-
Posts
9252 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
369
Everything posted by anyweb
-
it's failing to run the windowssetupcompatibilityscanresults.psq step here. Command line "C:\_SMSTaskSequence\Packages\00100224\ServiceUI.exe" -process:TSProgressUI.exe C:\Windows\sysnative\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -WindowStyle Hidden -NoProfile -ExecutionPolicy bypass -nologo -file WindowsSetupCompatibilityScanResults.ps1 returned 4294967295 probably because you are using the wrong version of serviceui.exe OR you made a mistake/edit in the powershell script which it does not understand,
-
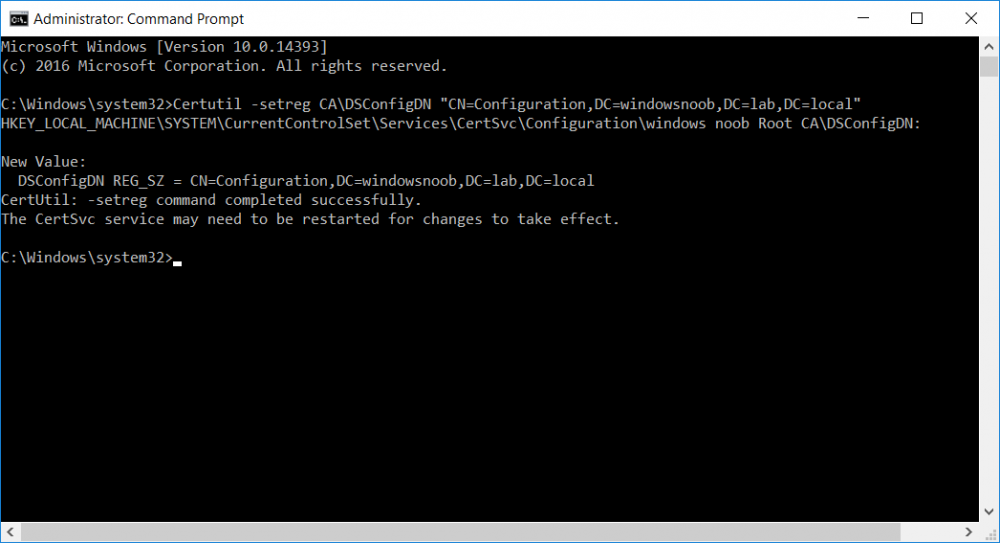
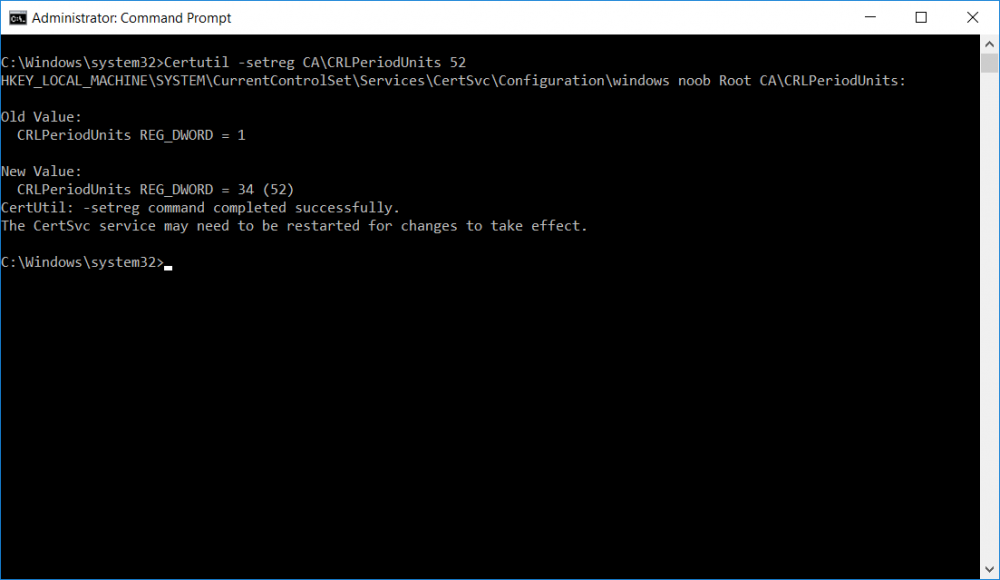
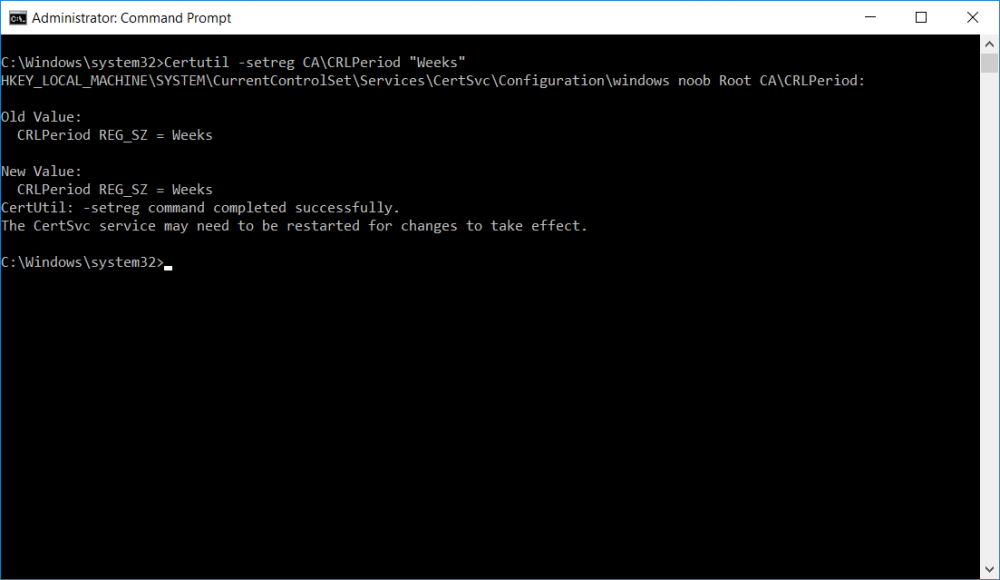
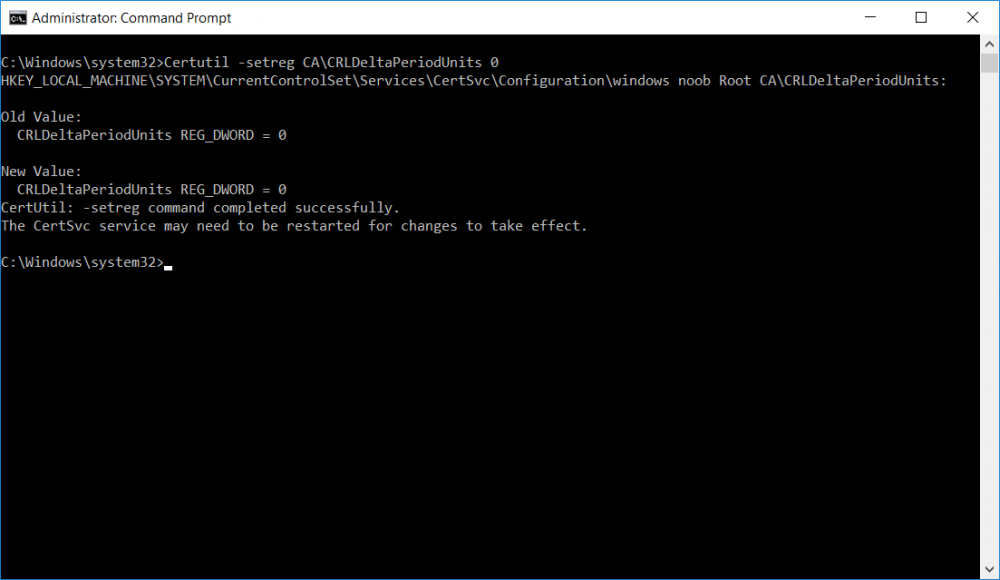
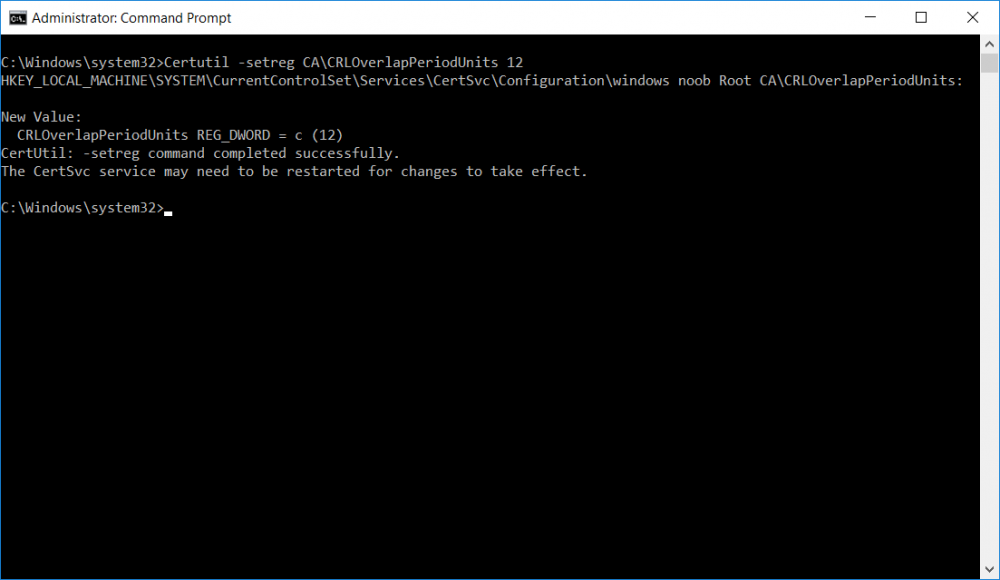
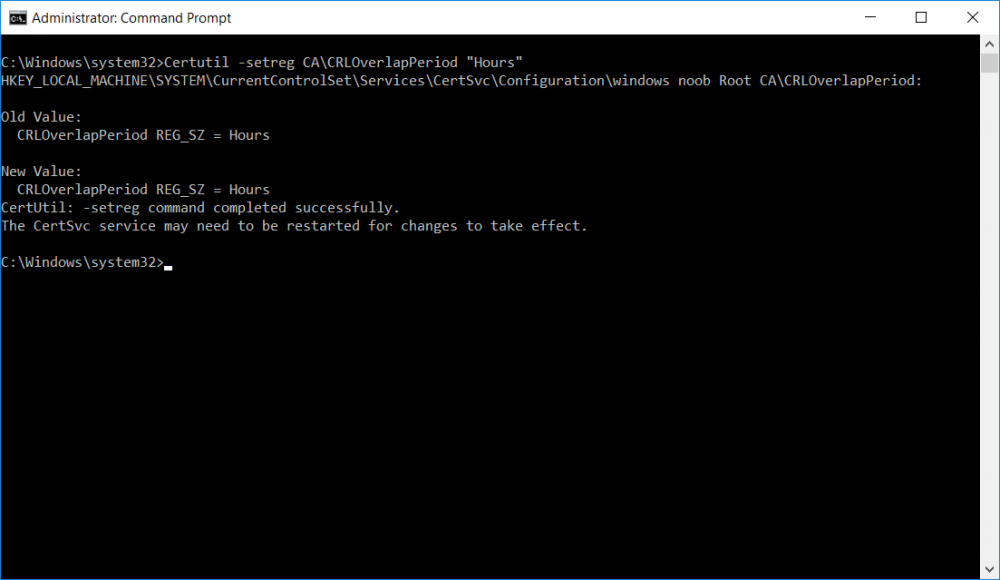
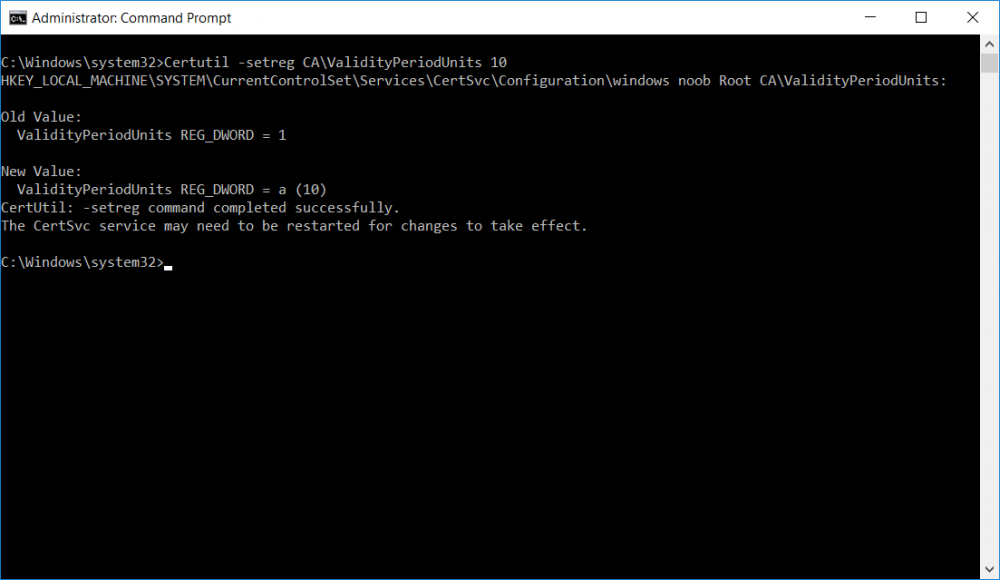
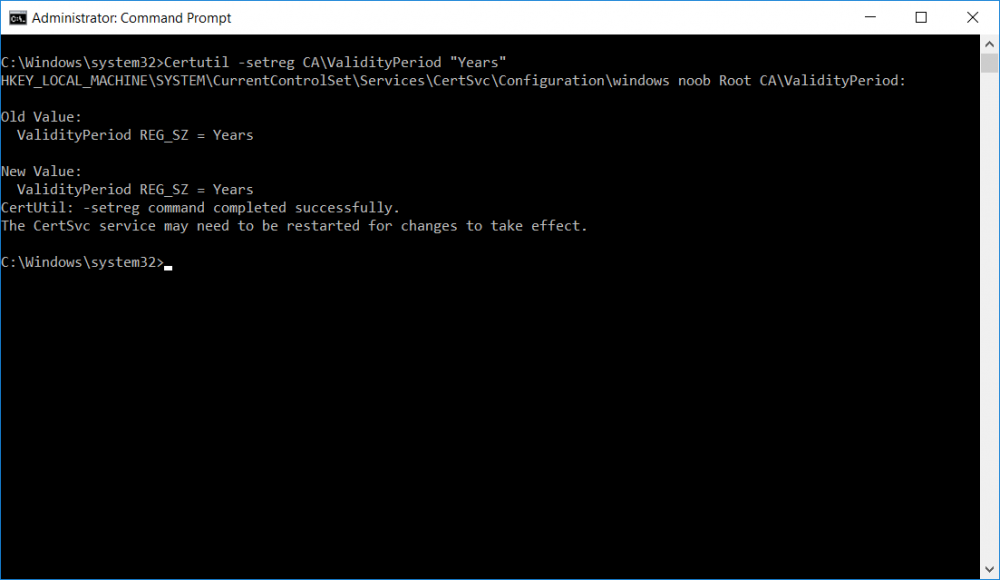
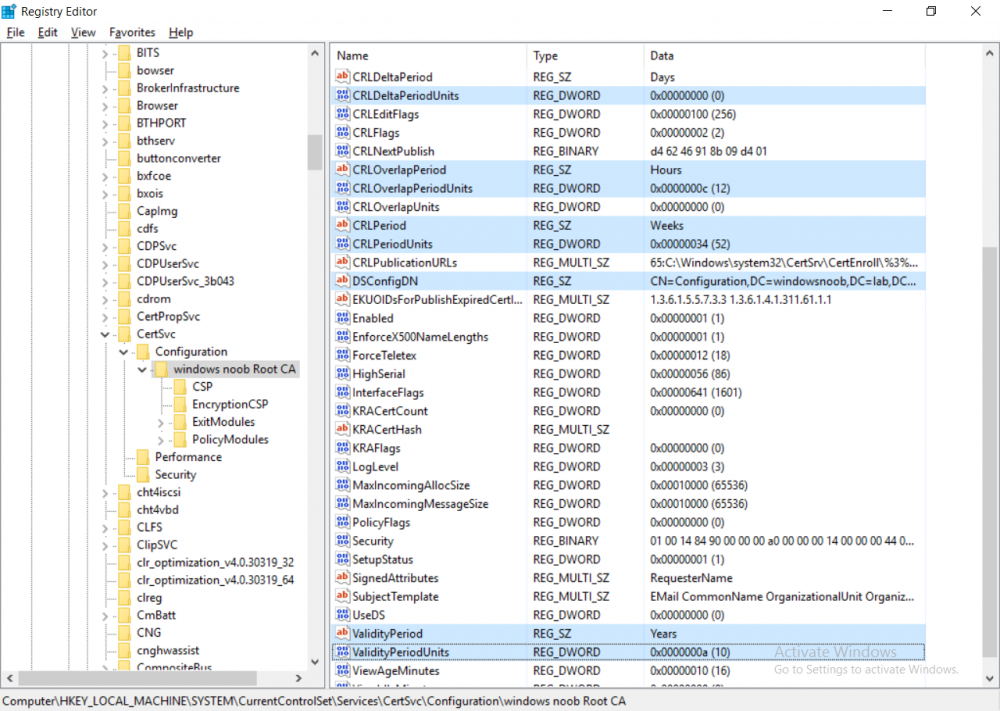
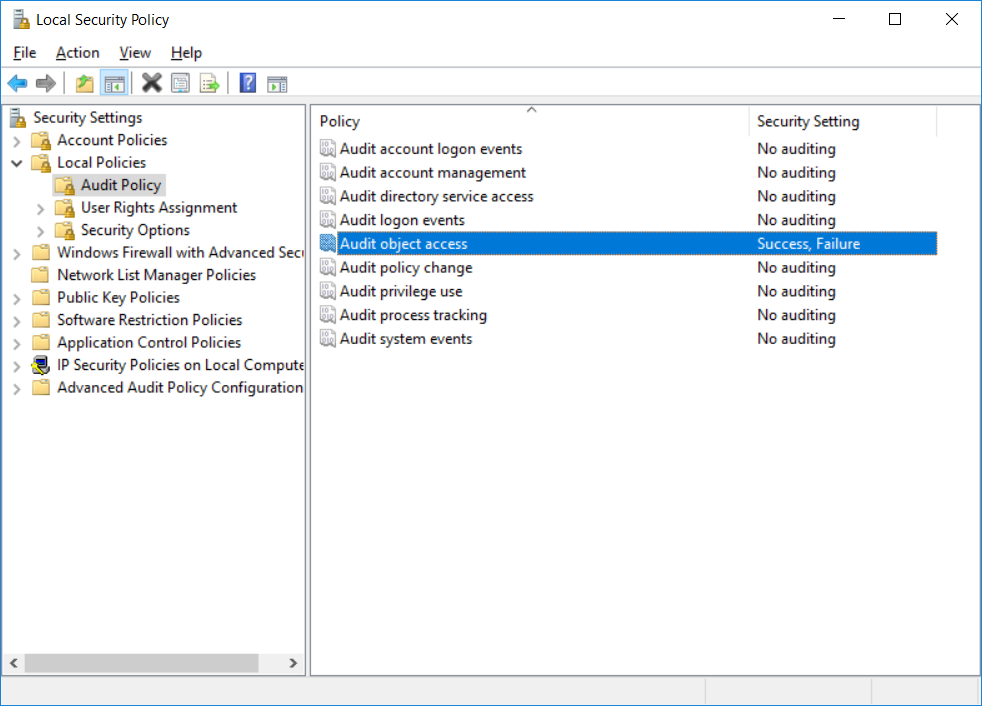
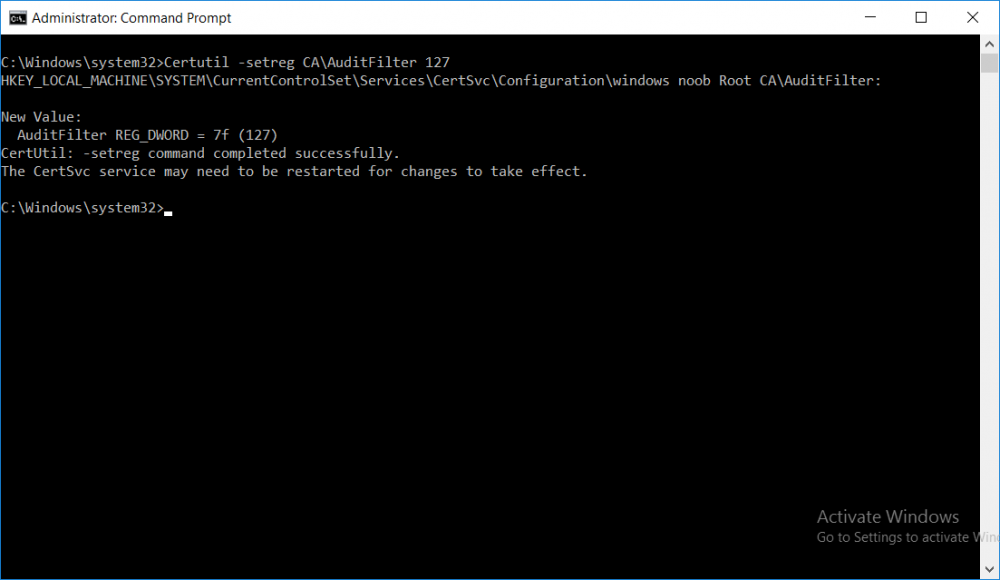
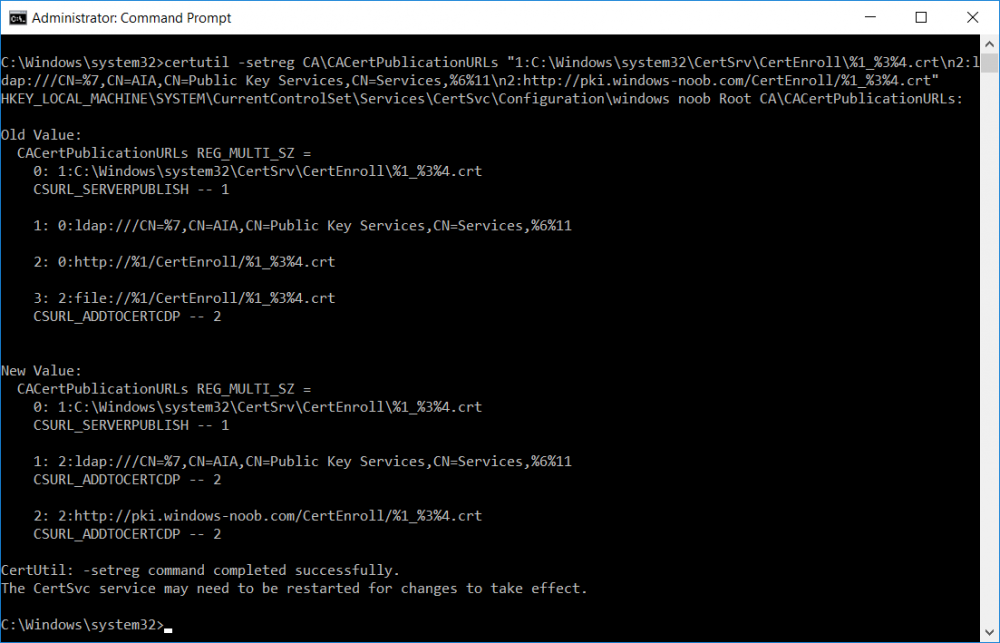
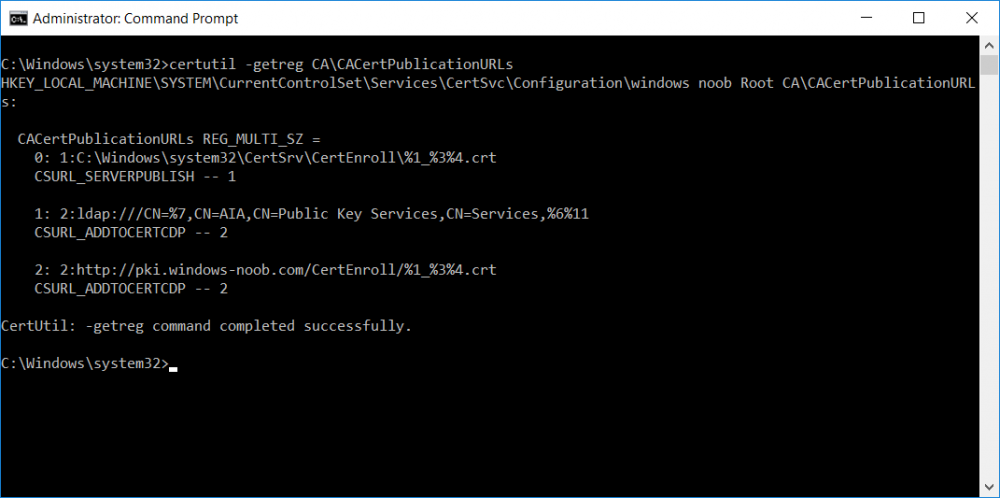
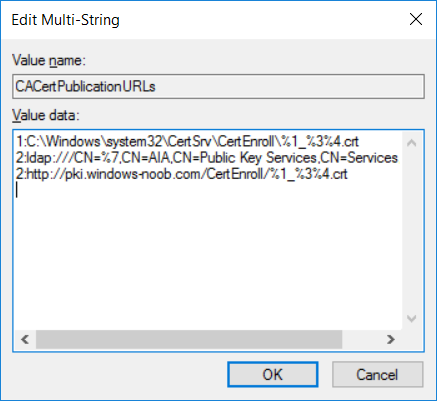
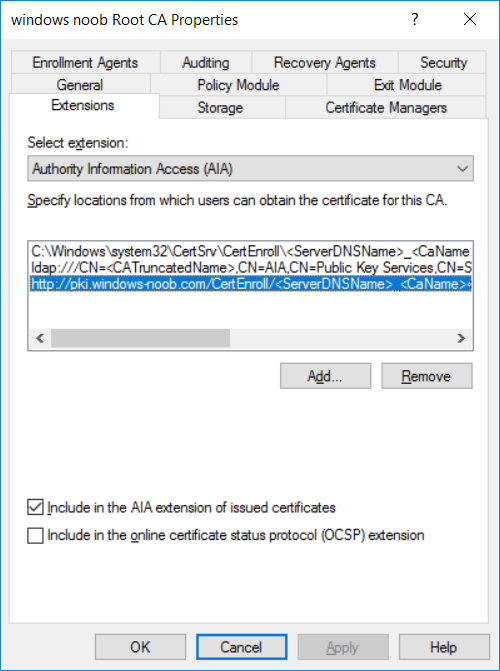
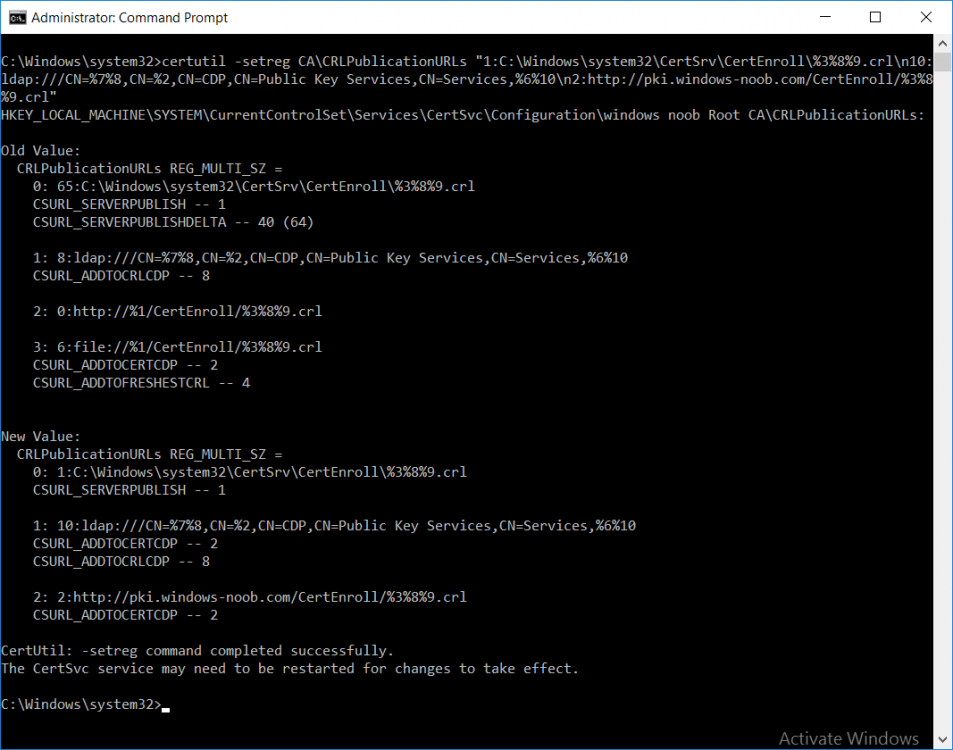
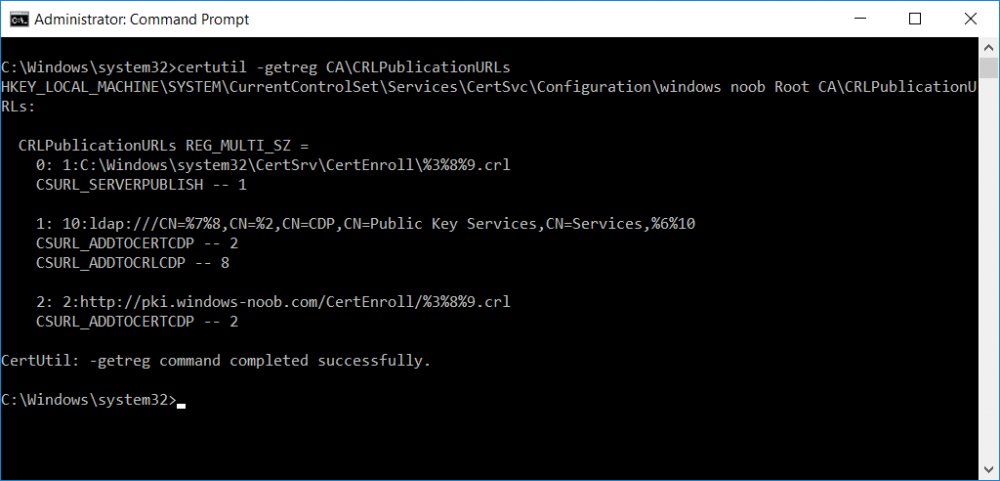
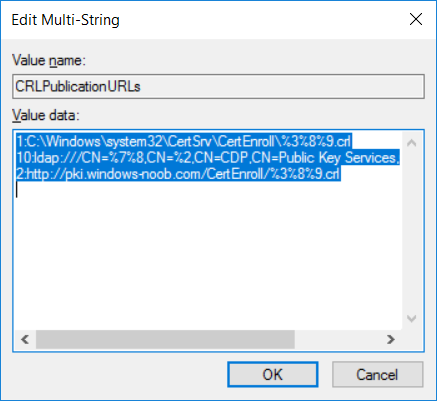
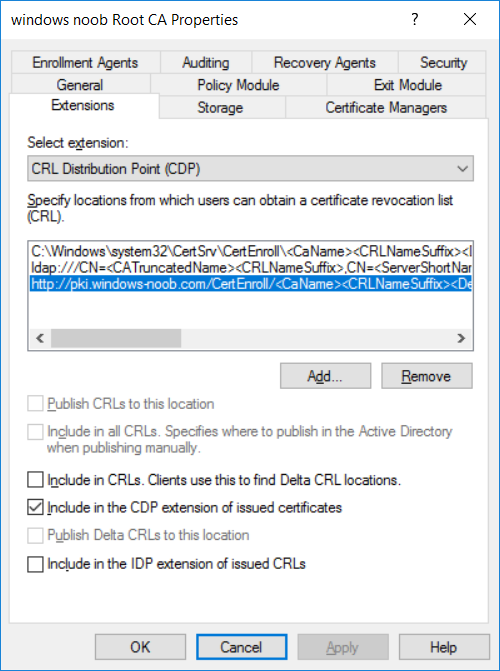
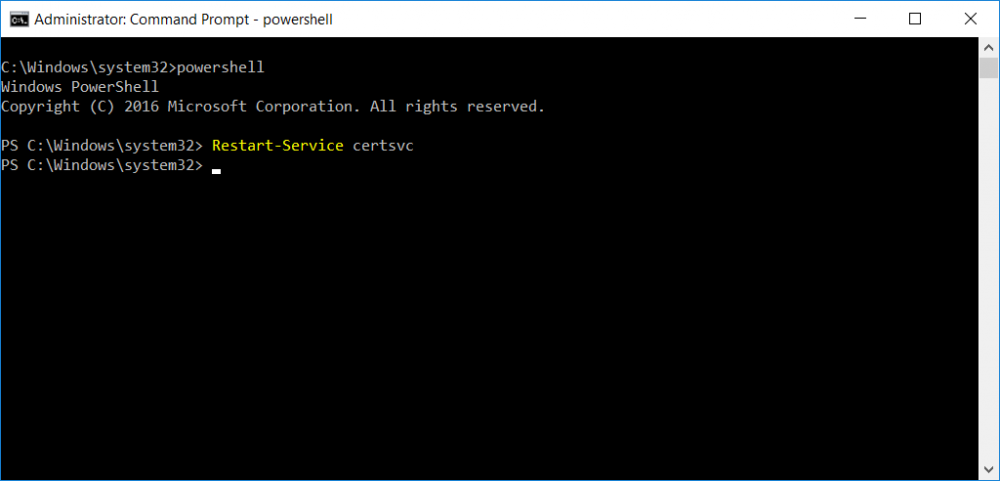
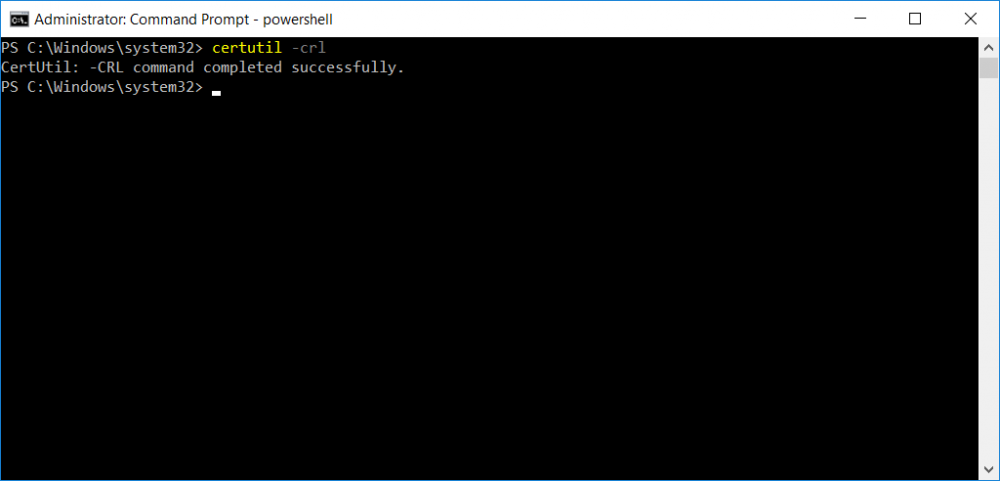
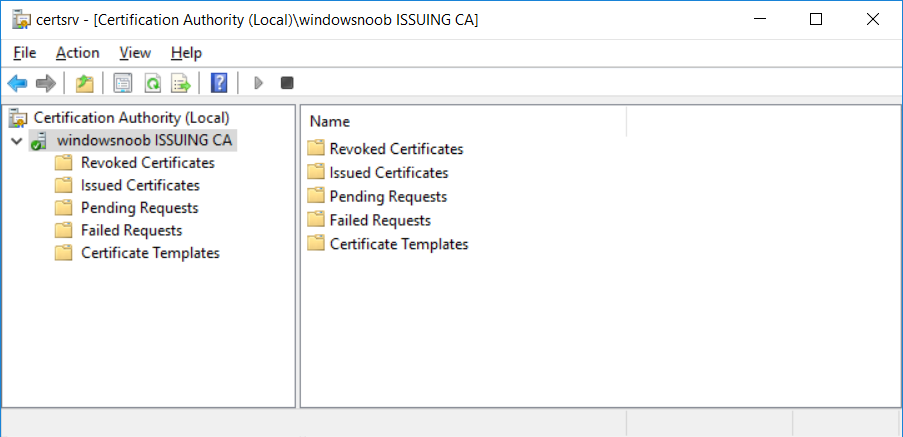
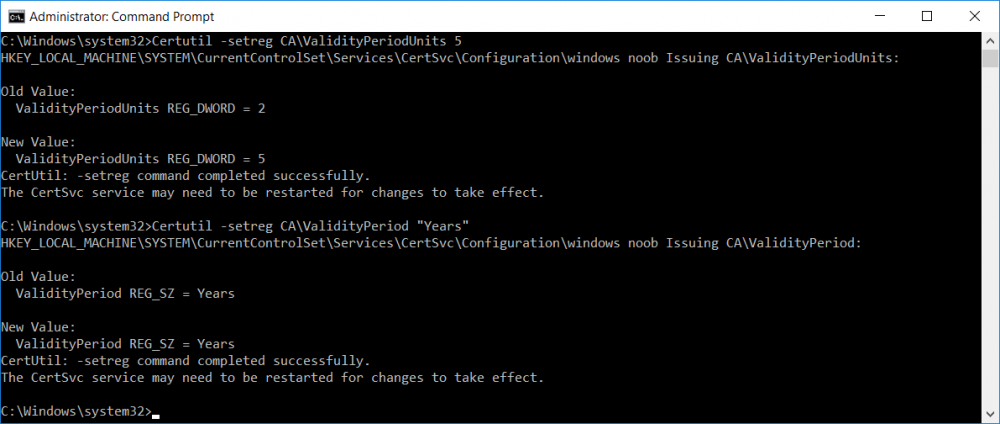
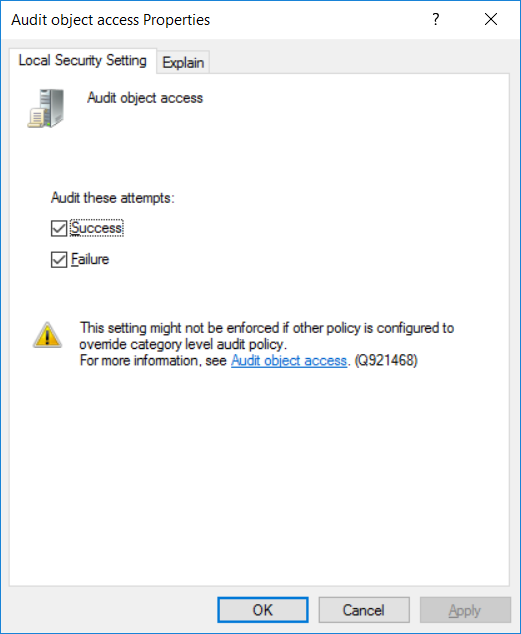
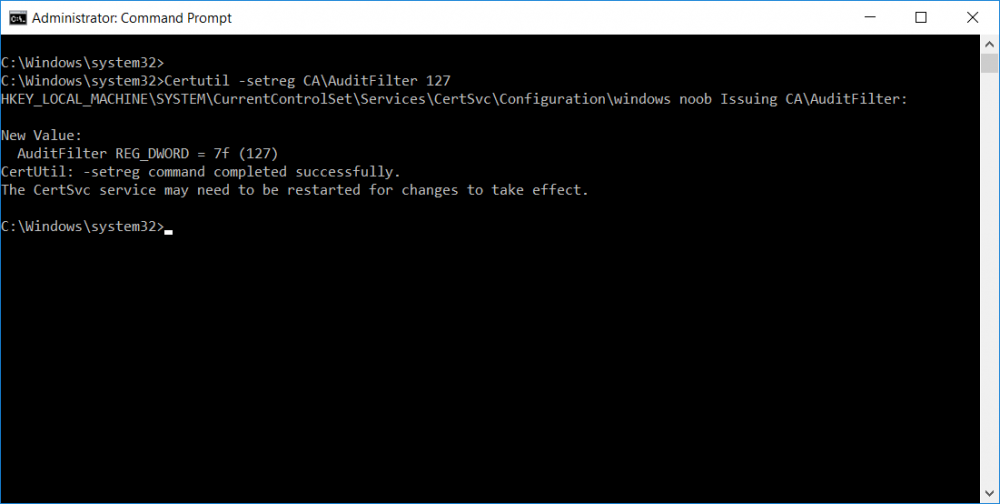
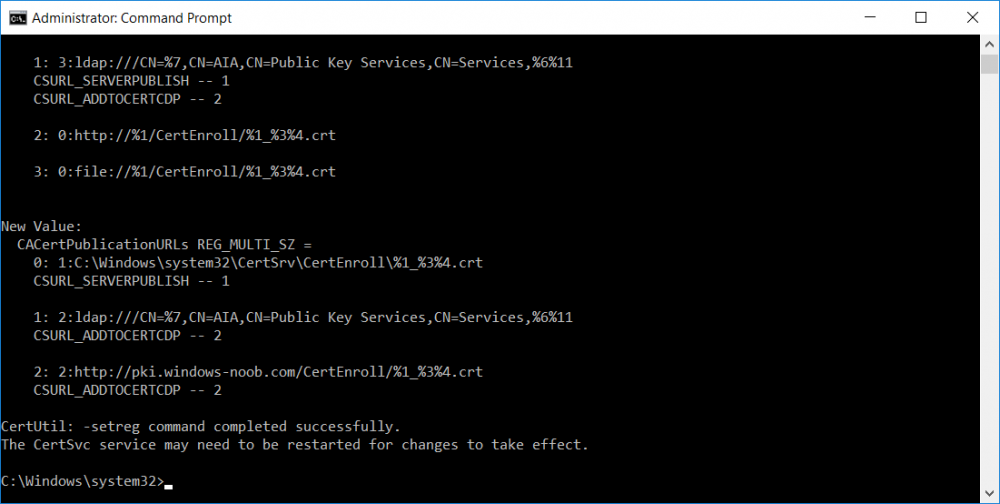
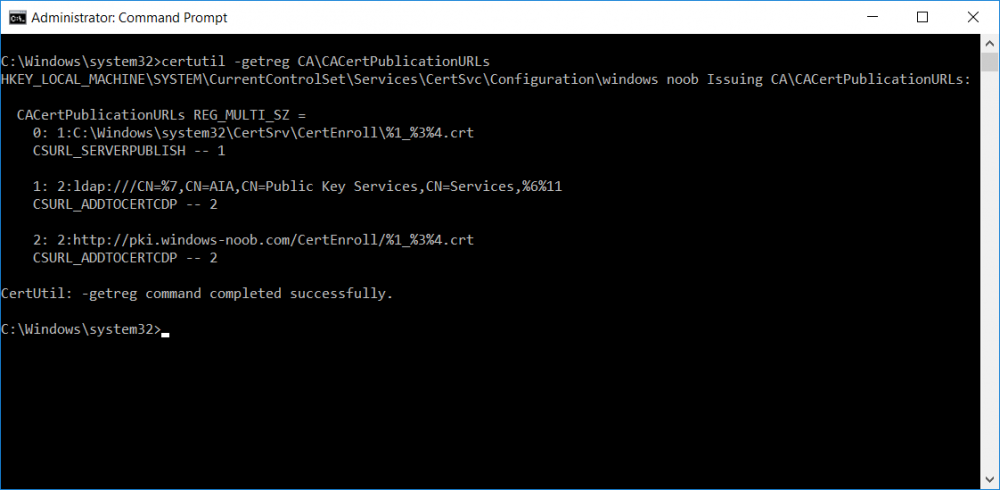
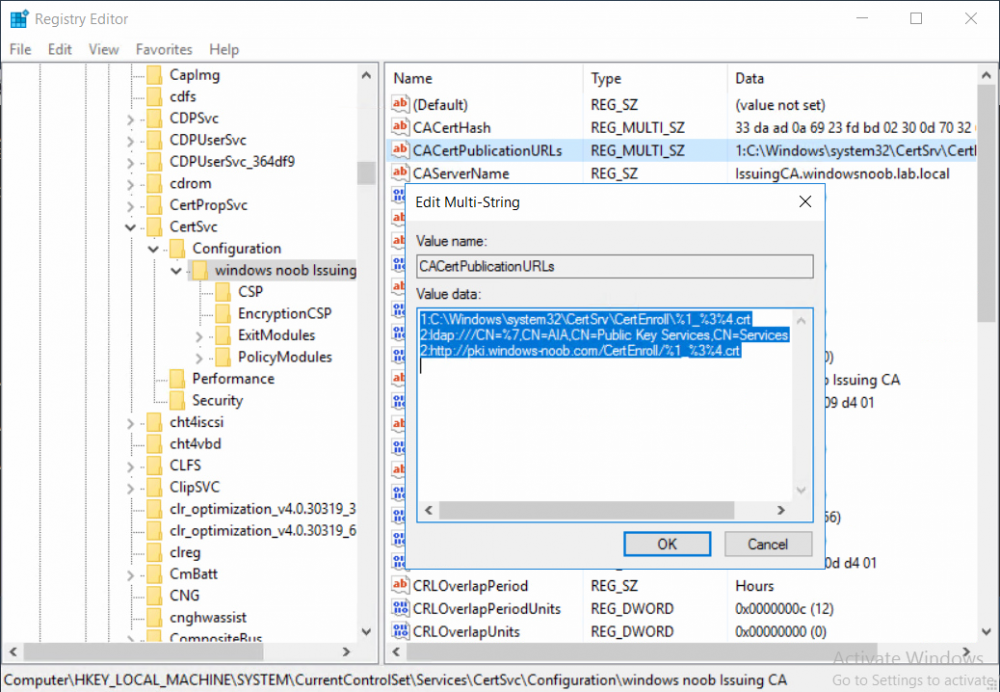
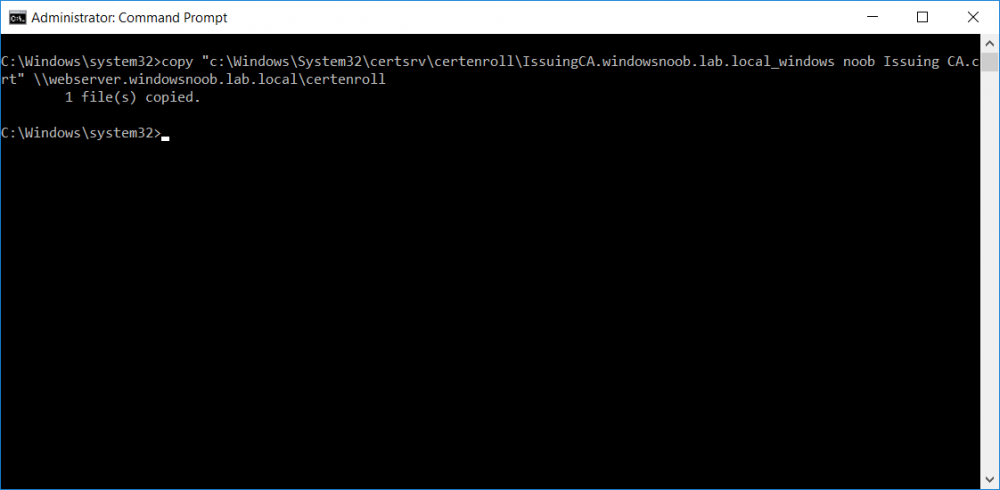
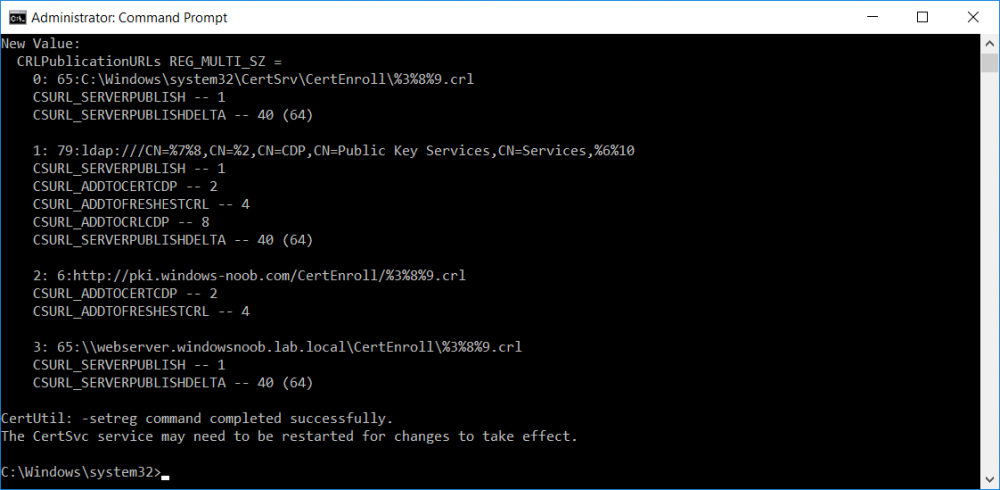
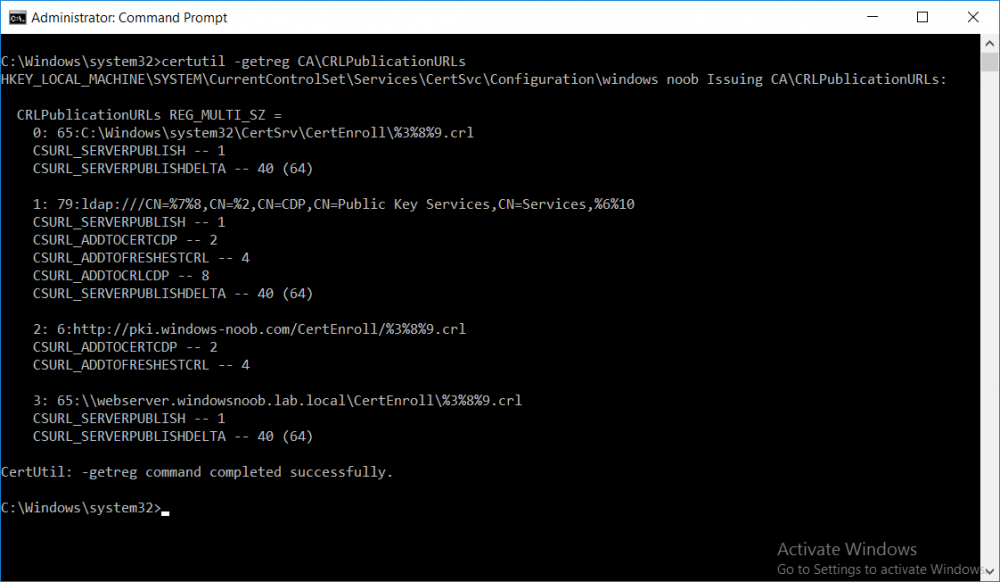
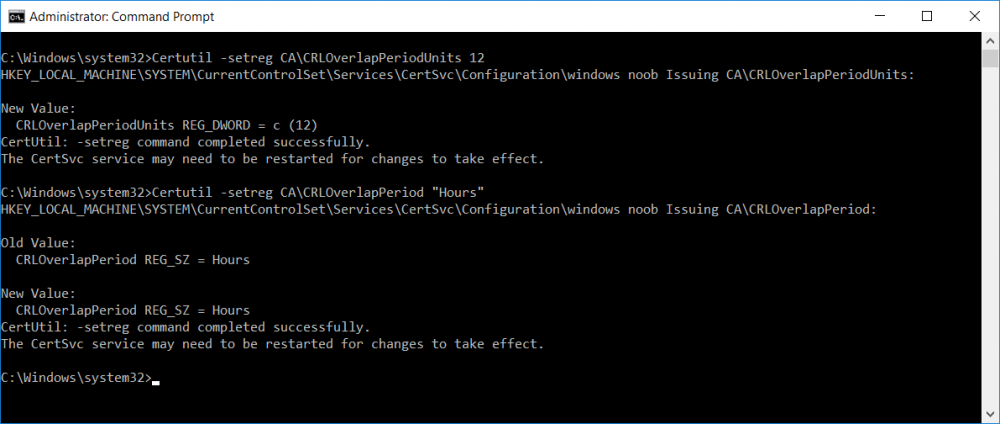
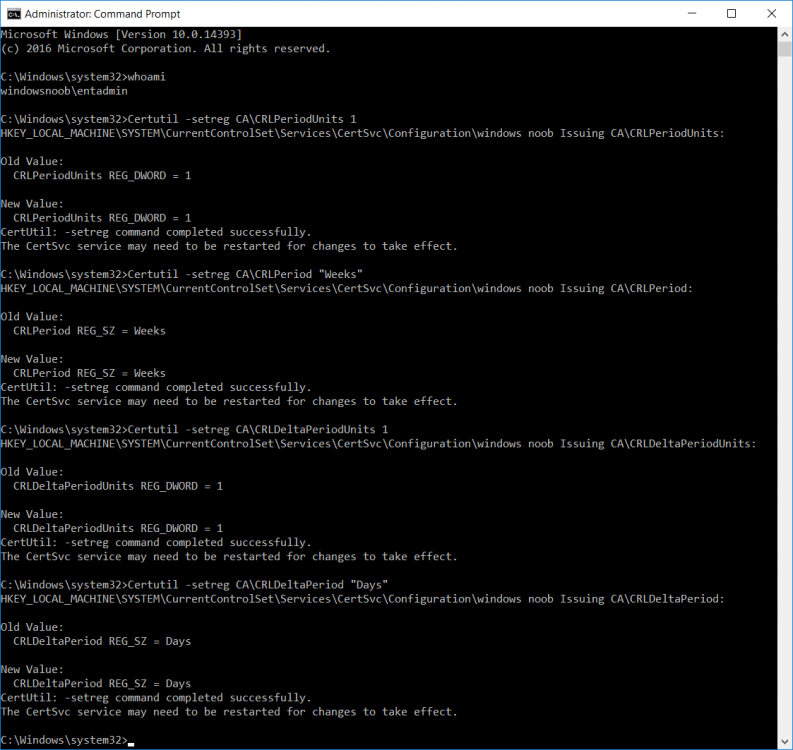
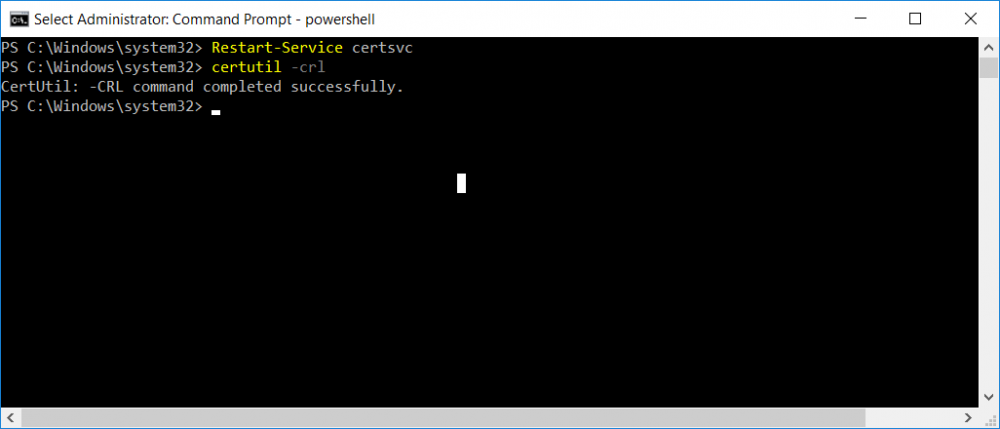
This series is comprised of different parts, listed below. Part 1 - Introduction and server setup Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication Part 4 - Post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 5 - Installing the Enterprise Issuing CA Part 6 - Perform post installation tasks on the Issuing CA (this part) Part 7 - Install and configure the OCSP Responder role service Part 8 - Configure AutoEnroll and Verify PKI health In part 1 of this series, you configured your LAB for a 2 tier PKI hierarchy running on Windows Server 2016. You used PowerShell to create some virtual machines, and then installed Windows Server 2016, Windows 10 Enterprise version 1803 and optionally Smoothwall 3.1 before configuring the IP address scheme and Computer Names on the virtual machines. Finally you configured ADDS on DC01 so that you have a working Domain Controller for the rest of this LAB. In part 2 you installed and did the initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA. In part 3 you prepared the HTTP Web Server for CDP and AIA Publication and you created a DNS record for the publicly available web server. In part 4 you performed post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA to set certificate revocation list (CRL) period registry settings using CertUtil, and then enabled object access Auditing and finally, you configured three locations for the Authority Information Access (AIA) and four locations for the Certificate revocation list Distribution Point (CDP), again using CertUtil. In part 5 you joined the IssuingCA computer to the windowsnoob domain before creating a new CAPolicy.inf file which was customized for the Issuing CA role. Next, you published the Root CA Certificate and CRL (both to Active Directory and the HTTP webserver) and you installed the Enterprise Issuing CA before submitting a request to the StandAlone Offline Root CA. Next you installed the Issuing CA Certificate using the response files from the StandAlone Offline Root CA on the removable media. In this part, you will perform post installation and configuration of the IssuingCA server. Step 1. Configure Certificate Revocation and CA Certificate Validity Periods To configure certificate revocation and CA certificate validity periods ensure that you are logged on to the IssuingCA server as windowsnoob\EntAdmin (you can use whoami in the command prompt to verify which user is logged on). Configure the CRL and Delta CRL settings Enter the following commands from an administrative command prompt: Certutil -setreg CA\CRLPeriodUnits 1 Press enter when done, then enter the following: Certutil -setreg CA\CRLPeriod "Weeks" Press enter when done, then enter the following: Certutil -setreg CA\CRLDeltaPeriodUnits 1 Press enter when done, then enter the following: Certutil -setreg CA\CRLDeltaPeriod "Days" The output of the above commands is shown below. Define CRL overlap settings Enter the following commands from an administrative command prompt: Certutil -setreg CA\CRLOverlapPeriodUnits 12 Press enter when done, then enter the following: Certutil -setreg CA\CRLOverlapPeriod "Hours" The output of the above commands is shown below. Configure the certificate validity period The default setting for ValidityPeriodUnits for certificates issued from the IssuingCA server is 2 years in the registry as shown here (HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\CertSvc\Configuration\windows noob Issuing CA). You can adjust this setting depending on your needs to define the lifetime of certificates issued from the IssuingCA server. It is recommended that you don't configure validity periods that are longer than half the total lifetime of the windows noob Issuing CA certificate (which was issued to be valid for 10 years based upon settings configured in the CAPolicy.inf you created on the IssuingCA in part 5, in particular, this line). RenewalValidityPeriodUnits=10 To limit issued certificates to 5 years, enter the following commands from an administrative command prompt: Certutil -setreg CA\ValidityPeriodUnits 5 Press enter when done, then enter the following: Certutil -setreg CA\ValidityPeriod "Years" Press enter. The output of the above commands is shown below. Step 2. Enable Auditing on the Issuing CA CA auditing requires system Audit Object Access to be enabled. To