as I've described then select Monthly Channel, update the office software on the client, and try again. Next, open a protected (work) txt document with Notepad. Notice the suitcase icon in the banner area. If you click on the suitcase, it will say Managed by your company. Try opening the same document with an app this is not allowed, and you'll see this. And next browse a work site (such as Sharepoint) in Microsoft Edge and you'll again see the suitcase icon, notifying you that Edge realizes this is a Work network resource. Downloading a document from Sharepoint automatically marks it as a Work document, and that means it's protected. as you can see here. Once the BYOD project comes to an end, have the user disconnect the work or school account in Account settings, and any Enterprise data left on the device will be revoked and can no longer be read or used. Hopefully this post helps you understand WIP capability on Windows 10 version 1703 devices (and later) that are not enrolled into MDM (MAM-WE) using policy created in Intune in Azure. I think we'll see more happening in this space in the coming months, hopefully with native reporting in Azure along with selective wipe. Until next time, adios. Recommend reading Introducing Windows Information Protection https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/windowsitpro/2016/06/29/introducing-windows-information-protection/ Windows Information Protection explained https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/cbernier/2017/05/19/windows-information-protection-explained-windows-10-creators-update/ App behaviour with WIP https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/threat-protection/windows-information-protection/app-behavior-with-wip Protect your enterprise data using Windows Information Protection (WIP) https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/threat-protection/windows-information-protection/protect-enterprise-data-using-wip Limitations using WIP https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/threat-protection/windows-information-protection/limitations-with-wip Create and Assign WIP application protection policies https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/windows-information-protection-policy-create Enlightened apps and WIP https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/threat-protection/windows-information-protection/enlightened-microsoft-apps-and-wip Walkthrough: Workplace Join with a Windows Device https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/identity/ad-fs/operations/walkthrough--workplace-join-with-a-windows-device How to configure hybrid Azure Active Directory joined devices https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/active-directory-conditional-access-automatic-device-registration-setup New to Office 365 https://blogs.office.com/en-us/2017/06/23/new-to-office-365-in-june-classroom-experiences-in-microsoft-teams-and-more/ Manage Windows Information Protection work and personal files https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/4012985/windows-10-manage-windows-information-protection-work-personal-files General guidance and best practices for Windows Information Protection (WIP) https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/threat-protection/windows-information-protection/guidance-and-best-practices-wip
-