use Local Security Policy to enable object access auditing do as follows. Click Start, click Administrative Tools, and then select Local Security Policy. Expand Local Policies and then select Audit Policy. Double click Audit Object Access and then select Success and Failure then click OK. Close Local Security Policy editor. Configure Auditing for all CA related events Enable auditing for the CA by selecting which group of events to audit in the Certificate Authority MMC snap-in or by configuring AuditFilter registry key setting. To configure Auditing for all CA related events, run the following command from an administrative command prompt: Certutil -setreg CA\AuditFilter 127 The results of that command are shown below. Step 3. Configure the AIA The AIA is used to point to the public key for the certification authority (CA). Using a certutil command is a quick and common method for configuring the AIA. When you run the following certutil command, you'll configure the following: a static file system location a lightweight directory access path (LDAP) location a http location for the AIA. To configure AIA using certutil, open an administrative command prompt and enter the following command, pay close attention to the http address it's currently pointing to my http webserver. certutil -setreg CA\CACertPublicationURLs "1:C:\Windows\system32\CertSrv\CertEnroll\%1_%3%4.crt\n2:ldap:///CN=%7,CN=AIA,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,%6%11\n2:http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/%1_%3%4.crt" The output of that command is shown below: After you have run that command, run the following command to confirm your settings: certutil -getreg CA\CACertPublicationURLs The result of that command is shown below: You can also confirm these settings in the registry by using regedit and browsing to the following path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\CertSvc\Configuration\windows noob Issuing CA you can confirm the CACertPublicationURLs by opening that REG_MULTI_SZ value. You should see the following: 1:C:\Windows\system32\CertSrv\CertEnroll\%1_%3%4.crt 2:ldap:///CN=%7,CN=AIA,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,%6%11 2:http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/%1_%3%4.crt as shown below: You can also see this in the the CA (certsrv.msc) console. Click Start, select Administrative Tools, and then click Certification Authority. In the navigation pane, expand the Certificate Authority (Local). Right-click windows noob Issuing CA and then click Properties. On the Extensions tab, under Select extension, click Authority Information Access (AIA) and you will see the graphical representation of the AIA settings. Copy the windows noob Issuing CA certificate to the http AIA location To copy the windows noob Issuing CA certificate (crt file) to the http AIA location, use the following command on the IssuingCA server while logged in as windowsnoob\EntAdmin, your CRT file will more than likely be named differently, so change the command below accordingly. copy "c:\Windows\System32\certsrv\certenroll\IssuingCA.windowsnoob.lab.local_windows noob Issuing CA.crt" \\webserver.windowsnoob.lab.local\certenroll\ as shown below: Step 4. Configure the CDP Clients will use the CDP to locate the CRL and delta CRLs for certificates issued by the CA. This allows clients to ensure that the certificates have not been revoked. You can also configure the CDP using the user interface (certsrv.msc), certutil, and the registry. Using a certutil command is a quick and common method for configuring the CDP. When you run the following certutil command, you'll configure: a static file system location a LDAP location a http location a file system location Note: The file system location that you set will allow the CRL to be copied over the network to the web server (webserver.windowsnoob.lab.local), which is why we earlier allowed the Cert Publishers group access to the share and folder. All CAs are members of the Cert Publishers group, so we effectively allowed all CAs to copy to the CertEnroll folder on the webserver. Some administrators decide to configure a separate group of specific computers for that purpose or even grant permissions to the CAs individually. Adjust this command so that it points to your public web server http and file location address, then open a command prompt as Administrator and enter the following: certutil -setreg CA\CRLPublicationURLs "65:C:\Windows\system32\CertSrv\CertEnroll\%3%8%9.crl\n79:ldap:///CN=%7%8,CN=%2,CN=CDP,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,%6%10\n6:http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/%3%8%9.crl\n65:\\webserver.windowsnoob.lab.local\CertEnroll\%3%8%9.crl" as shown below: After you run that command, run the following certutil command to verify your settings: certutil -getreg CA\CRLPublicationURLs as shown below: and of course, you can also verify it in the registry by browsing to : HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CertSvc\Configuration\windows noob Issuing CA using regedit, you should see the following values: 65:C:\Windows\system32\CertSrv\CertEnroll\%3%8%9.crl 79:ldap:///CN=%7%8,CN=%2,CN=CDP,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,%6%10 6:http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/%3%8%9.crl 65:\\webserver.windowsnoob.lab.local\CertEnroll\%3%8%9.crl as shown below: Using an administrative command prompt, start PowerShell, then run the following commands to restart Active Directory Certificate Services and to publish the CRL. Restart-Service certsvc followed by: certutil -crl as shown below: That's it for this part, join me in Part 7 where you will Install and configure the OCSP Responder role service.
-

HPMIK...Worth it?
anyweb replied to itrider's topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
I'd recommend you install it to get a feel, and make sure to get your HP tam to guide you through it, i mean, that's what you are paying them for, it has some nice features and integrates nicely into SCCM when it works, have fun cheers niall- 1 reply
-
- 1
-

-
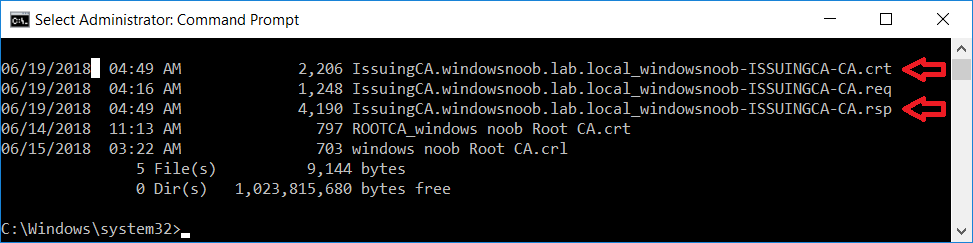
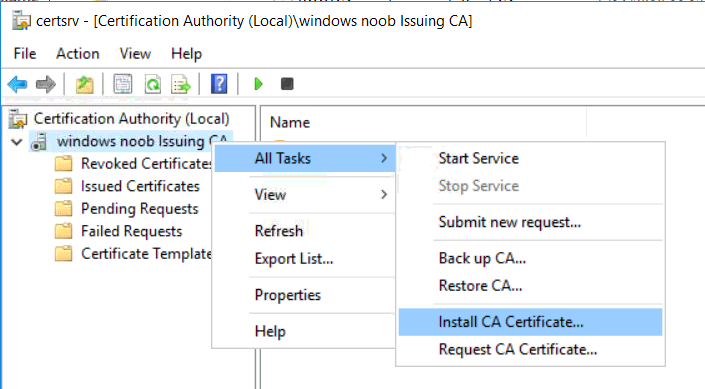
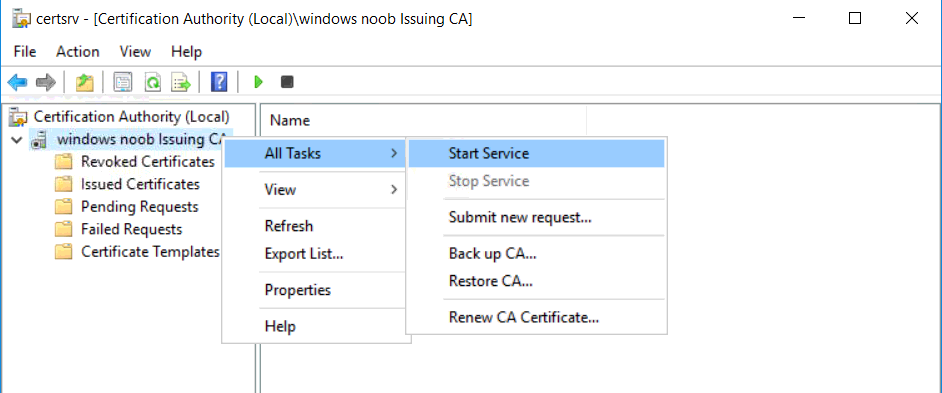
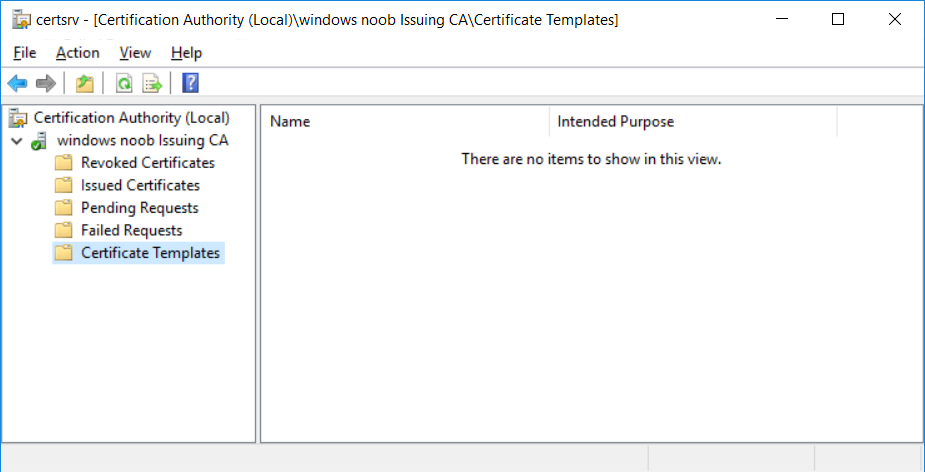
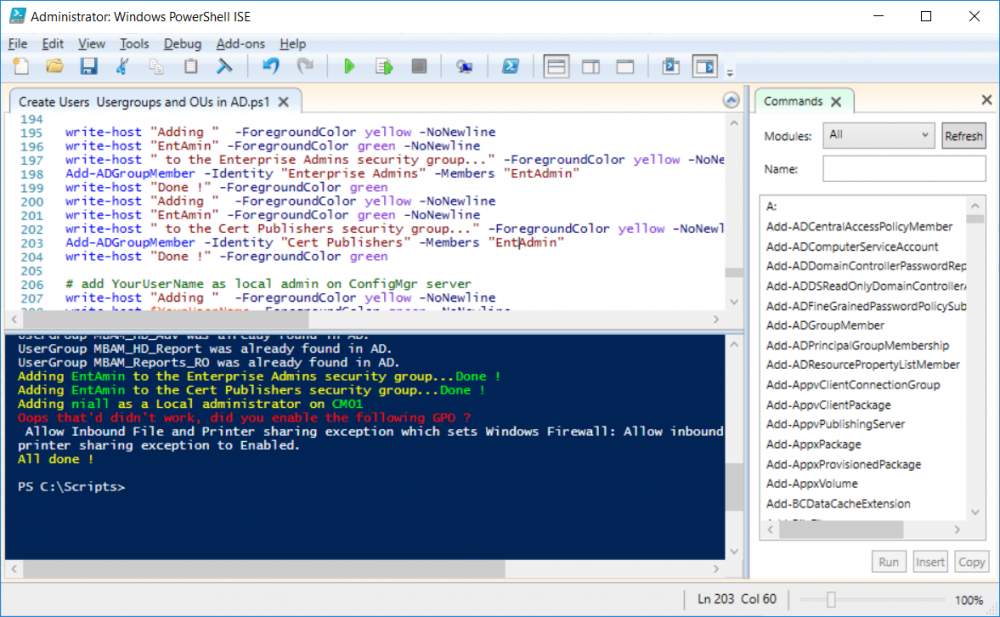
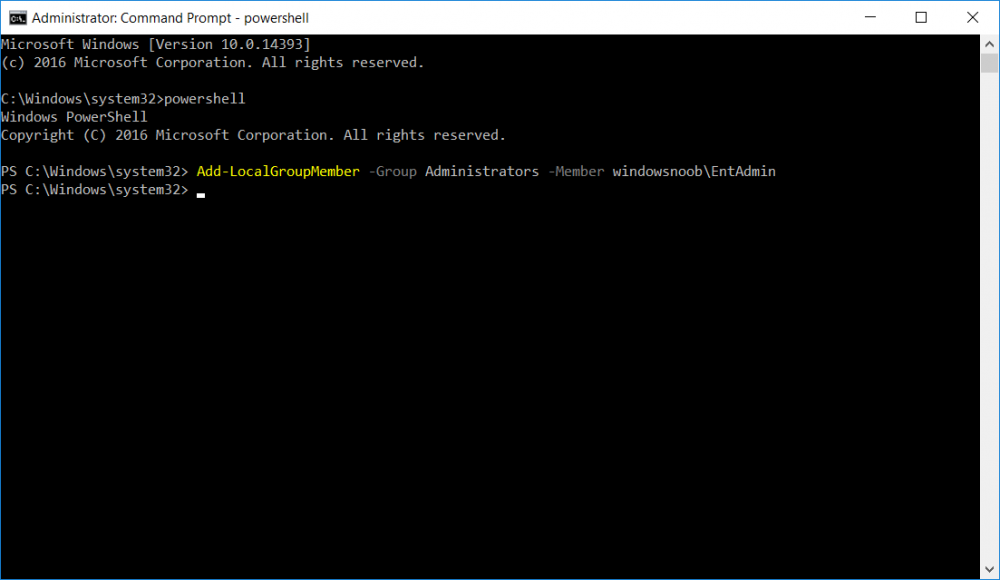
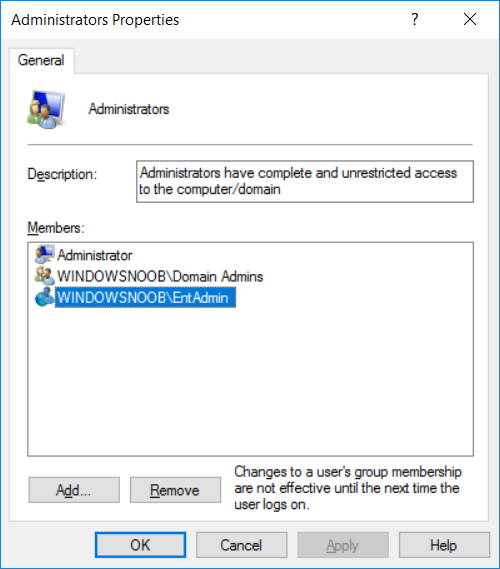
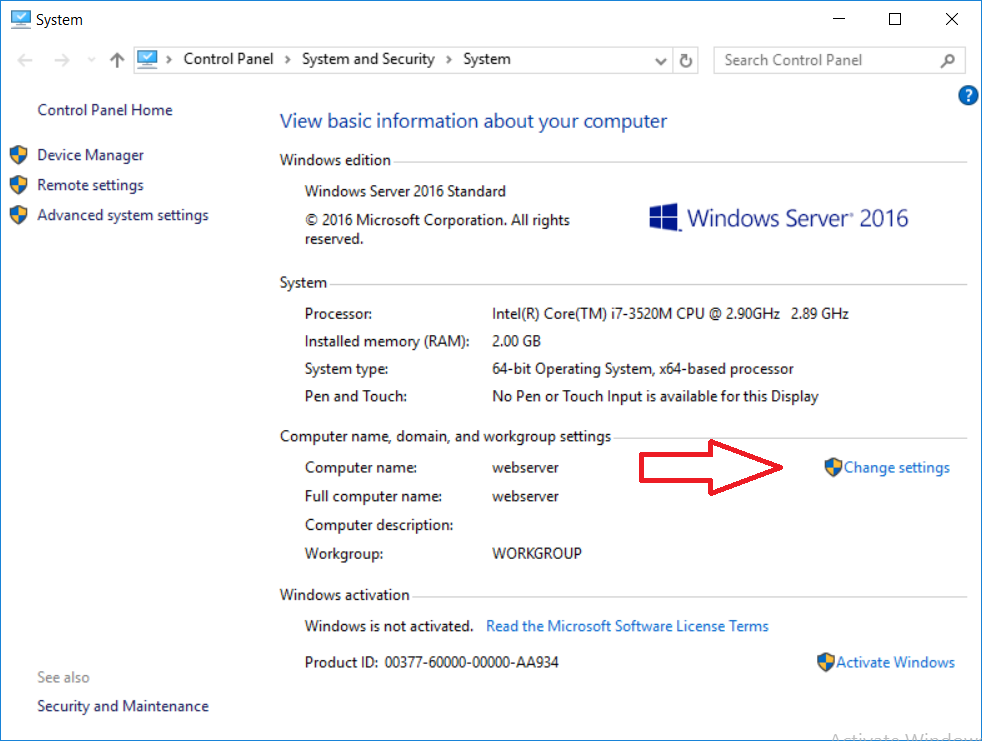
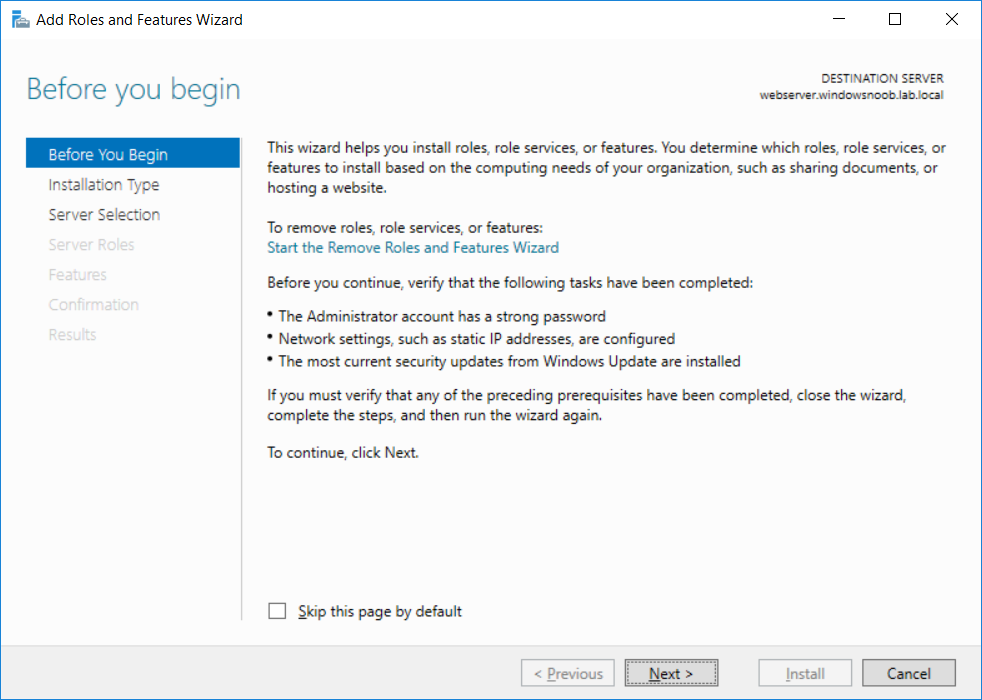
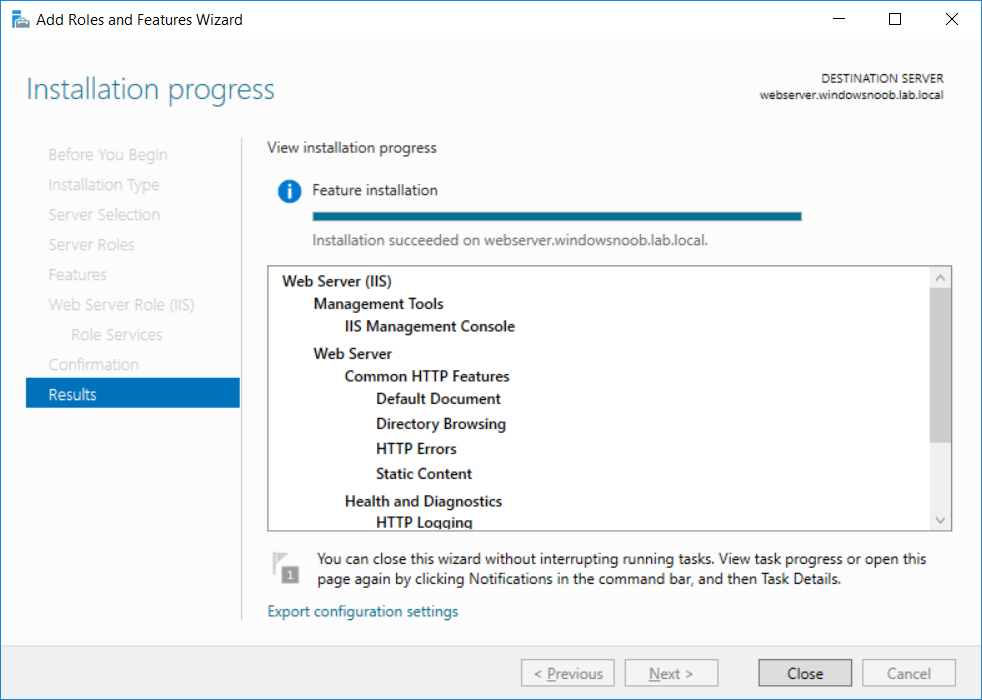
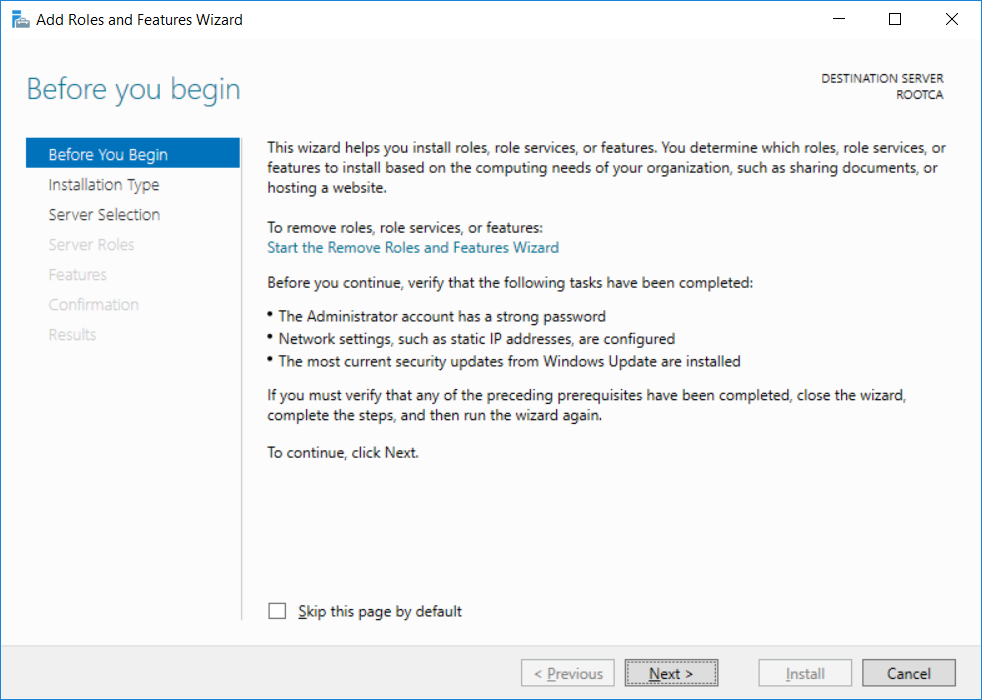
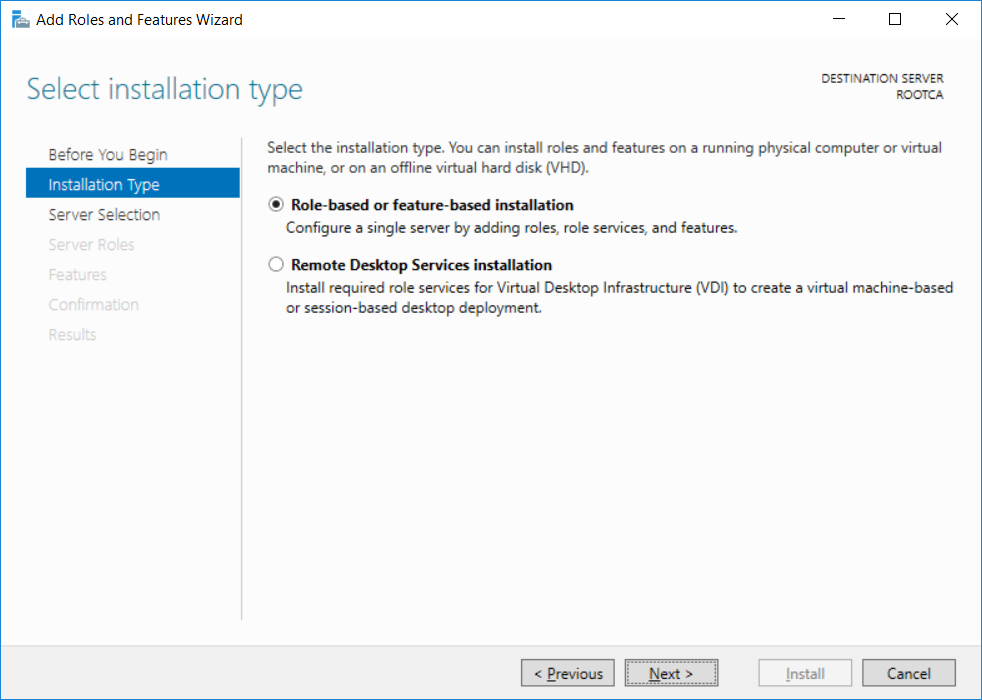
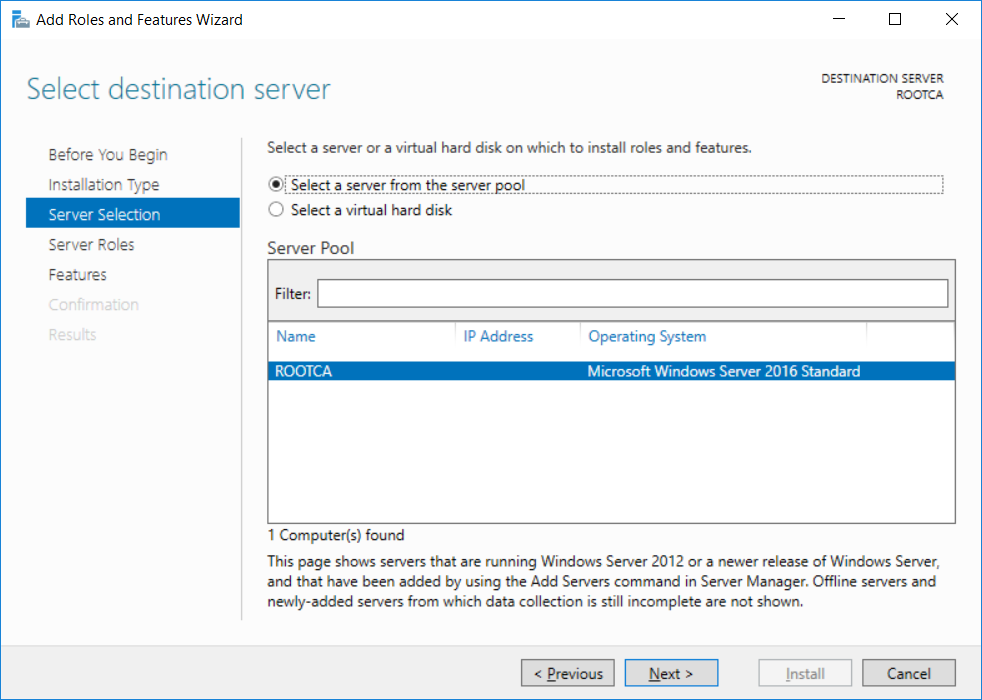
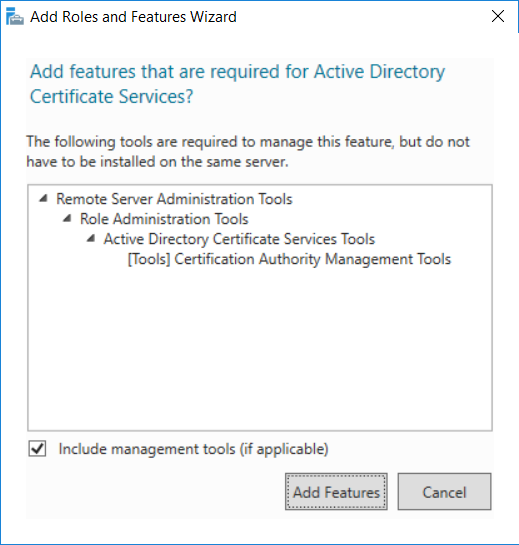
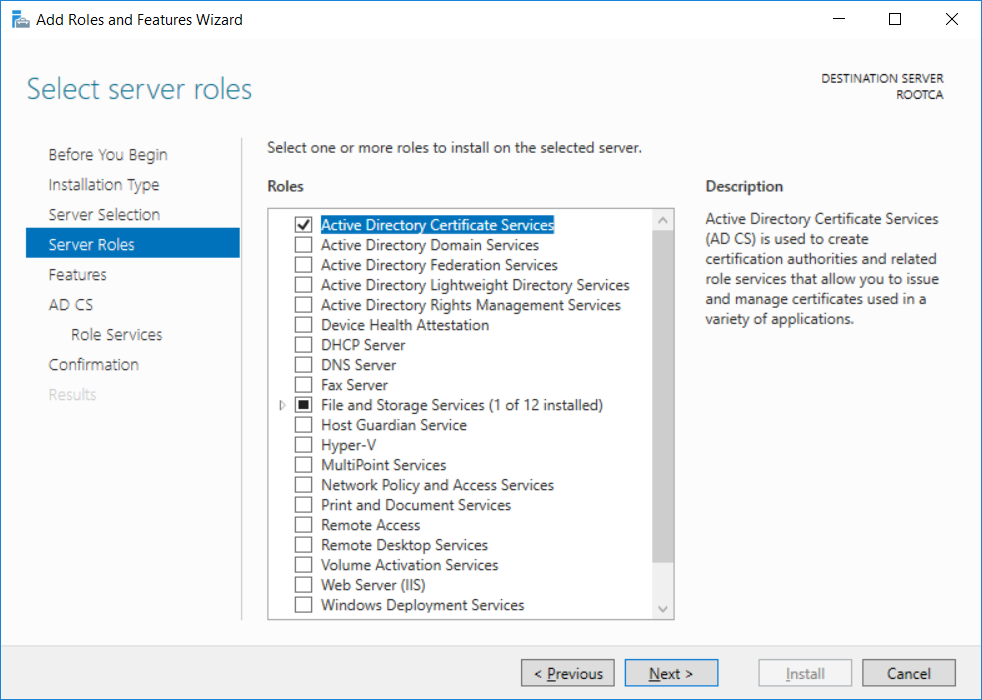
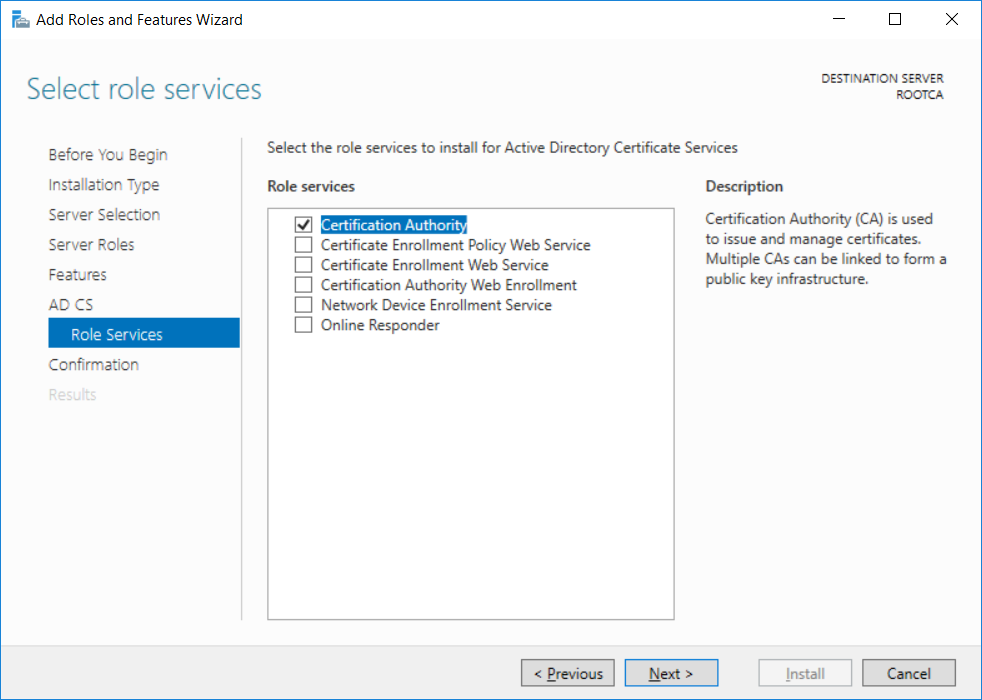
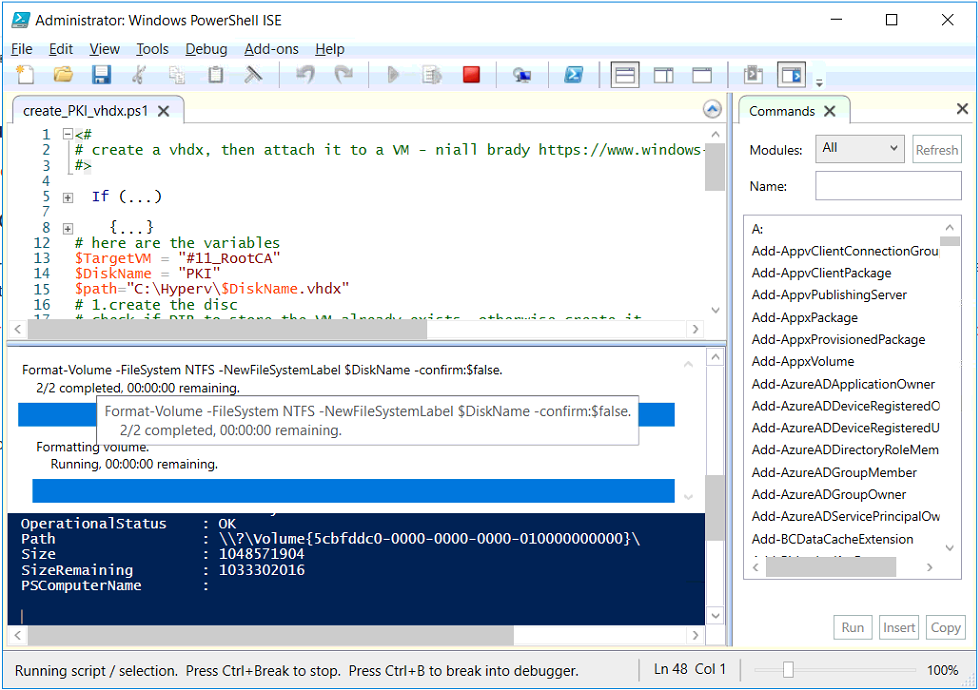
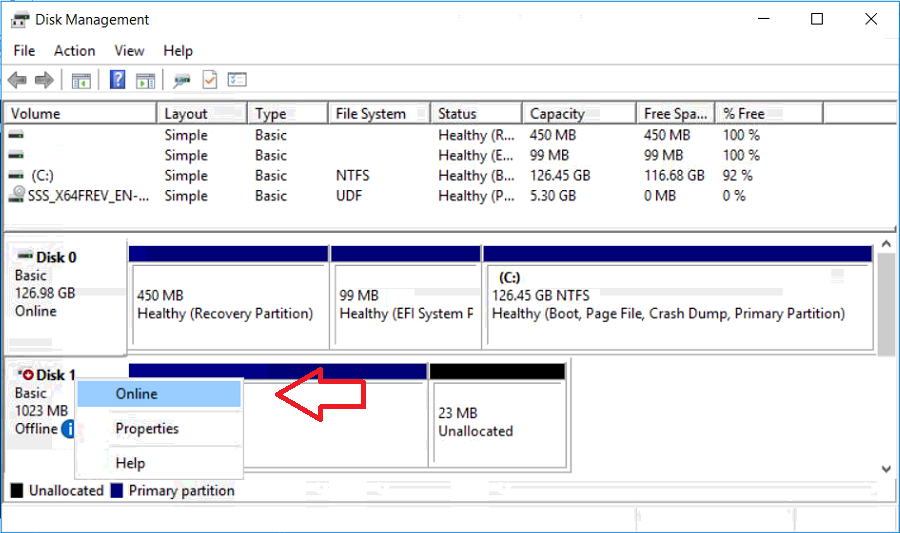
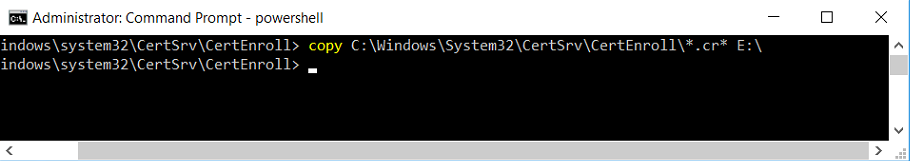
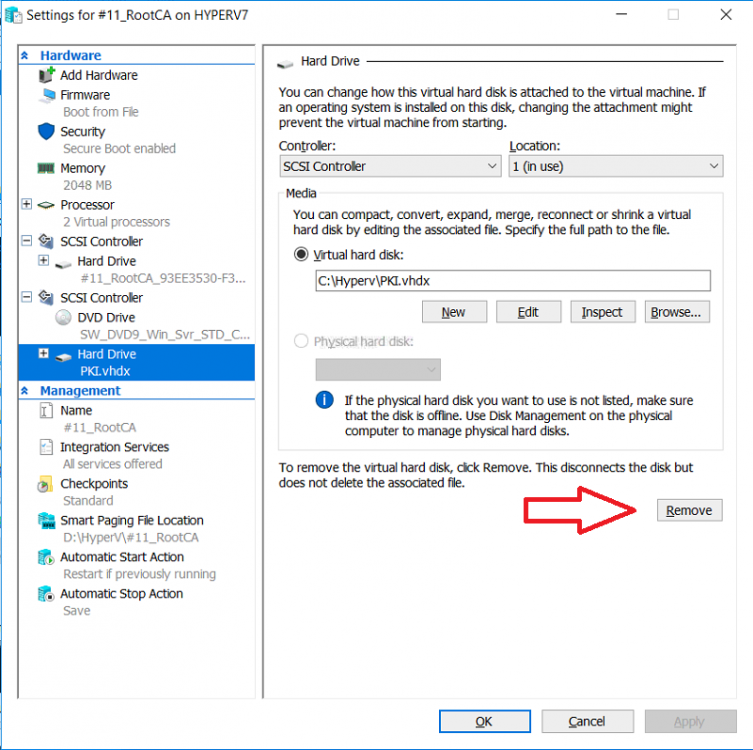
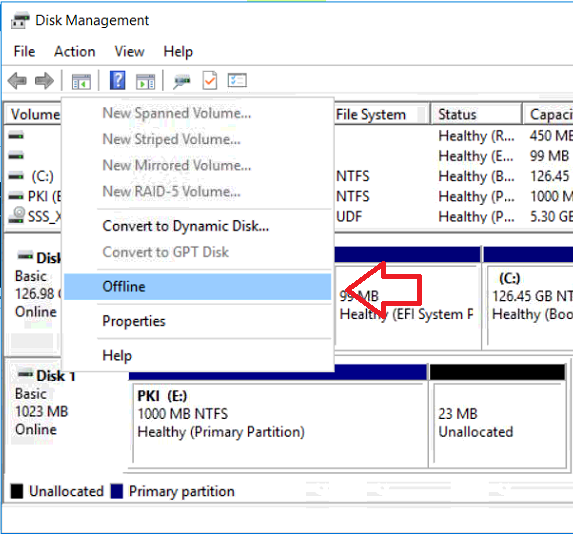
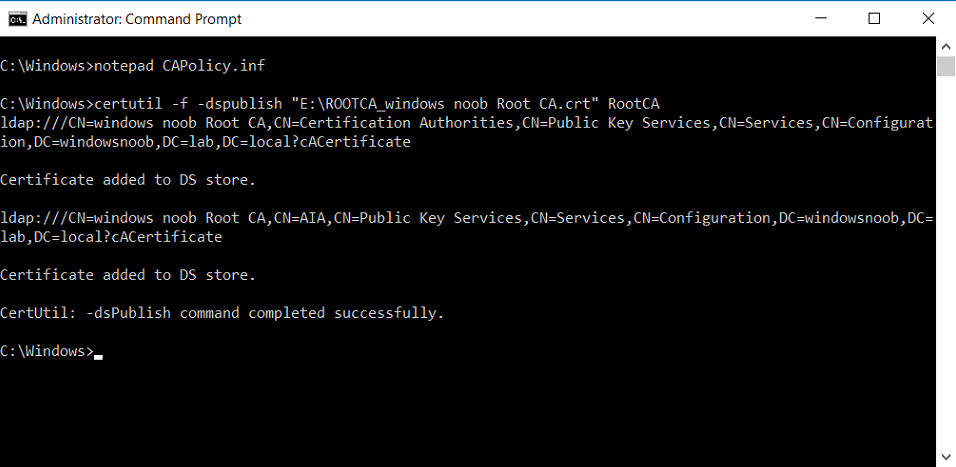
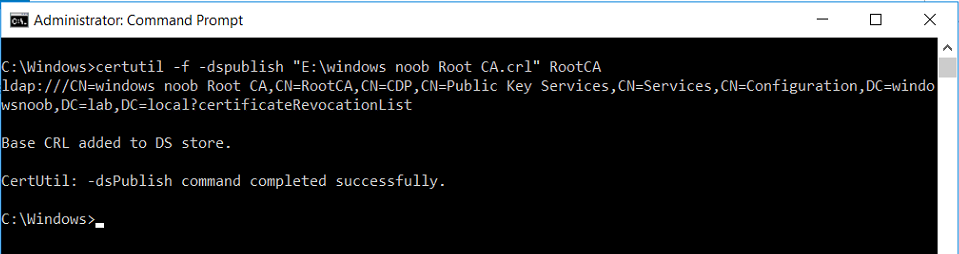
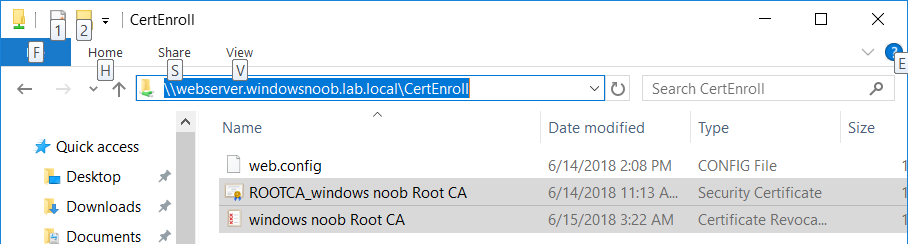
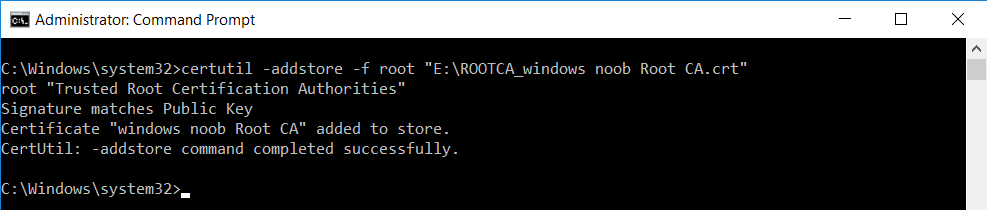
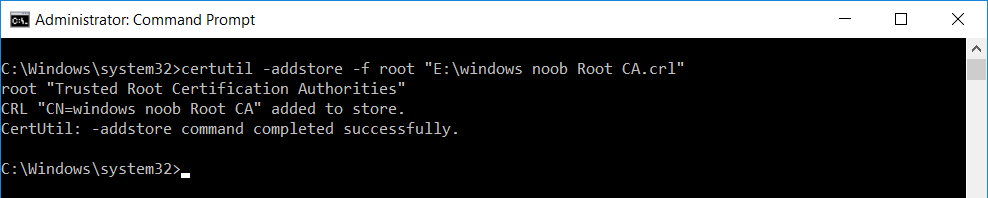
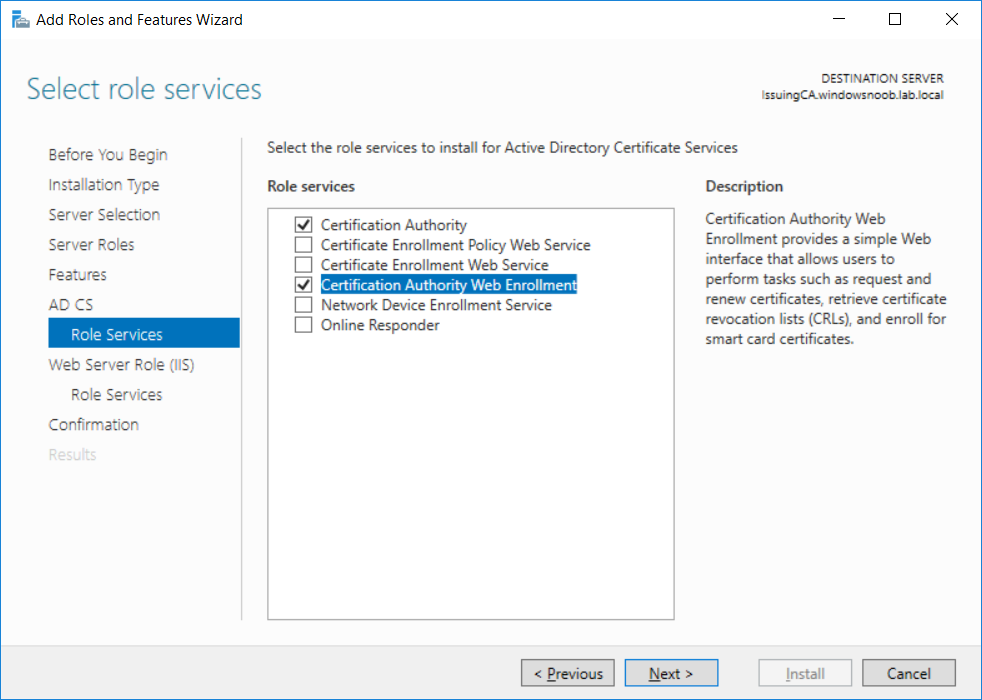
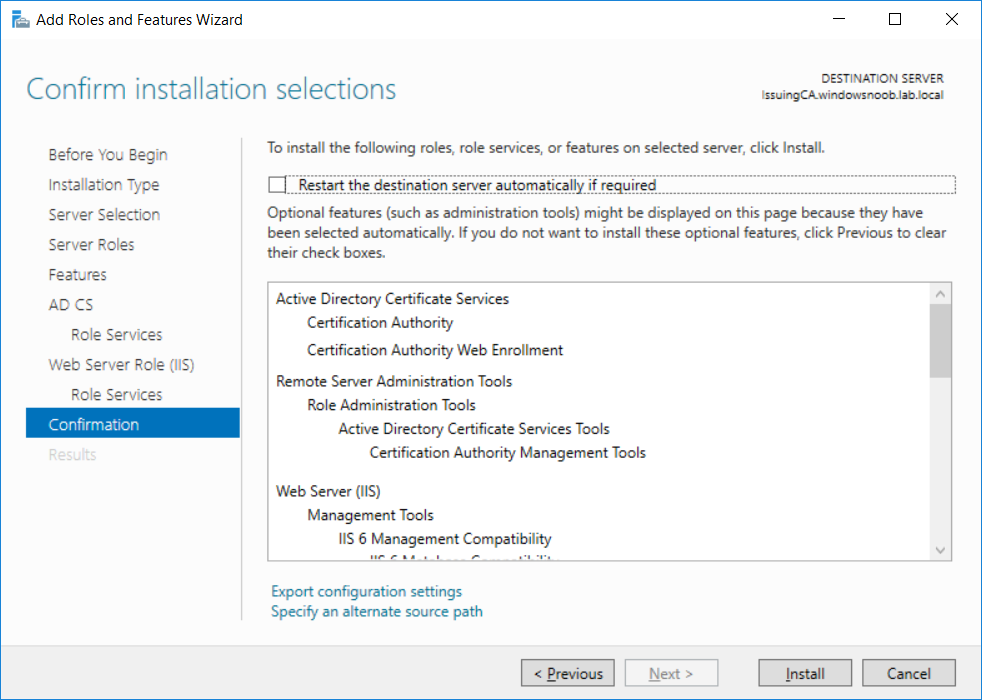
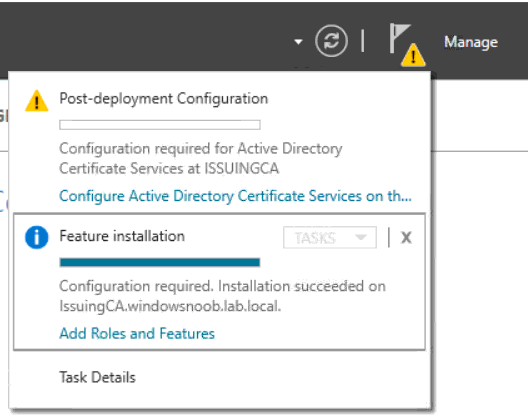
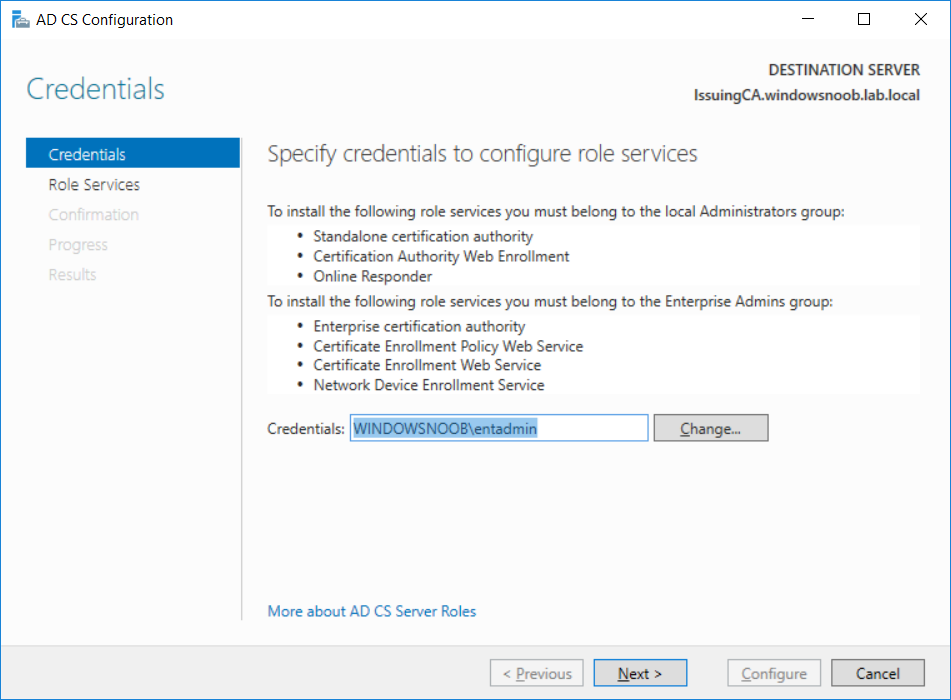
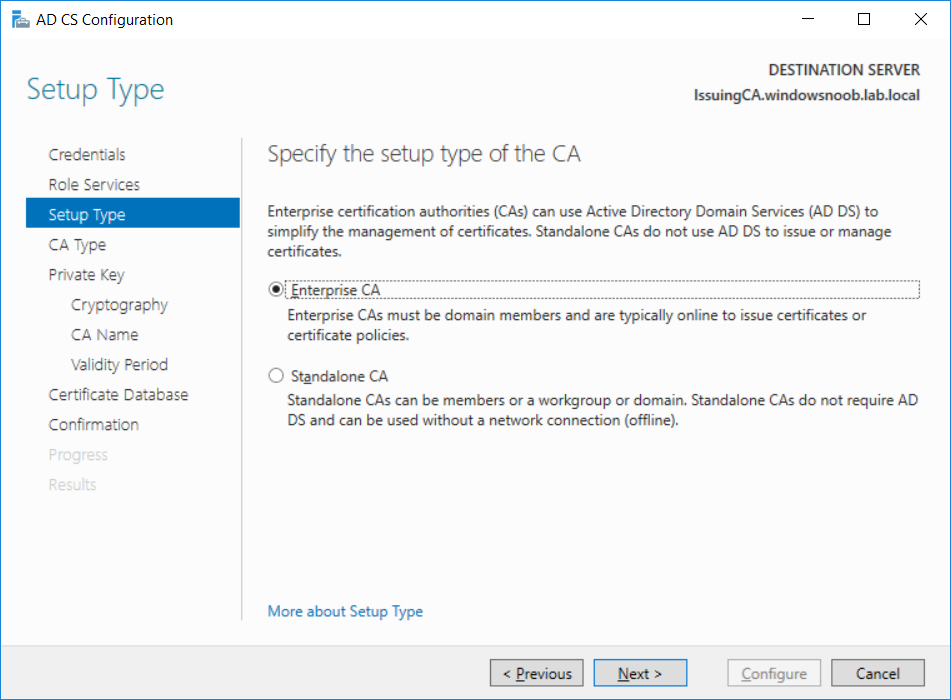
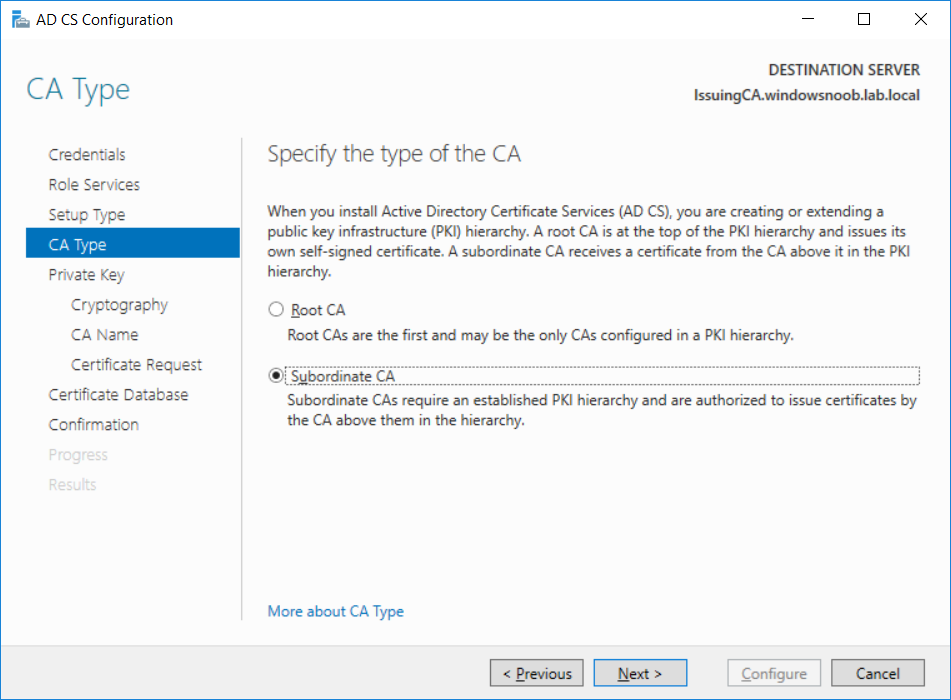
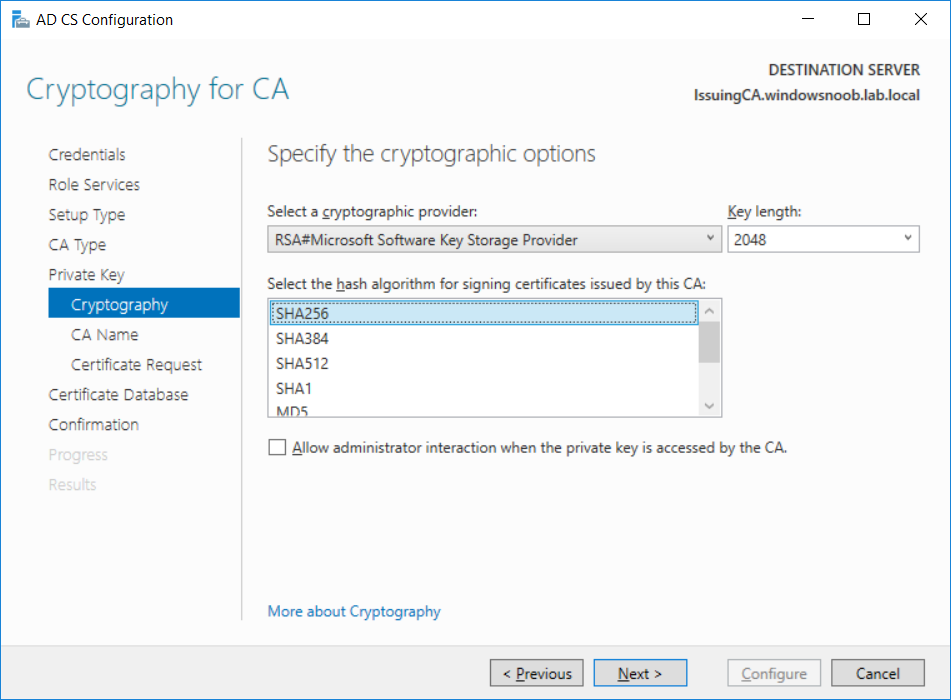
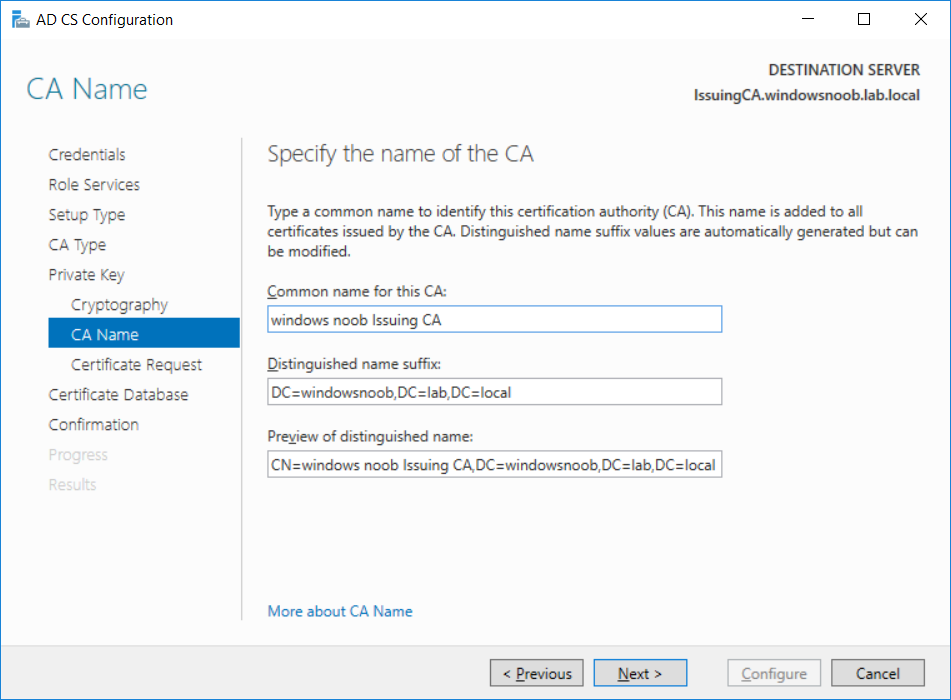
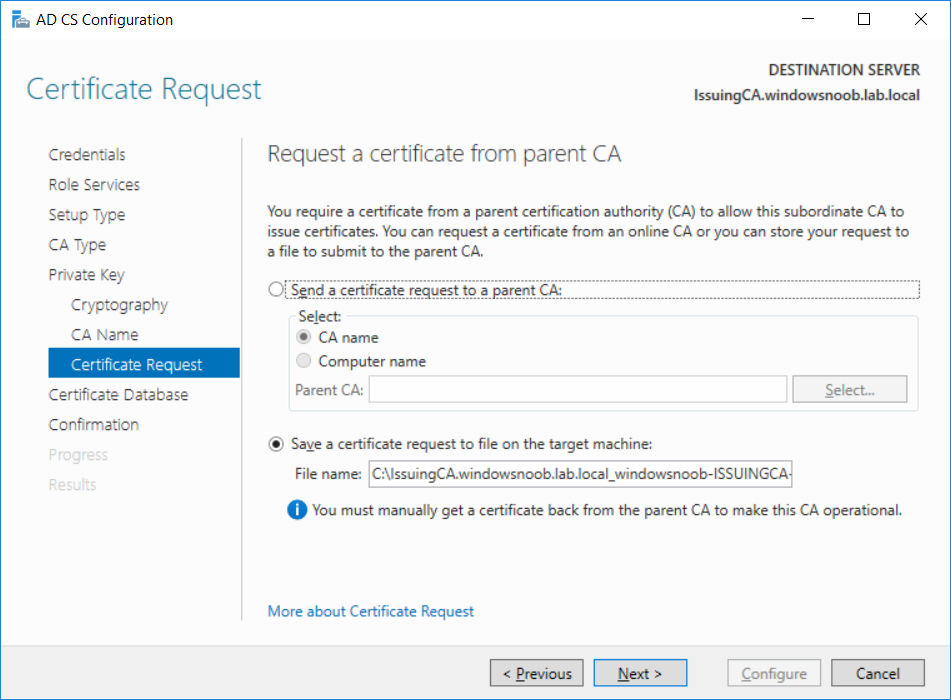
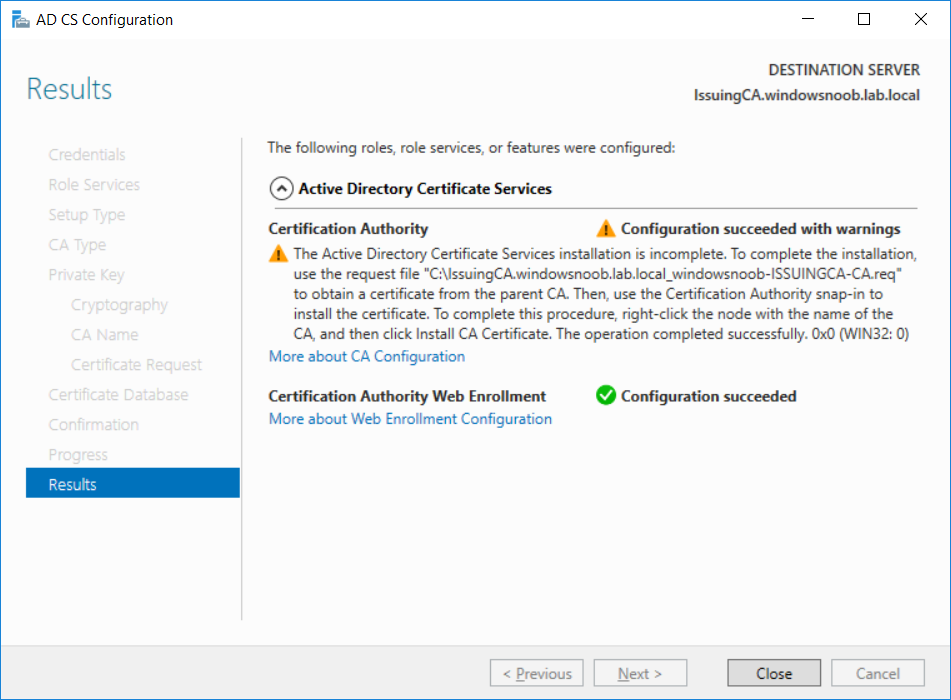
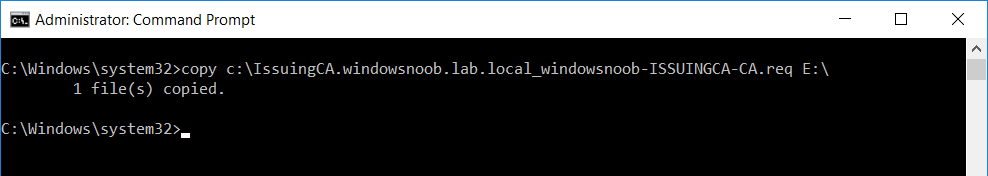
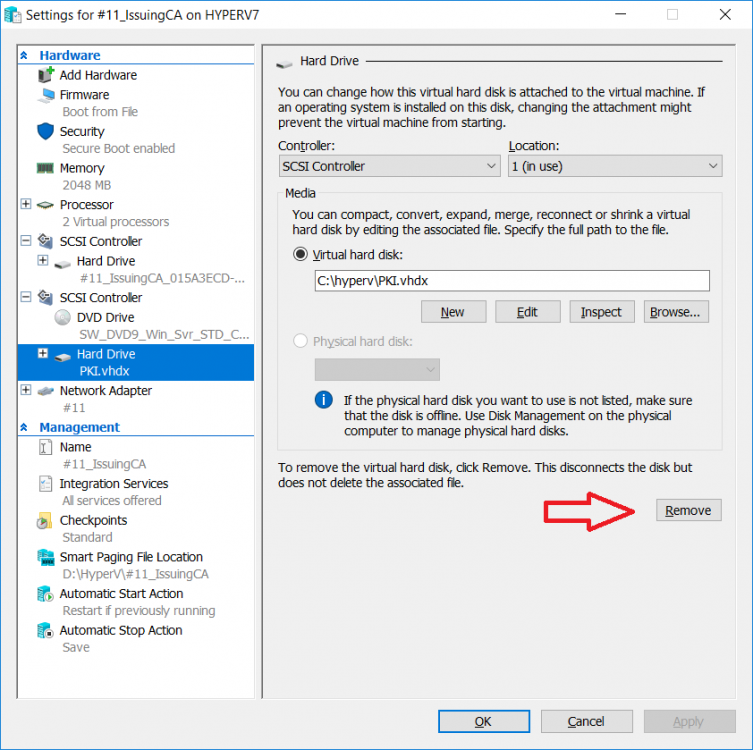
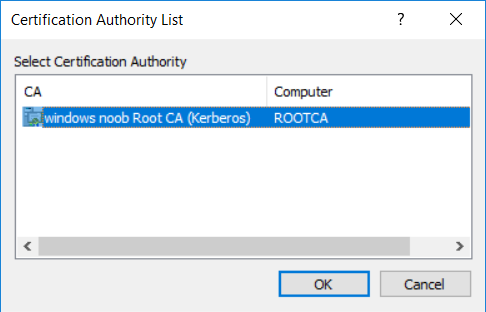
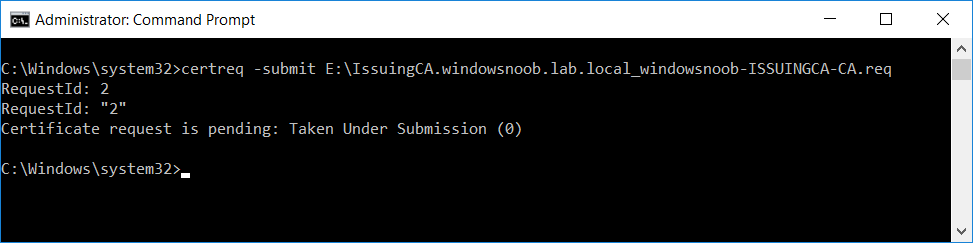
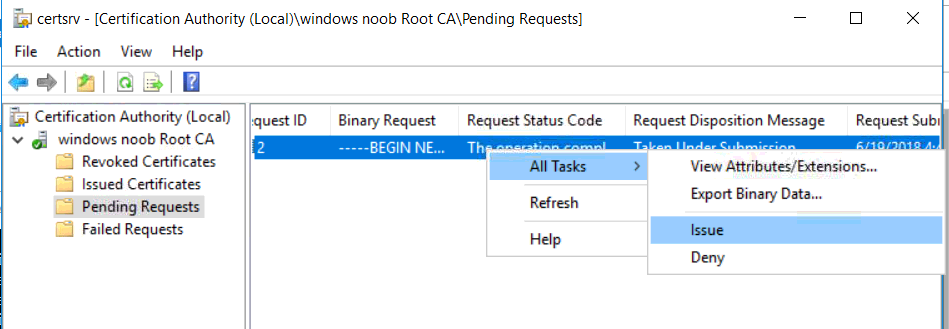
This series is comprised of different parts, listed below. Part 1 - Introduction and server setup Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication Part 4 - Post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 5 - Installing the Enterprise Issuing CA (this part) Part 6 - Perform post installation tasks on the Issuing CA Part 7 - Install and configure the OCSP Responder role service Part 8 - Configure AutoEnroll and Verify PKI health In part 1 of this series, you configured your LAB for a 2 tier PKI hierarchy running on Windows Server 2016. You used PowerShell to create some virtual machines, and then installed Windows Server 2016, Windows 10 Enterprise version 1803 and optionally Smoothwall 3.1 before configuring the IP address scheme and Computer Names on the virtual machines. Finally you configured ADDS on DC01 so that you have a working Domain Controller for the rest of this LAB. In part 2 you installed and did the initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA. In part 3 you prepared the HTTP Web Server for CDP and AIA Publication and you created a DNS record for the publicly available web server. In part 4 you performed post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA to set certificate revocation list (CRL) period registry settings using CertUtil, and then enabled object access Auditing and finally, you configured three locations for the Authority Information Access (AIA) and four locations for the Certificate revocation list Distribution Point (CDP), again using CertUtil. In this part you will install and do initial configuration on the Enterprise Issuing CA. This is a long blog post so make sure you've got lots of coffee or beer handy (depending on your preference). Step 1. Add EntAdmin user to groups We'll be using a special user called EntAdmin (an Enterprise Admin and a member of Cert Publishers) for some tasks on the IssuingCA computer, but before doing so, we need to add that user as a member of the Enterprise Admins group and the Cert Publishers on the domain controller. You could do so simply by issuing the following in Windows PowerShell ISE on DC01. Import-Module ActiveDirectory Add-ADGroupMember -Identity "Enterprise Admins" -Members "EntAdmin" Add-ADGroupMember -Identity "Cert Publishers" -Members "EntAdmin" Alternatively you can run this script in Windows PowerShell ISE as windowsnoob\Administrator on DC01. Create Users Usergroups and OUs in AD.ps1 Step 2. join IssuingCA to the domain When you installed the Issuing CA virtual machine (#11_IssuingCA) in part 1, it was workgroup joined. To join the domain do as follows. Logon to the web server virtual machine as Administrator. In Windows File Explorer, right click on This PC and choose Properties. Click on Change Settings beside Computer name, domain and workgroup settings. You can follow the instructions in Part 3, Step 1 for how to join a domain manually or use the JoinDomain.ps1 PowerShell script here. JoinDomain.ps1 1. Copy the script to C:\Scripts on the IssuingCA server. 2. Edit the variables (lines 16-18) as desired before running. 3. Start Windows PowerShell ISE as Administrator and run the script by clicking on the green triangle. Note: After running the script, the computer will restart automatically. Step 3. Add EntAdmin as a local admin on IssuingCA Next, logon to the IssuingCA domain joined computer as windowsnoob\administrator. Once logged in, start compmgmt.msc and add EntAdmin as to the Local Administrators group by expanding System Tools, Local Users or Groups, Administrators, Members tab and clicking Add, Enter EntAdmin as the user. Alternatively use this PowerShell command to do it for you on the IssuingCA computer while logged in as windowsnoob\administrator. Add-LocalGroupMember -Group Administrators -Member windowsnoob\EntAdmin Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. The user is now listed as a member of Local Administrators group on IssuingCA. After doing the above, logoff (Sign out) from IssuingCA. Step 4. Create an OID Before creating the CAPolicy.inf file in the next step, we should use our own OID rather than the default Microsoft one (OID= 1.2.3.4.1455.67.89.5). I'm using a PowerShell script found here for that purpose (1). You can download that script below: createOID.ps1 Step 5. Create a CAPolicy.inf file for the Enterprise Issuing CA. Before installing the Issuing CA, you should create a CAPolicy.inf to define 'default' settings for CA templates, some of these settings cannot be changed later and you want them in place before creating any certificates on the Issuing CA. On the #11_IssuingCA virtual machine (IssuingCA), login as windowsnoob\Entadmin using the password specified. Open an administrative command prompt and type the following: notepad C:\Windows\CAPolicy.inf and press ENTER, when prompted to create new file, click Yes. Paste in the following text