Getting Started with SCCM
anyweb replied to Elad's topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
you came to the right place ! let me start off by saying welcome and to show you the following link, this link has many guides that pertain to SCCM Current Branch (the latest and greatest from Microsoft) as well as the Technical Preview releases (for lab only) In addition to the above, you should also checkout these guides between those two you'll be able to get going in no time, my advice would be to create a lab in HyperV and build yourself your own SCCM Current Branch lab that you can experiment with this link will get you up and running in less than a day if you have any questions or issues let us know cheers niall -
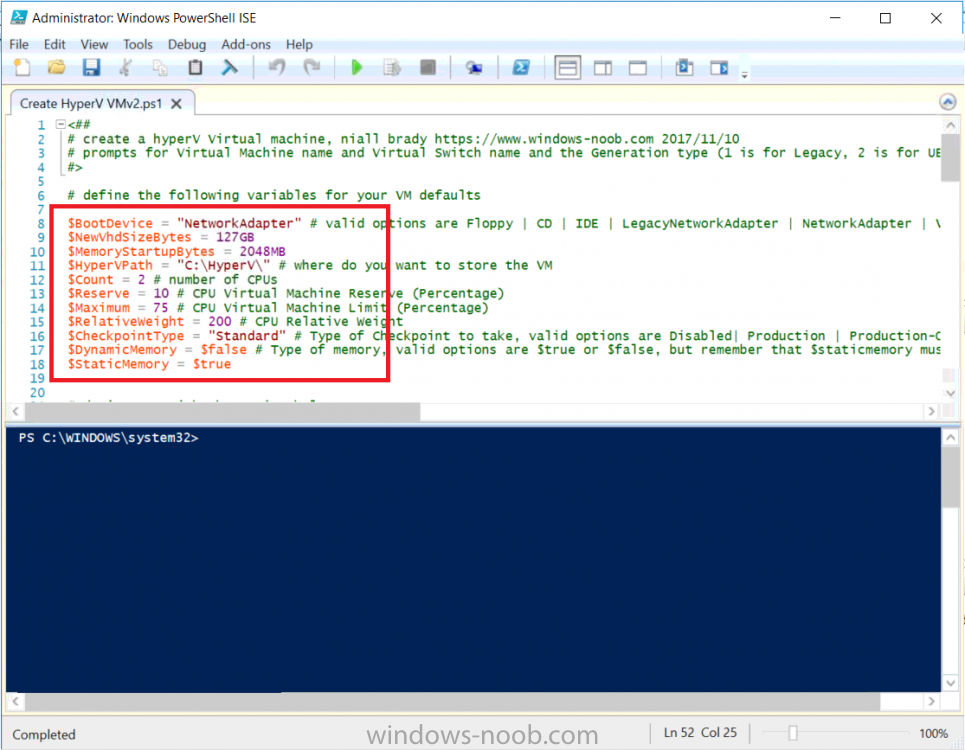
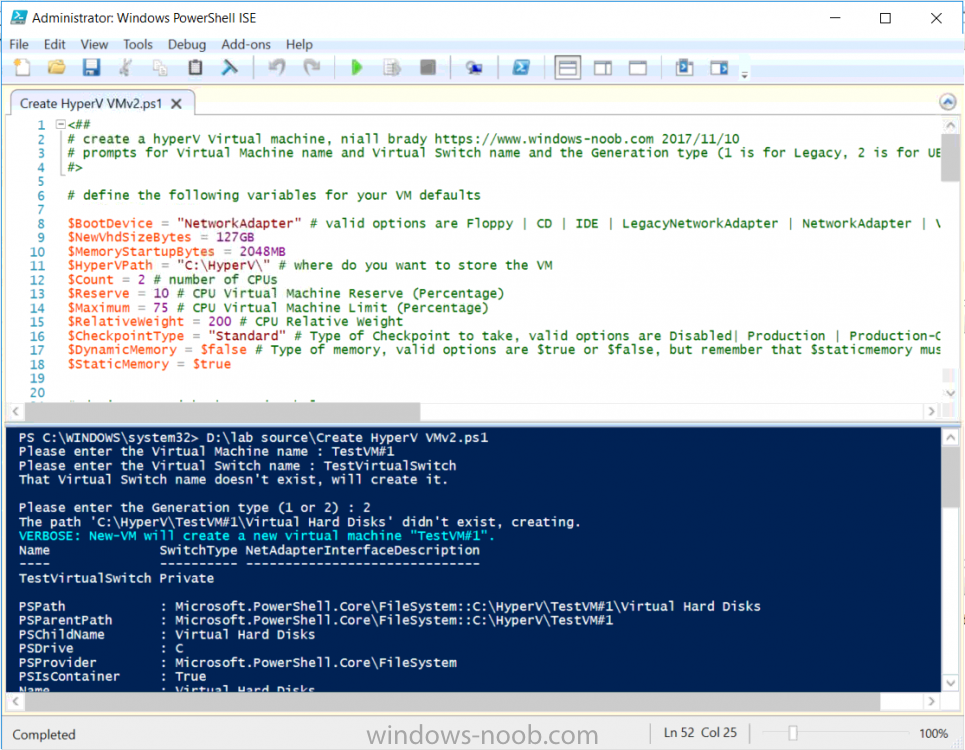
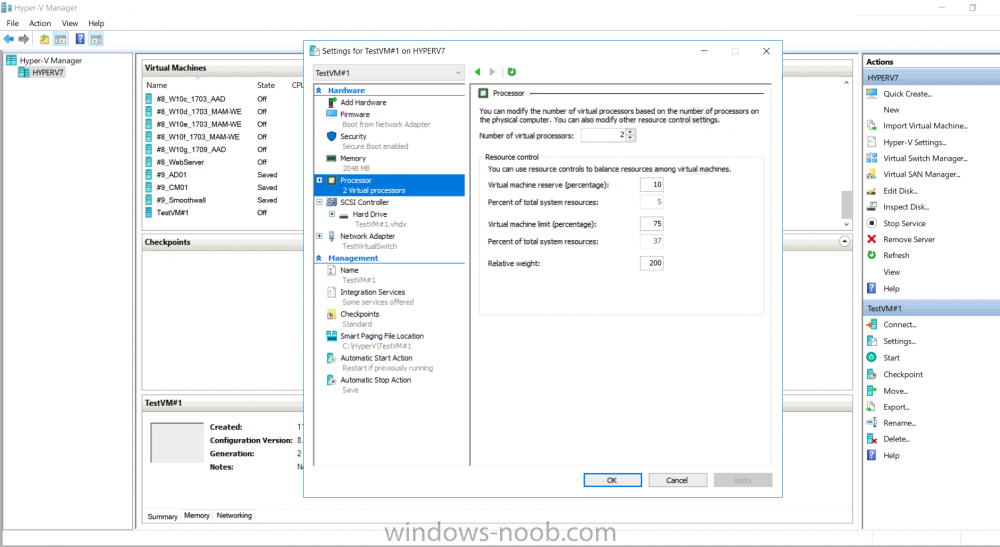
Introduction Update: This script was updated 2017/11/10 with several new abilities to customize most of what you can define in the Virtual Machine settings. This is an extremely quick post to help you create Hyper-V virtual machines using PowerShell. The script assumes you've already installed the Hyper-V feature in Windows. You can define a bunch of variables *highlighted in red below* such as type of Checkpoint, or Memory or CPU settings, to define how your Virtual Machines are created, The script prompts you for three inputs: Virtual Machine name Virtual Switch Name Generation type (Gen1=legacy, Gen 2=UEFI) Here's a screenshot of the script in action: And after running you can see the Virtual Machine properties match what you specified (Gen 2, switch name, cpu settings and so on...) and the New Virtual Switch is created (if it didn't already exist) that's it, have fun. Downloads You can download a copy of the script here. Create HyperV VM2.ps1
-

1602 upgrade Nightmare
anyweb replied to Ghost Image's topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
no it get's an ip address starting with 172.. <![LOG[Found network adapter "Intel(R) 82579LM Gigabit Network Connection" with IP Address 172.16.1.188.]LOG]!><time="12:55:13.959+480" date="08-03-2017" component="TSPxe" context="" type="0" thread="1364" file="tsmbootstraputil.cpp:517"> <![LOG[Loading Media Variables from "X:\sms\data\variables.dat"]LOG]!><time="12:55:13.959+480" date="08-03-2017" component="TSPxe" context="" type="1" thread="1364" file="tsremovablemedia.cpp:322"> and later you see this There are no task sequences available to this computer.. Please ensure you have at least one task sequence so are you sure this computer is in a collection targeted by a task sequence ? you can email the logs to me at niall@windows-noob.com -

1602 upgrade Nightmare
anyweb replied to Ghost Image's topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
that's an osd problem and very doubtful that it's anything to do with a failed upgrade, in relation to the failed upgrade can you email me your cmupdate.log and any config mgr logs in the root of c:, zip them up and i'll take a look as regards the osd problem, press F8 and grab the smsts.log in x:\windows\temp\smstslog attach it here cheers niall