into the new CAPolicy.inf file. [Version] Signature="$Windows NT$" [PolicyStatementExtension] Policies=InternalPolicy [InternalPolicy] OID=1.2.3.4.1455.67.89.5 URL=http://pki.windows-noob.com/cps.txt [Certsrv_Server] RenewalKeyLength=2048 RenewalValidityPeriod=Years RenewalValidityPeriodUnits=10 LoadDefaultTemplates=0 AlternateSignatureAlgorithm=0 Once done, paste in the OID created in Step 4 and then save the file as C:\Windows\CAPolicy.inf. Note: The OID in the CAPolicy.inf pasted above uses Microsoft's own OID, you should use the one generated in Step 4 or obtain one from here (2). Step 6. Publish the Root CA Certificate and CRL In this step, you will copy CER and CRT files from the Standalone Offline Root CA virtual machine to the IssuingCA virtual machine before publishing the Root CA Certificate and CRL. I'm showing you a few methods how to copy the files (PowerShell or manually) but you are doing so using a 1GB VHDX disk. The reason for this is you should not connect the StandAlone Offline Root CA to the network. On your Hyper-V host (the computer that you use to host this LAB), run the following PowerShell script (after adjusting the variables as necessary) to create a 1GB VHDX disk which we will use to copy CER and CRL files between the StandAlone Offline Root CA (RootCA) to the IssuingCA virtual machines. Note: The first time your run this script it will automatically attach the VHDX to the #11_RootCA virtual machine. You may need to open disk administrator on that virtual machine and change the disk to Online before use. Download the PowerShell script - create_PKI_vhdx.ps1 Note: Before taking any new snapshots (checkpoints) of your virtual machines, please ensure that you have first offlined the PKI disk and then removed it from the respective vm's. Logon to the StandAlone Offline Root CA (RootCA) as Administrator, and if necessary, change the just attached vhdx disk to Online using Disk Management. Using a command prompt, copy the StandAlone Offline Root CA Certificate (ROOTCA_windows noob Root CA.crt) and Root CA CRL (windows noob Root CA.crl) files from the C:\Windows\System32\CertSrv\CertEnroll directory on RootCA server to the VHDX removable media (probably E:\). copy C:\Windows\System32\CertSrv\CertEnroll\*.cr* E:\ Now, using Disk Management, set the PKI disk to Offline Using the virtual machine settings GUI for #11_RootCA (RootCA), remove the previously attached PKI disk. or alternatively, use the following PowerShell (on the Hyper-v host), where $TargetVM="#11_RootCA" Remove-VMHardDiskDrive -VMName $TargetVM -ControllerType SCSI -ControllerNumber 1 -ControllerLocation 1 On the #11_IssuingCA virtual machine, use the Virtual Machine GUI settings to attach the PKI disk, or use Powershell where $TargetVM="#11_IssuingCA" and $path=the path to the VHDX file Add-VMHardDiskDrive -VMName $TargetVM -ControllerType SCSI -ControllerNumber 1 -ControllerLocation 1 -Path $path On the #11_IssuingCA virtual machine, login as windowsnoob\EntAdmin and using Disk Management, change the PKI disk to Online. Issue the following command as windowsnoob\EntAdmin where E:\somefile.crt is the path to the CRT file. Note: Pay close attention when doing this step, getting it wrong will cause problems with PKIview and other areas. RootCA in this case is not the host name here, but the DS Trusted Root store store name, see this comment for more details. certutil -f -dspublish "E:\ROOTCA_windows noob Root CA.crt" RootCA Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. You should see "Certificate added to DS store". Next, issue the following command as windowsnoob\EntAdmin where E:\somefile.crl is the path to the CRL file and where RootCA is the HOSTNAME of your Standalone Offline Root CA server. certutil -f -dspublish "E:\windows noob Root CA.crl" RootCA Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. You should see "Base CRL added to DS store". Using Windows File Explorer on IssuingCA as windowsnoob\Entadmin, copy the CR* files on E:\ (or whatever drive letter the PKI disk is mounted as) to \\webserver.windowsnoob.lab.local\CertEnroll On the IssuingCA, to add the windows noob Root CA Certificate and CRL to the IssuingCA local store, run the following command from an administrative command prompt as windowsnoob\EntAdmin. Ensure that you substitute the correct drive letter of your removable media (for E:) in the command below: certutil -addstore -f root "E:\ROOTCA_windows noob Root CA.crt" Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. You should see "CertUtil: -addstore command completed successfully". Next, run the following command from an administrative command prompt as windowsnoob\EntAdmin. Ensure that you substitute the correct drive letter of your removable media (for E:) in the command below: certutil -addstore -f root "E:\windows noob Root CA.crl" Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. You should see "CertUtil: -addstore command completed successfully". Step 7. Install the Subordinate Issuing CA Now that you've created the CAPolicy.inf file and published the CRT and CRL files (from the StandAlone Offline Root CA) to Active Directory, copied them to the Webserver CertEnroll folder and to the local store on the Issuing CA, you are ready to install Active Directory Certificate Services (on the Issuing CA). To do so, open Server Manager and select Add Roles and Features, on the Before You Begin page select Next. On the Select Server Roles page select Active Directory Certificate Services and then click Next, if prompted to Add features that are required for Active Directory Certificate Services, click Add features. On the Introduction to Active Directory Certificate Services page, click Next. On the Select Role Services page (shown below), select Certification Authority and Certification Authority Web Enrollment. If you see the Add Roles Wizard, click Add Required Role Services. Click Next. Continue through the wizard and click on Install. Leave the wizard open until the feature installation completes successfully, then click Close. In Server Manager, click on Configure Active Directory Certificate Services (yellow exclamation mark). Ensure that your credentials are windowsnoob\EntAdmin click Next. On the Select roles to configure, ensure that both Certification Authority and Certification Authority Web Enrollment are selected. On the Specify the setup type of the CA page, ensure that Enterprise is selected, and then click Next. Note: The Enterprise option will be greyed out if you are not logged on as Enterprise Admin (windowsnoob\EntAdmin) or do not have local administrator permission. On the Specify the type of CA page, select Subordinate CA, and then click Next. On the Set Up Private Key page, ensure that Create a new private key is selected, and then click Next. Ensure that Sha256 is selected on the Specify the cryptographic options page, then click Next. Note: When installing in a production environment, the CSP, Hash Algorithm and Key length selected must support application compatibility requirements of your organization. On the Specify the name of the CA page, clear the existing entry for Common name for this CA box, and enter windows noob Issuing CA, then click Next. On the Request certificate from a parent CA page, select Save a certificate request to file and manually send it later to a parent CA option then click Next Continue through the wizard and finally click on Configure in the Confirm Installation Selections page, finally, click on Close at the Configuration Succeeded screen. Take note of the warning, it is expected. Step 8. Copy the certificate request file to the StandAlone Offline Root CA Run the following command from an administrative command prompt as windowsnoob\EntAdmin on the IssuingCA computer. Ensure that you substitute the correct drive letter of your removable media (for E:) in the command below: copy c:\IssuingCA.windowsnoob.lab.local_windowsnoob-ISSUINGCA-CA.req E:\ Next, take the PKI disk offline in Disk Management on the IssuingCA Next, Remove the PKI disk from the IssuingCA virtual machine using the GUI settings or use the PowerShell commands shown earlier to do it. And insert the PKI disk into the StandAlone Offline Root CA virtual machine, then make if Online in Disk Management (on RootCA). Step 9. Submit the Request and Issue windows noob Issuing CA Certificate On the StandAlone Offline Root CA, login as Administrator and use the following command in an Administrative command prompt where E:\ is the PKI disk certreq -submit E:\IssuingCA.windowsnoob.lab.local_windowsnoob-ISSUINGCA-CA.req When prompted which CA to use, select the windows noob Root CA and click OK. Take note of the certificate requestID On the StandAlone Offline Root CA, start CertSrv.msc and click on Pending requests, right click the matching RequestID, choose All Tasks then select Issue. Return to the administrative command prompt to accept the issued certificate by running the following command. Make sure you are using the correct drive letter for your removable media for E: as well as the correct RequestID for 2: Note: Notice the .crt in the command line below, you must make sure it's typed correctly. certreq -retrieve 2 E:\IssuingCA.windowsnoob.lab.local_windowsnoob-ISSUINGCA-CA.crt When prompted which CA to use, select the windows noob Root CA and click OK. If everything went ok you'll see output like the below. If you now do a DIR on the PKI disk you'll see new files have been generated. Next, take the PKI disk offline in Disk Management on the StandAlone Offline Root CA Finally, Remove the PKI disk from the StandAlone Offline Root CA virtual machine using the GUI settings or use the PowerShell commands shown earlier to do it. Step 10. Install the windows noob Issuing CA Certificate on IssuingCA Once again, add the PKI disk to the IssuingCA virtual machine, and take it Online in Disk Management. Ensure you are logged on to IssuingCA as windowsnoob\EntAdmin. Next, open the Certification Authority console (CertSrv.msc) and in the Certification Authority console tree, right-click windows noob Issuing CA, and then click Install CA Certificate. In the Select file to complete CA installation, navigate to your removable media (PKI disk). Ensure that you are displaying All Files (*.*) and click the IssuingCA.windowsnoob.lab.local_windowsnoob-ISSUINGCA-CA.rsp, (response file), click Open. The CertSrv console will reload itself. Next, In the console tree, right-click windows noob Issuing CA, click All Tasks, and then click Start Service. In the console tree, expand windows noob Issuing CA and then click Certificate Templates. Notice there are no certificates shown in the details pane. This is because the CAPolicy.inf specified not to install the default templates in the line LoadDefaultTemplates=0. Next, take the PKI disk offline in Disk Management on the IssuingCA and finally, Remove the PKI disk from the IssuingCA virtual machine using the GUI settings or use the PowerShell commands shown earlier to do it. That's all for this Part, phew... Please join me in Part 6 when you will perform post installation tasks on the Subordinate Issuing CA. Recommended reading (1) - https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/56b78004-40d0-41cf-b95e-6e795b2e8a06#content (2) - http://msdn.microsoft.com/library/windows/desktop/ms677621.aspx
-
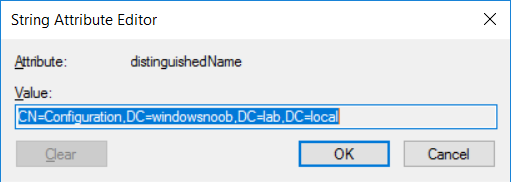
This series is comprised of different parts, listed below. Part 1 - Introduction and server setup Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication Part 4 - Post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA (this part) Part 5 - Installing the Enterprise Issuing CA Part 6 - Perform post installation tasks on the Issuing CA Part 7 - Install and configure the OCSP Responder role service Part 8 - Configure AutoEnroll and Verify PKI health In part 1 of this series, you configured your LAB for a 2 tier PKI hierarchy running on Windows Server 2016. You used PowerShell to create some virtual machines, and then installed Windows Server 2016, Windows 10 Enterprise version 1803 and optionally Smoothwall 3.1 before configuring the IP address scheme and Computer Names on the virtual machines. Finally you configured ADDS on DC01 so that you have a working Domain Controller for the rest of this LAB. In part 2 you installed and did the initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA. In part 3 you prepared the HTTP Web Server for CDP and AIA Publication and you created a DNS record for the publicly available web server. Now you will perform post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA to set certificate revocation list (CRL) period registry settings using CertUtil, and then enable object access Auditing and finally, to configure three locations for the Authority Information Access (AIA) and four locations for the Certificate revocation list Distribution Point (CDP), again using CertUtil. Step 1. Configure CRL period registry settings using CertUtil In this step, you'll use CertUtil to set various related registry settings for the Certificate Revocation List periods in the registry on the Standalone Offline Root CA. Logon to the Standalone Offline Root CA as RootCA\Administrator. Right-click on Start, and choose Command Prompt (admin). I'll show screenshots of the output of each command separately so that you can compare it to your environment. To start off, you need to define the Active Directory Configuration Partition Distinguished Name, and to do that using certutil enter the following command: Certutil -setreg CA\DSConfigDN "CN=Configuration,DC=windowsnoob,DC=lab,DC=local" Note: You can determine what the configuration path should be (for your LAB) for the command above by logging on to the Domain Controller (DC01), and by opening Adsi Edit, and click on Action then select Connect to. In the window that appears, change Select a well known naming context to Configuration. In the Adsi Edit pane, right click on CN=Configuration,DC=windowsnoob,DC=lab,DC=local and choose Properties, scroll down and double click on Distinguished Name, copy the Value listed in the String attribute editor. The results of the certutil -setreg command on the Standalone Offline Root CA are shown below. Be sure that it states CertUtil: -setreg command completed successfully. Next you will define the Certificate Revocation List (CRL) Period Units, CRL Period and CRL Delta Period Units. To do so run the following commands from an administrative command prompt: Certutil -setreg CA\CRLPeriodUnits 52 Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. Certutil -setreg CA\CRLPeriod "Weeks" Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. Certutil -setreg CA\CRLDeltaPeriodUnits 0 Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. To define the CRL Overlap Period Units and the CRL Overlap Period, run the following commands from an administrative command prompt: Certutil -setreg CA\CRLOverlapPeriodUnits 12 Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. Certutil -setreg CA\CRLOverlapPeriod "Hours" Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. To define the Validity Period Units for all certificates issued by this CA, type following command and then press Enter. In this lab, the Enterprise Issuing CA should receive a 10 year lifetime for its CA certificate. To configure this, run the following commands from an administrative command prompt: Certutil -setreg CA\ValidityPeriodUnits 10 Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. Certutil -setreg CA\ValidityPeriod "Years" Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. Note: You can confirm all these 8 settings that you have just set on the Standalone Offline Root CA, by using CertUtil -getreg (and query the appropriate setting, for example Certutil -getreg CA\CRLPeriod), or simply browse the registry using RegEdit to the following address. HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CertSvc\Configuration\windows noob Root CA You can see those values highlighted in the screenshot below. Can the above all be done with PowerShell ? yup, and i'll add the commands later, check back for that. Step 2. Enable Auditing on the Standalone Offline Root CA Note: You cannot configure these setting via Group Policy as the Standalone Offline Root CA should not be connected to any Domain and is Offline (disconnected from the network). Auditing is the ability to log successful or failed attempts when performing certain actions, and as the Standalone Offline Root CA is an important security resource, you want to enable auditing. To enable auditing on the Standalone Offline Root CA click start, select Administrative Tools, and then select Local Security Policy. Expand Local Policies and then select Audit Policy. Double click Audit Object Access and then select Success and Failure then click OK (2). After configuring this, you'll see the following. To enable auditing for the CA you can select which group of events to audit in the Certificate Authority MMC snap-in or by configuring the AuditFilter registry key setting. To configure Auditing for all CA related events, run the following command from an administrative command prompt: Certutil -setreg CA\AuditFilter 127 Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. Step 3. Configure the AIA There are multiple different methods for configuring the Authority Information Access (AIA) and certificate revocation list distribution point (CDP) locations. You can use the user interface (in the Properties of the CA object), the certutil command, or directly edit the registry. The Authority Information Access (AIA) is used to point to the public key for the certification authority (CA). To configure the Authority Information Access (AIA) using certutil to set the following three locations on the Standalone Offline Root CA: Static file system LDAP (lightweight directory access path) HTTP Note: Edit the command below to use your public facing HTTP web server address, I'm using http://pki.windows-noob.com, you should use your own address. Open an administrative command prompt and do as follows: certutil -setreg CA\CACertPublicationURLs "1:C:\Windows\system32\CertSrv\CertEnroll\%1_%3%4.crt\n2:ldap:///CN=%7,CN=AIA,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,%6%11\n2:http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/%1_%3%4.crt" Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. To confirm the output you can issue the following command: certutil -getreg CA\CACertPublicationURLs Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. If you look in the registry, under the following path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\CertSvc\Configuration\windows noob RootCA, you can confirm the CACertPublicationURLs by opening that REG_MULTI_SZ value. You should see the following: 1:C:\Windows\system32\CertSrv\CertEnroll\%1_%3%4.crt 2:ldap:///CN=%7,CN=AIA,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,%6%11 2:http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/%1_%3%4.crt as shown in the screenshot below. You can also see this in the the Certification Authority console (certsrv) . To open the console, click Start, click Administrative Tools, and then click Certification Authority. In the navigation pane, expand the Certificate Authority (Local). Right-click windows noob Root CA and then click Properties. On the Extensions tab, under Select extension, click Authority Information Access (AIA) and you will see the graphical representation of the AIA settings that you've just configured using certutil. In the above step, you have used the following three different methods to confirm the specified settings. certutil registry certsrv.msc Step 4. Configure the CDP The CDP is where the certificate revocation list is maintained, which allows client computers to determine if a certificate has been revoked. To configure the Certificate revocation list Distribution Point (CDP) using certutil to set the following four locations on the Standalone Offline Root CA: Static file system LDAP (lightweight directory access path) HTTP File system The file system location (4th option) that you will set will allow the CRL to be copied over the network to the web server (webserver), which is why we earlier allowed the Cert Publishers group access to the share and folder. All CAs are members of the Cert Publishers group, so we effectively allowed all CAs to copy to the CertEnroll folder on the webserver computer. You may wish to grant a specific group rights to access this share instead, it's up to you. Note: Edit the command below to use your public facing HTTP web server address, I'm using http://pki.windows-noob.com, you should use your own address. certutil -setreg CA\CRLPublicationURLs "1:C:\Windows\system32\CertSrv\CertEnroll\%3%8%9.crl\n10:ldap:///CN=%7%8,CN=%2,CN=CDP,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,%6%10\n2:http://pki.windows-noob.com/CertEnroll/%3%8%9.crl" Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. After you run that command, run the following certutil command to verify your settings: certutil -getreg CA\CRLPublicationURLs Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. You can also verify it in the following registry location: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CertSvc\Configuration\windows noob Root CA and in CertSrv.msc Step 5. restart the CertSvc service On the Standalone Offline Root CA, open an Administrative command prompt and type PowerShell. In the PowerShell command prompt issue the following command: Restart-Service certsvc Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. Step 6. Publish the CRL On the Standalone Offline Root CA, open an Administrative command prompt and type PowerShell. In the PowerShell command prompt issue the following command: certutil -crl Press Enter. The output of the above command is shown below. That's it for this part, please continue to Part 5 where you will Install the Enterprise Issuing CA. Recommended reading (1) - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/certutil (2) - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-server-2003/cc776774(v=ws.10)
-
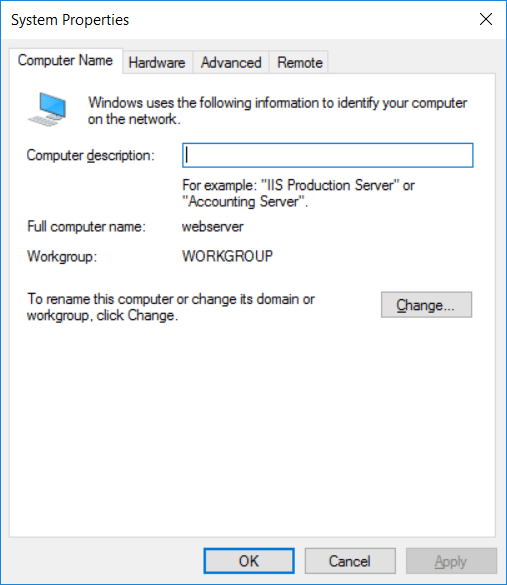
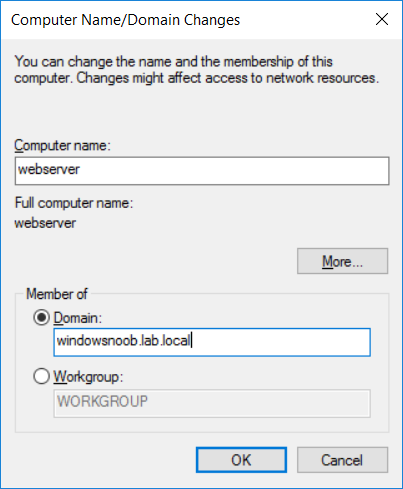
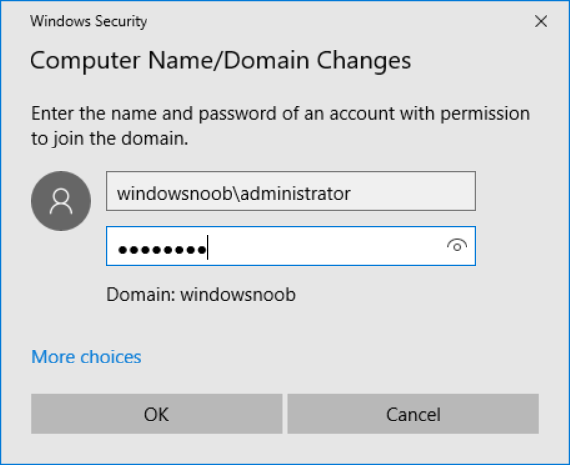
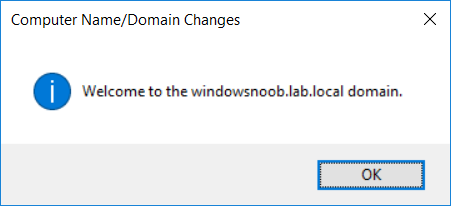
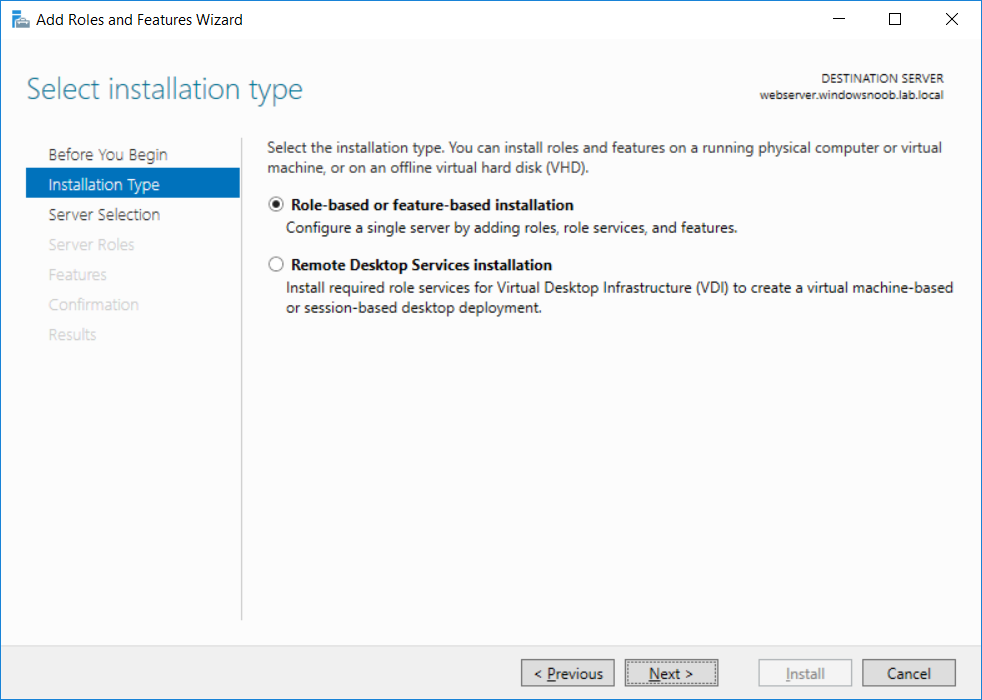
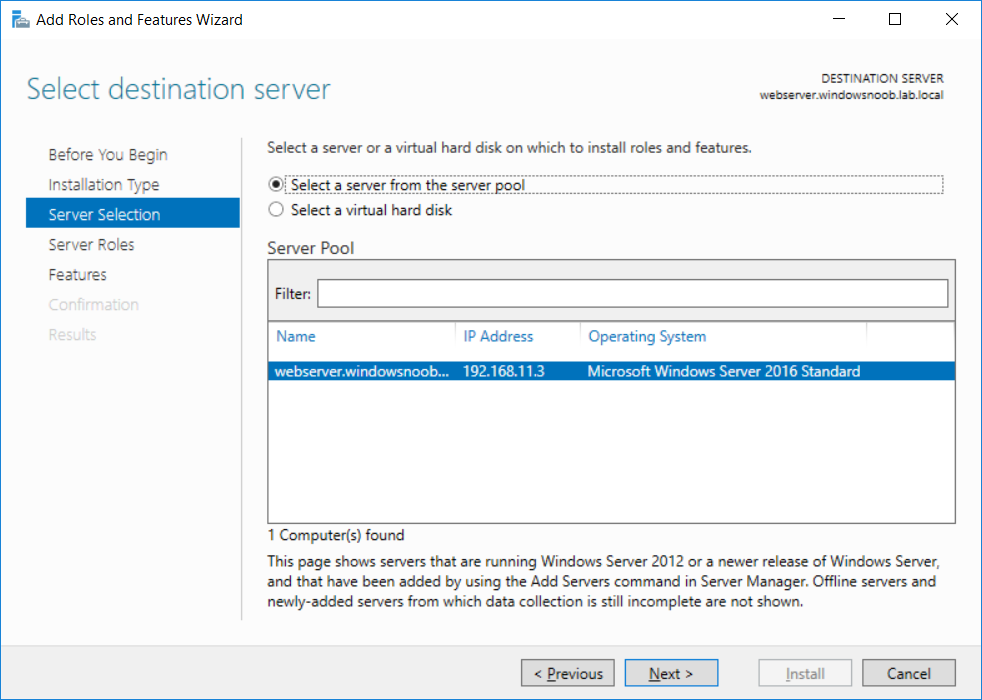
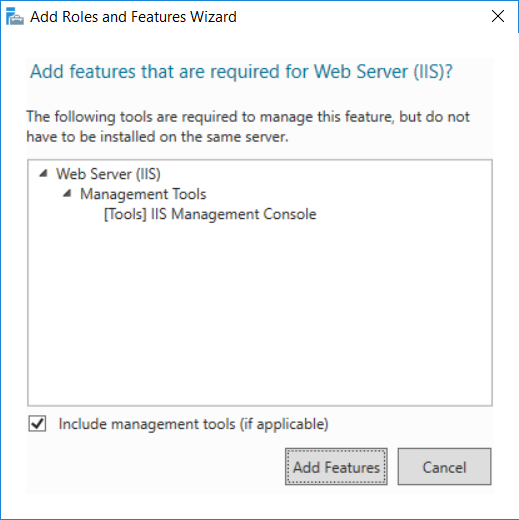
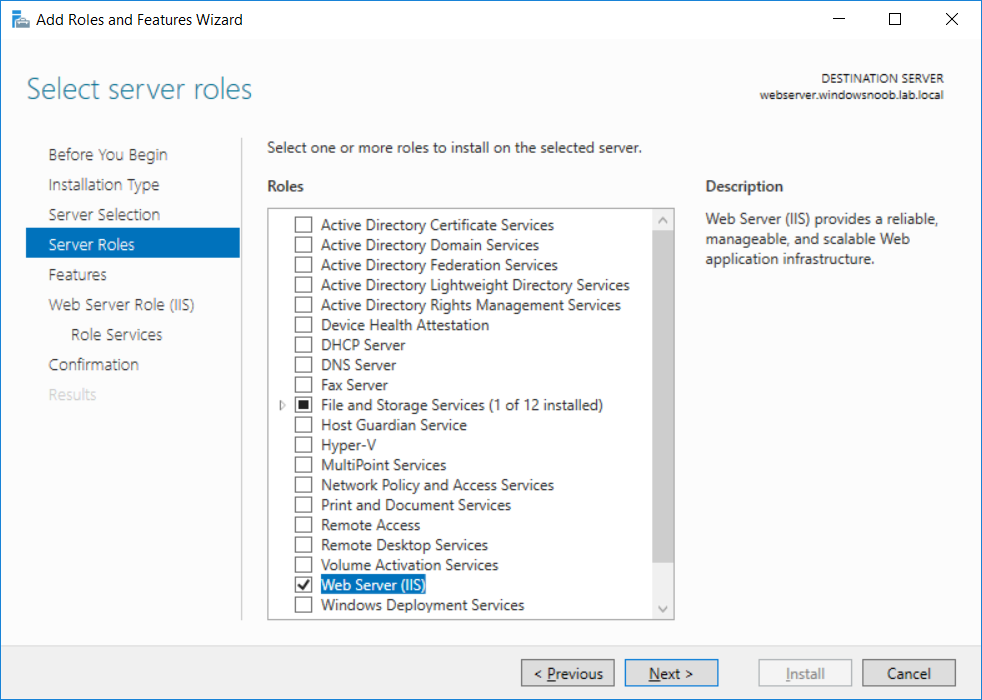
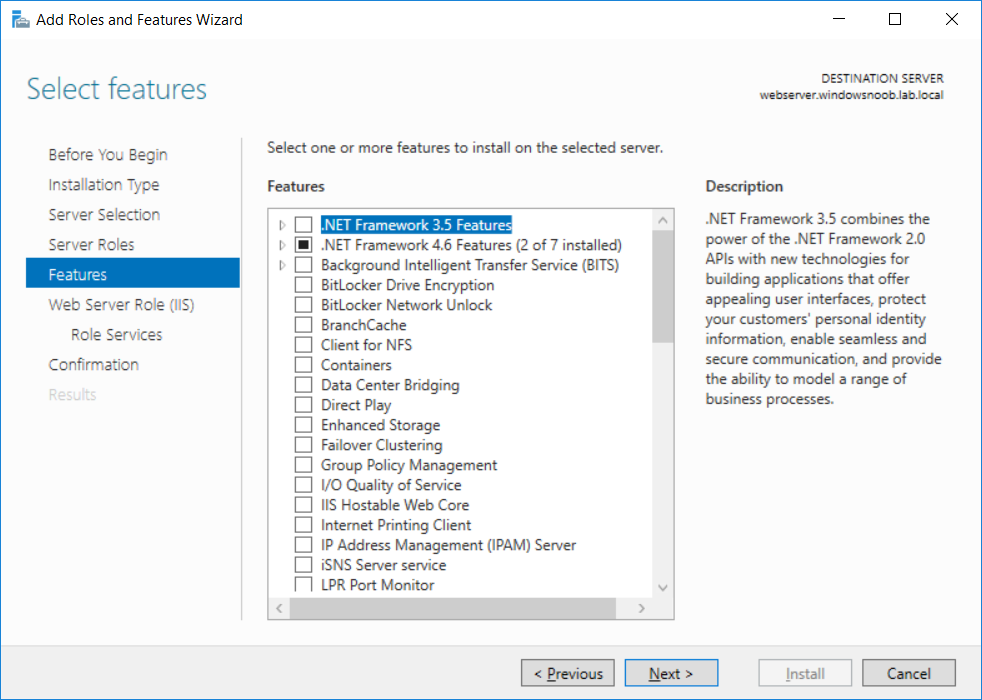
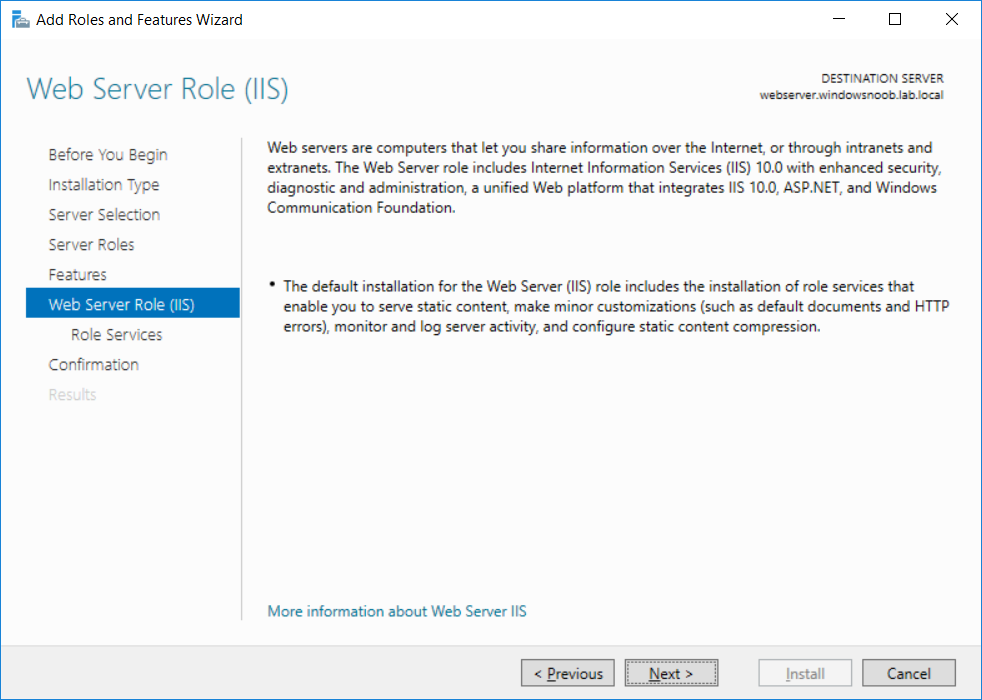
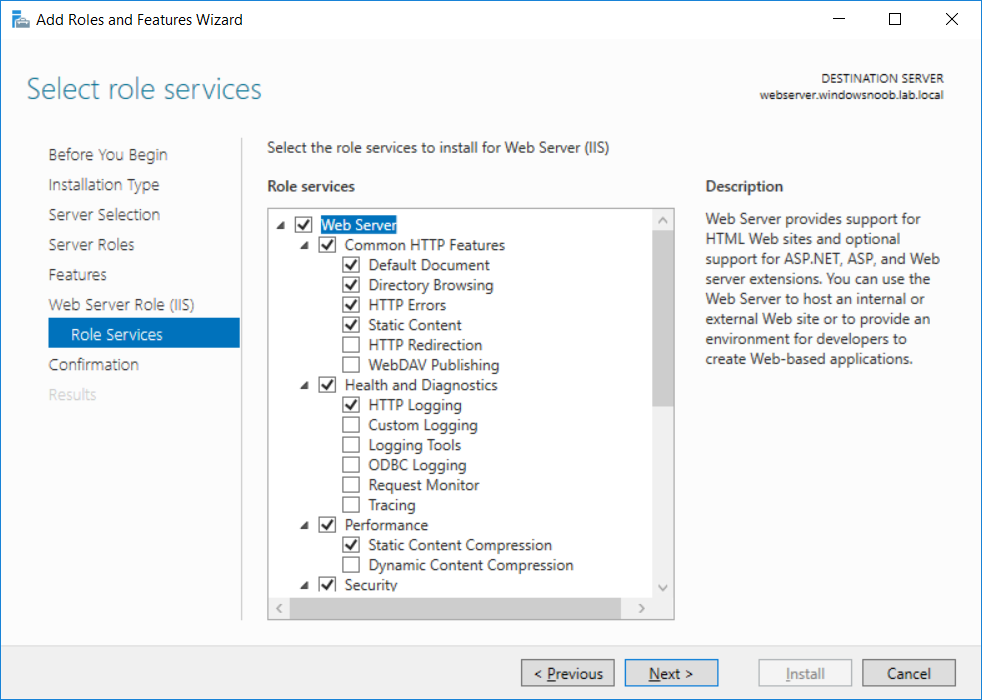
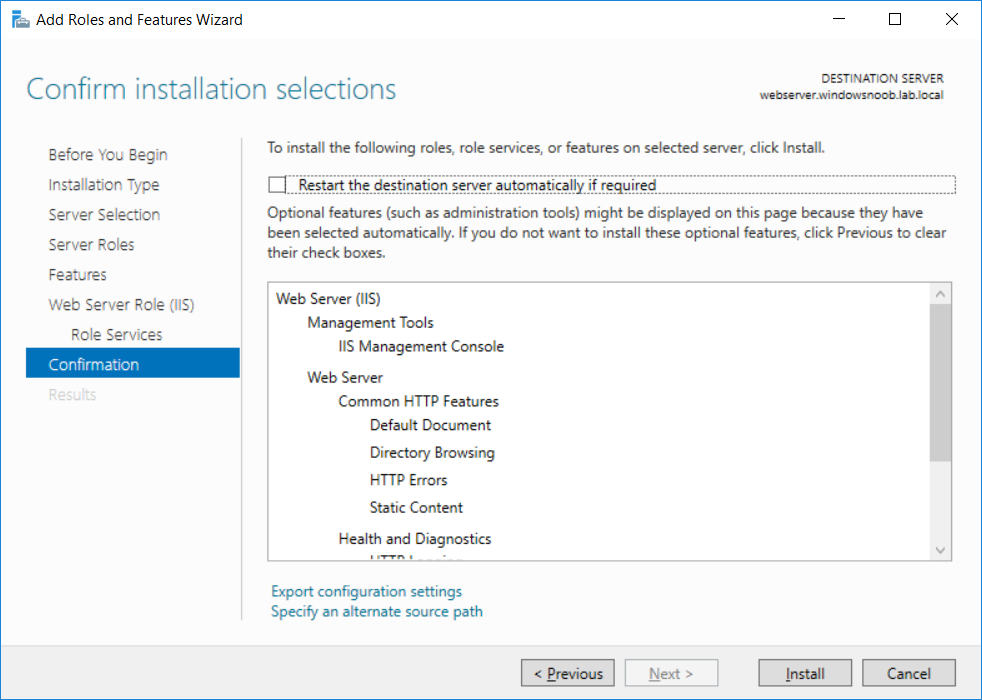
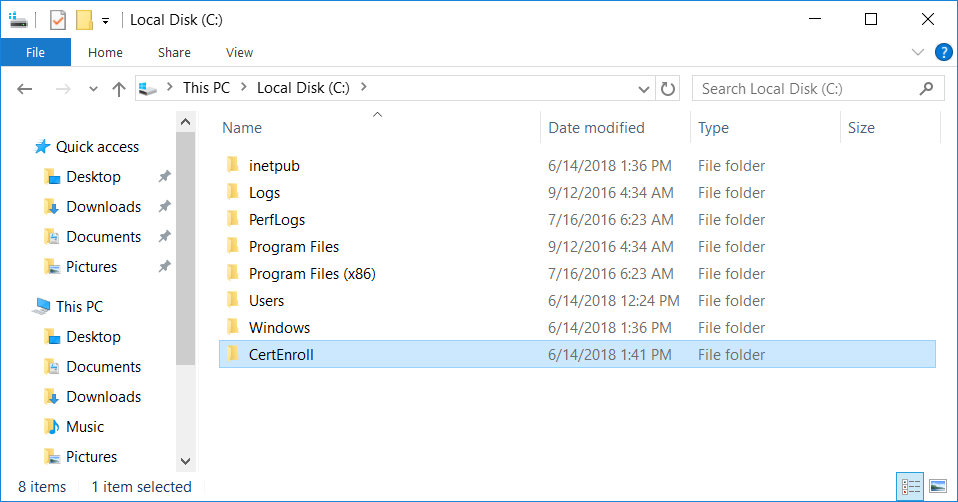
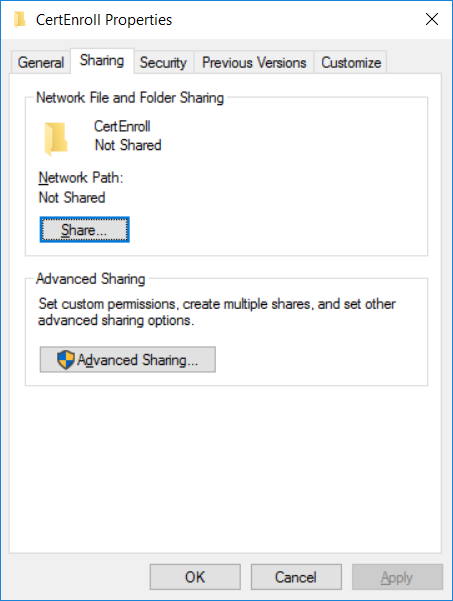
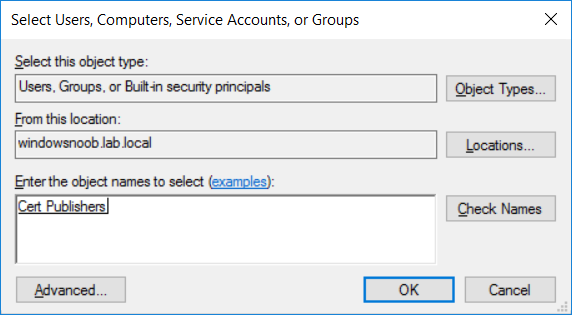
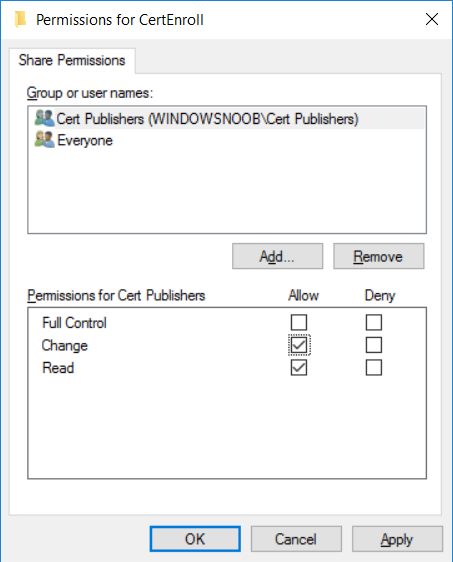
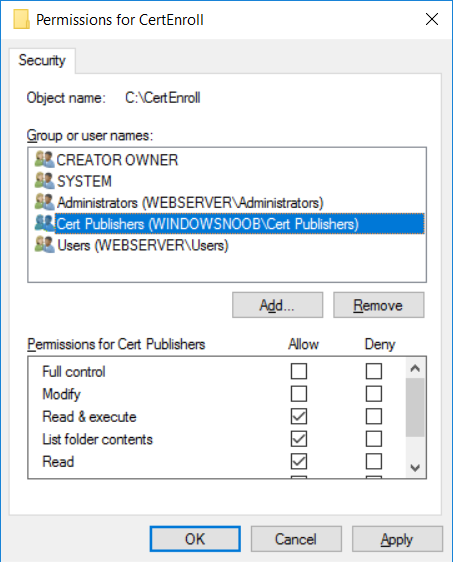
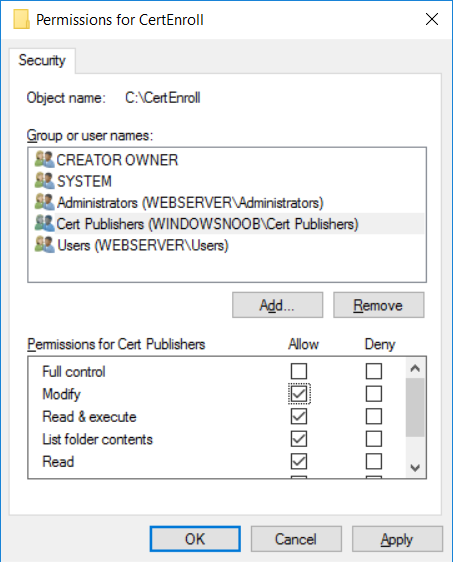
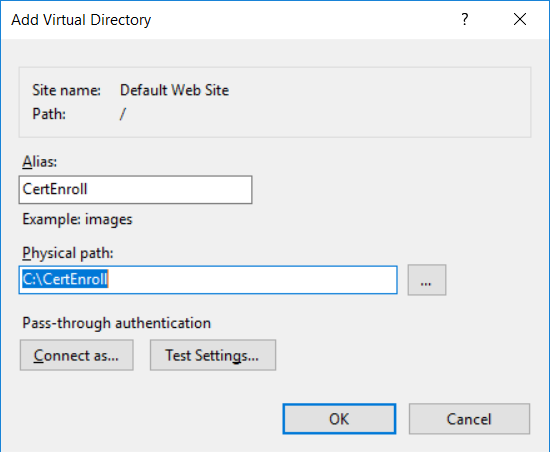
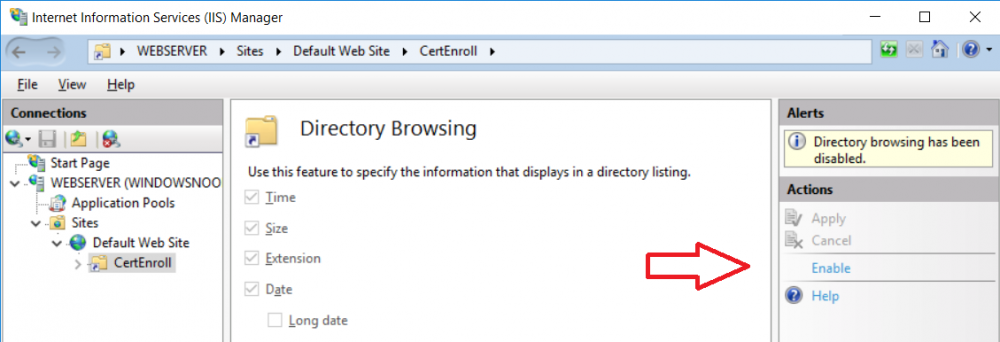
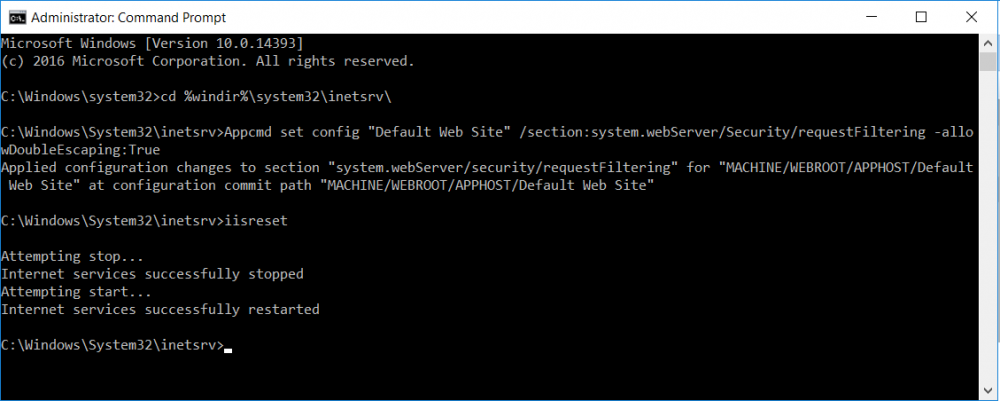
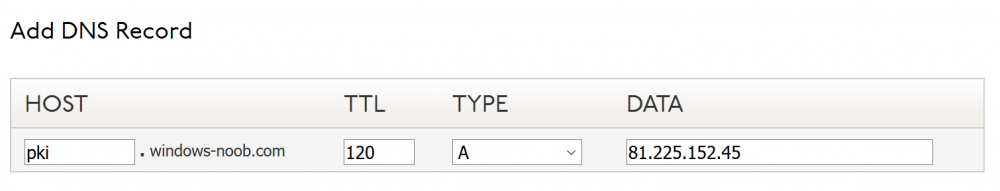
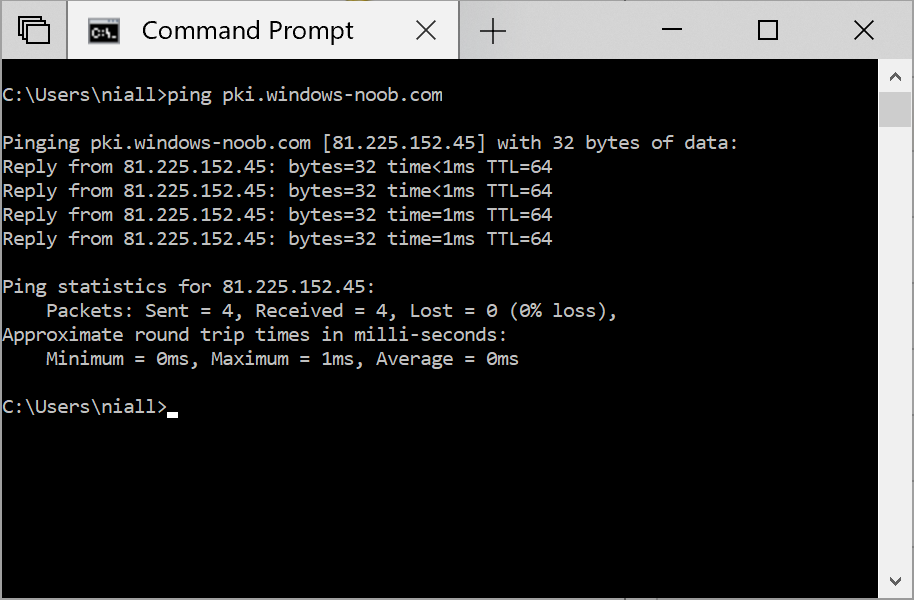
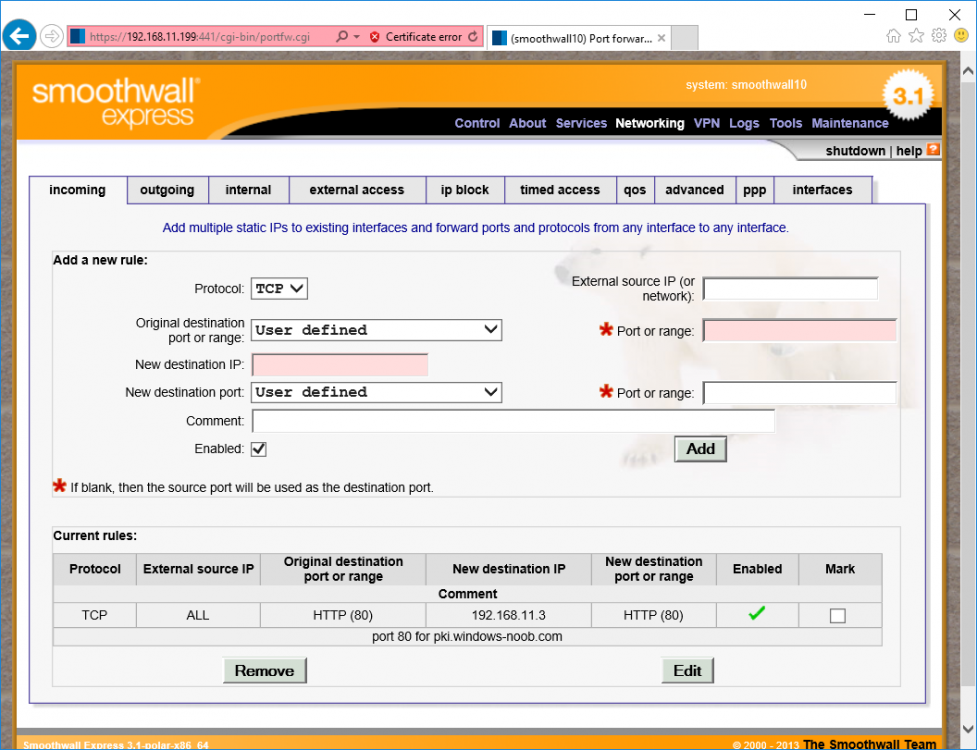
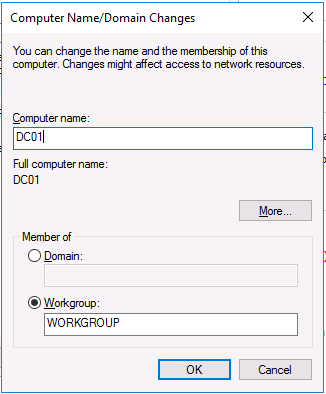
This series is comprised of different parts, listed below. Part 1 - Introduction and server setup Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication (this part) Part 4 - Post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 5 - Installing the Enterprise Issuing CA Part 6 - Perform post installation tasks on the Issuing CA Part 7 - Install and configure the OCSP Responder role service Part 8 - Configure AutoEnroll and Verify PKI health In part 1 of this series, you configured your LAB for a 2 tier PKI hierarchy running on Windows Server 2016. You used PowerShell to create some virtual machines, and then installed Windows Server 2016, Windows 10 Enterprise version 1803 and optionally Smoothwall 3.1 before configuring the IP address scheme and Computer Names on the virtual machines. Finally you configured ADDS on DC01 so that you have a working Domain Controller for the rest of this LAB. In part 2 you installed and did the initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA. In this part you will prepare the HTTP Web Server for CDP and AIA Publication. But before you get started with that, please have a read below of what a CDP and AIA actually are. What is a CDP ? A CDP (CRL Distribution Point) is an extension that contains links to the CRL of the issuer of the certificate which is being verified (1). What is an AIA ? An AIA (Authority Information Access) is an extension that contains links to the certificate of the issuer of the certificate which is being verified. Step 1. Join the web server computer to the domain When you installed the web server virtual machine (#11_Webserver) in part 1, it was workgroup joined. To join the domain do as follows. Logon to the web server virtual machine as Administrator. In Windows File Explorer, right click on This PC and choose Properties. Click on Change Settings beside Computer name, domain and workgroup settings. In the System Properties screen, click on Change. In the Member of field select Domain and enter the domain name you configured in part 1. enter credentials required for Domain join membership (eg: windowsnoob\administrator) click OK and click OK again when prompted with the welcome click OK Click OK, click Close then click Restart Now. After the reboot login to the domain as windowsnoob\administrator Alternatively, to join the domain automatically, use the joindomain.ps1 PowerShell script which you can download from here. JoinDomain.ps1 1. Copy the script to C:\Scripts on the webserver. 2. Edit the variables (lines 16-18) as desired before running. 3. Start Windows PowerShell ISE as Administrator and run the script by clicking on the green triangle. Step 2. Install the Web Server (IIS) Role Logon to the web server as windowsnoob\administrator and open Server Manager, select Add Roles and Features. In the wizard that appears click Next. Click Next and select Role-based or feature-based installation. Click Next and Select Select a server from the server pool, ensure that webserver.windowsnoob.lab.local is selected. Click Next and select Web Server(IIS) from the choices available on the Select server roles page, if prompted to Add features that are required for Active Directory Certificate Services, click Add features. Here you can see the Web Server (IIS) role selected. On Select features click Next. In the introduction to Web Server (IIS) screen, select Next. Accept the defaults and click Next. on the Confirm Installation Selections screen click Install. Click Close when the installation succeeds. Step 3. Create a CertEnroll Folder and grant Share & NTFS Permissions to the Cert Publishers group Create the CertEnroll Folder Now you need to create a shared folder where certificates and delta certificates can be stored from the PKI infrastructure. Open Windows File Explorer and then browse to the C:\ drive, Create a folder called CertEnroll at the root of the drive. Share the CertEnroll folder Right-click on the CertEnroll folder and select Properties. On the CertEnroll Properties page select the Sharing tab to configure share permissions. Click on the Advanced Sharing option and then select Share this folder. Click on Permissions and then click Add, on the Select Users or Groups page, in the Enter the object names to select, type windowsnoob\Cert Publishers and then click OK. On Permissions for CertEnroll dialog box, select the Cert Publishers group and then in the Allow column select Change permission. Click OK twice to go back to the CertEnroll Properties page. Edit NTFS permissions on the CertEnroll folder Select the Security tab and click Edit to configure NTFS permissions. On Permissions for CertEnroll page click Add. On the Select Users or Groups page, under the Enter the object names to select, enter windowsnoob\Cert Publishers and then click OK. On the Permissions for CertEnroll page highlight the Cert Publishers group and then under the Allow column select the Modify permission and then click OK. On the Permissions for CertEnroll page, click OK to close the window and click OK again to close CertEnrolls properties page. Step 4. Create a Virtual Directory in IIS Ensure you are logged on to webserver as windowsnoob\Administrator. Click Start, select Administrative Tools and then select Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. In the Connections pane, expand WEBSERVER and then expand Sites. Right-click on Default Web Site and select Add Virtual Directory. On the Add Virtual Directory page, in Alias, type CertEnroll and for Physical path, type C:\Certenroll, and then click OK. In the Connections pane, under the Default Web Site, ensure the CertEnroll virtual directory is selected then in the CertEnroll Home pane, double-click on Directory Browsing. In the Actions pane click Enable. Step 4. Enable Double Escaping on the IIS Server Allowing double escaping makes it possible for the web server to host Delta CRLs. For more information about this see KB Article 942076 (3). Ensure you are logged on to the webserver as windowsnoob\Administrator. Open an Administrative Command Prompt. Then enter the following cd %windir%\system32\inetsrv\ and press ENTER. Type following command and press Enter. Appcmd set config "Default Web Site" /section:system.webServer/Security/requestFiltering -allowDoubleEscaping:True Type the following to restart IIS. iisreset and press ENTER. Step 5. Create a DNS record for externally accessible website address To answer requests for OCSP and CRL, AIA via a publicly available URL, login to your DNS provider and create a new DNS record for your chosen public URL, eg: http://pki.windows-noob.com Note: http://pki.windows-noob.com is a website address that I own and use, and I'm using it in this guide to show you what you need to do, obviously you need to use your own website address, for example http://pki.yourdomain.com. This should point to the IP address of your internet connection that is being shared via the smoothwall. Once it's setup, you can verify pinging the URL Lastly, you need to configure your Smoothwall (or use another method) to port forward port 80 (http) internet requests to the webserver. To do that, login to https://192.168.11.199:441 (the Smoothwall IP address) via the Internet Explorer Web browser on the WebServer. Note that you may have to disable IE enhanced security information temporarily to allow access. Once connected, login as Admin/password, which you defined when you installed the Smoothwall. Below you can see the Port Forward I've configured for port 80 requests. After doing so, anyone can browse to http://pki.windows-noob.com using a web browser which means they'll be able to retrieve CRL's when they are published to http://pki.windows-noob.com/certenroll Join me in part 4 to further configure the Standalone Offline Root CA. Recommended reading (1) - https://www.sysadmins.lv/blog-en/root-certification-authority-ca-cdp-and-aia-extension-question.aspx (2) - https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/nexthop/2012/12/17/updated-creating-a-certificate-revocation-list-distribution-point-for-your-internal-certification-authority/ (3) - http://support.microsoft.com/kb/942076
-
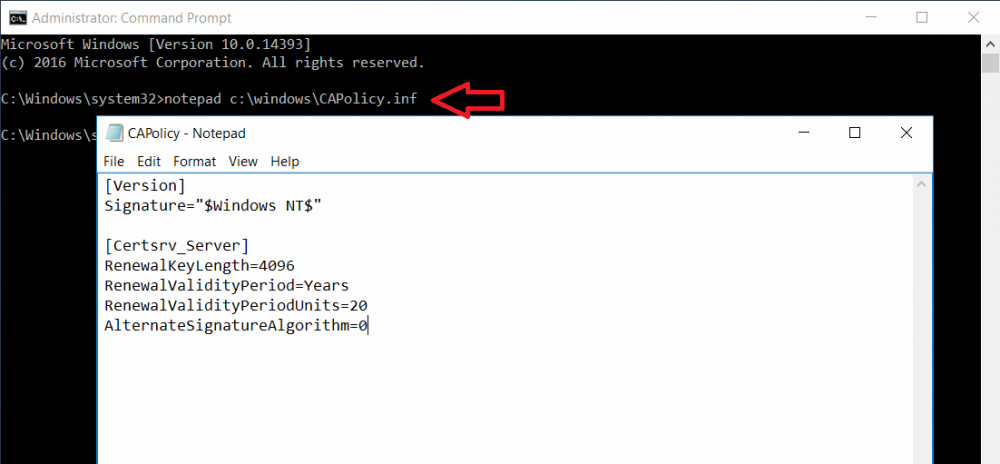
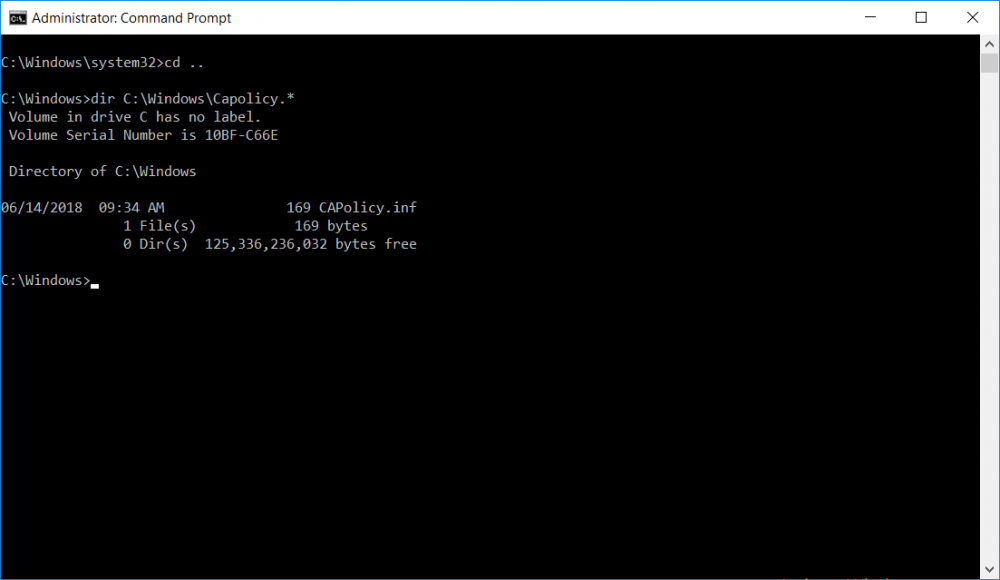
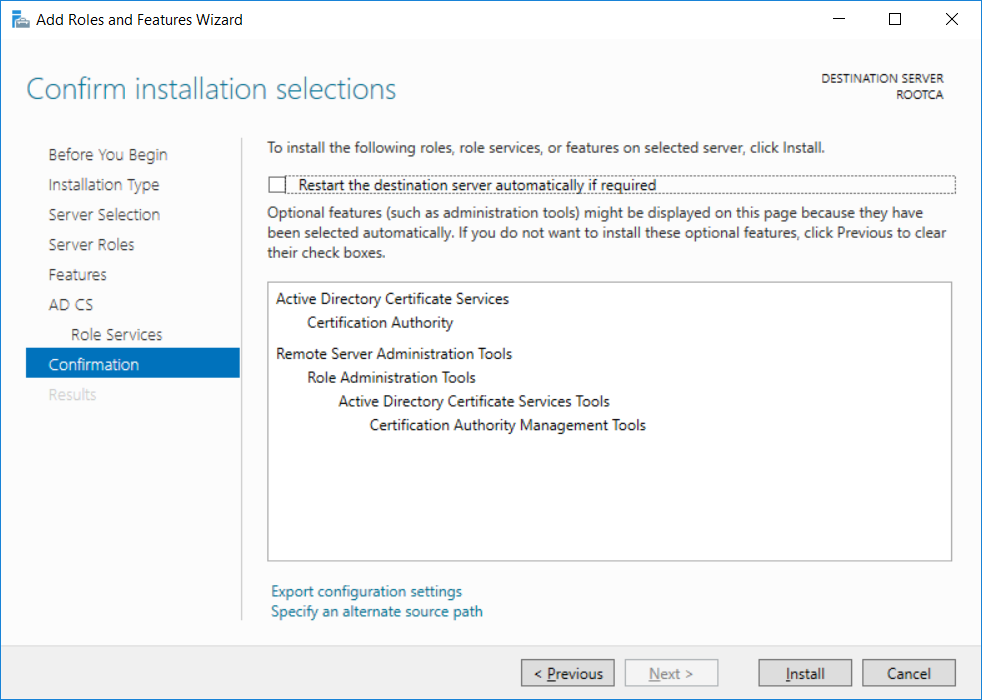
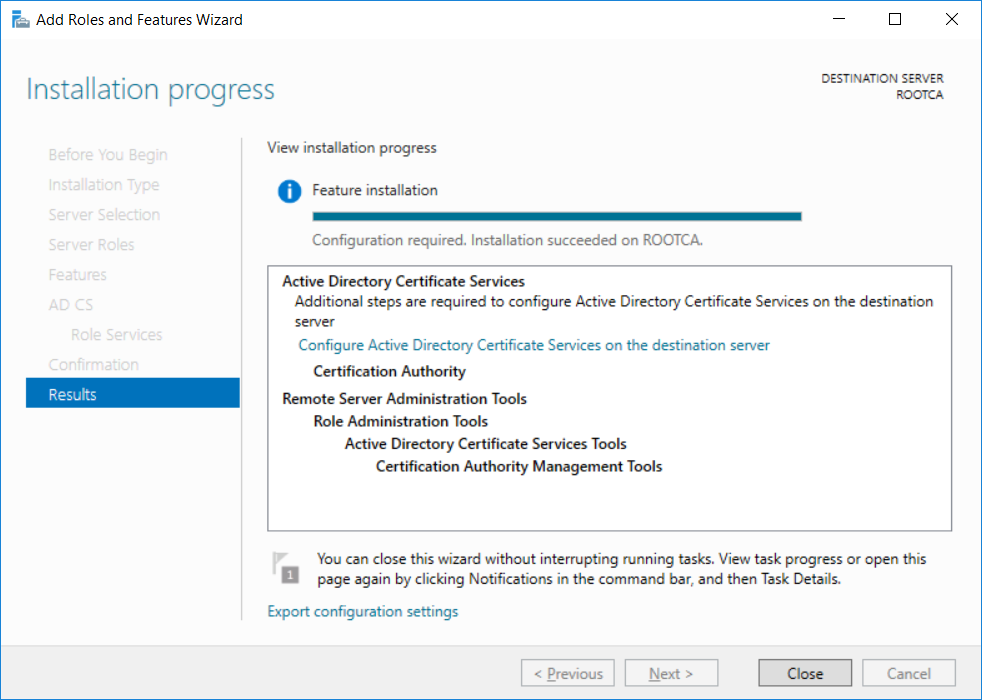
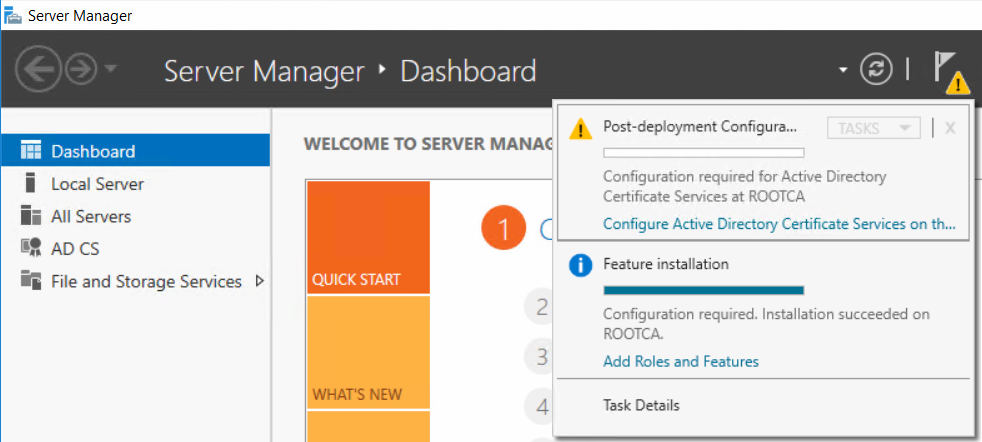
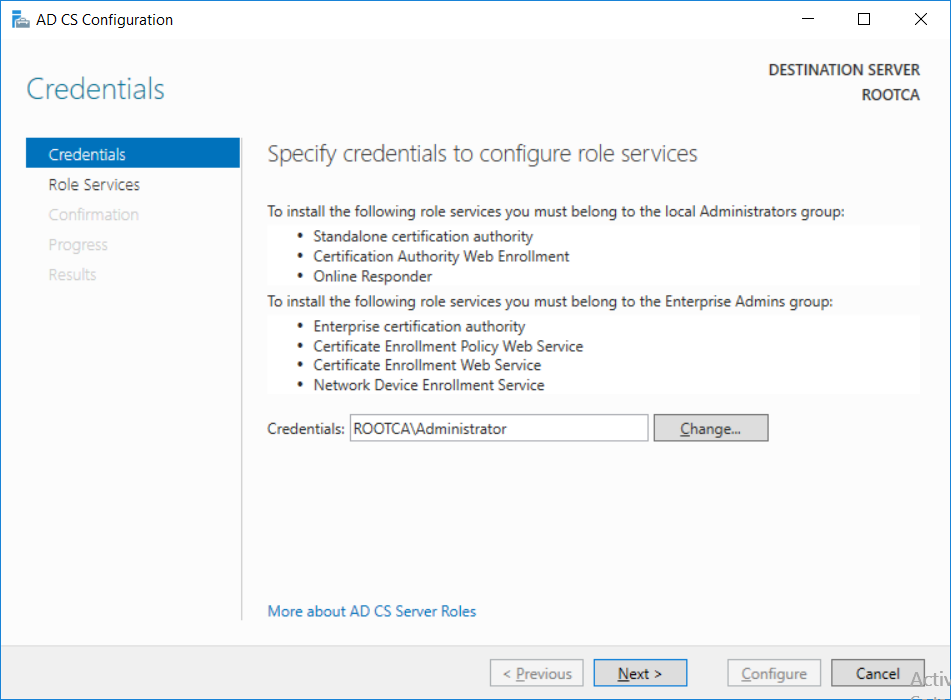
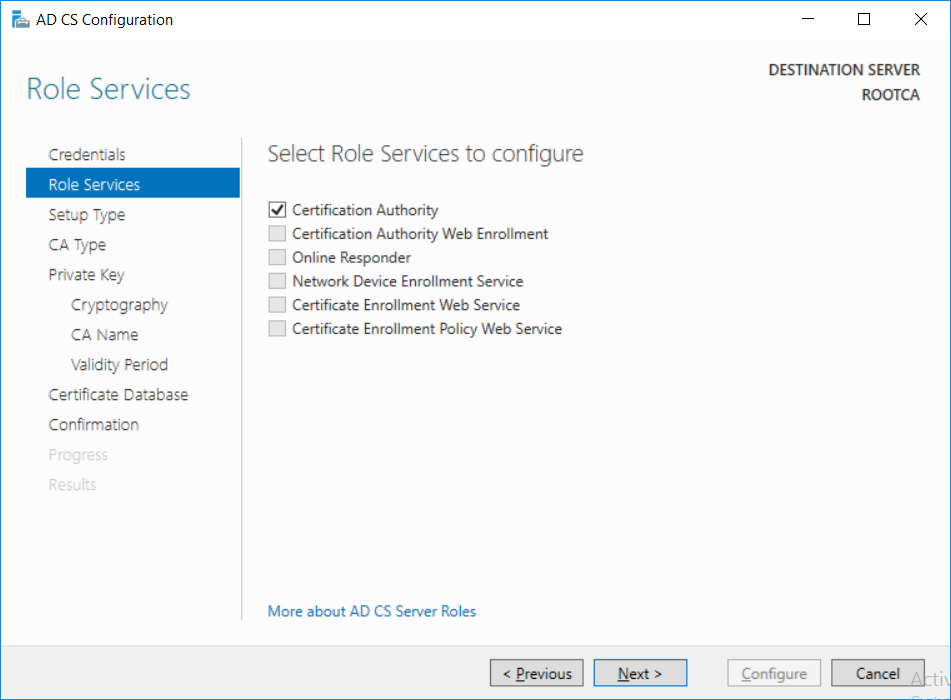
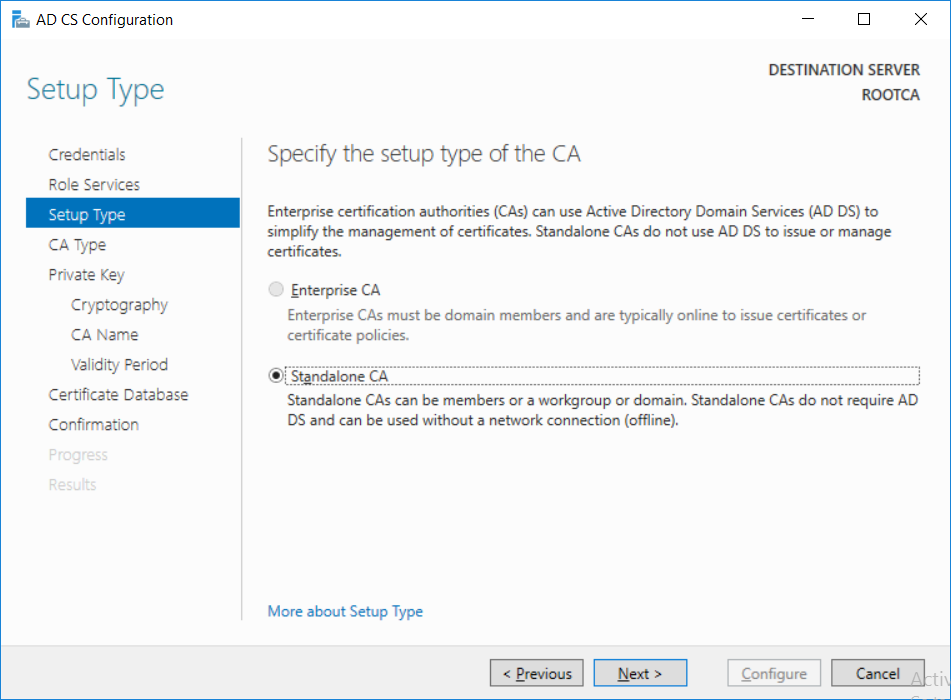
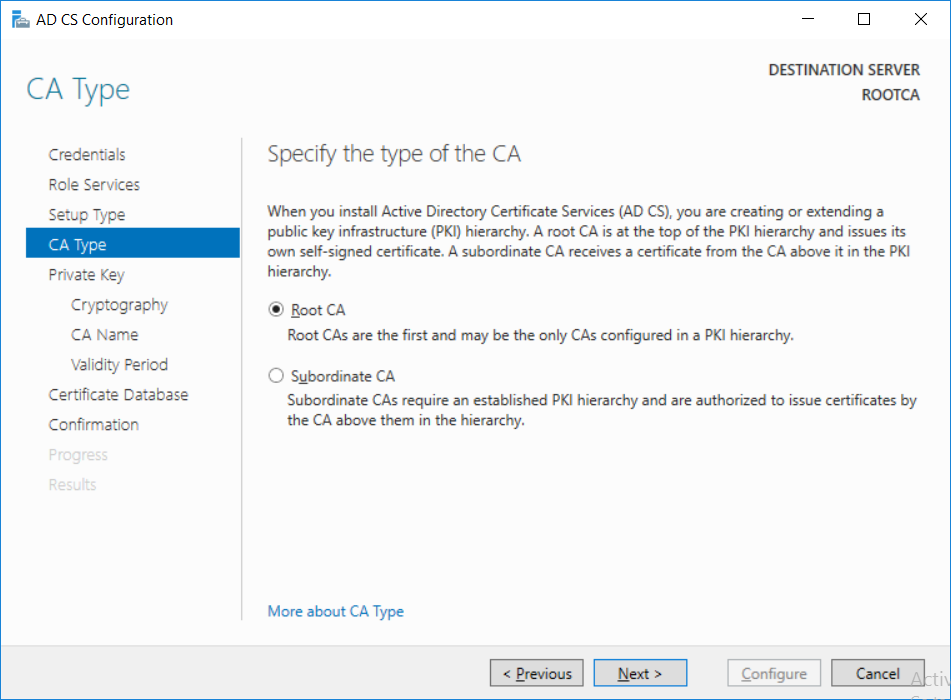
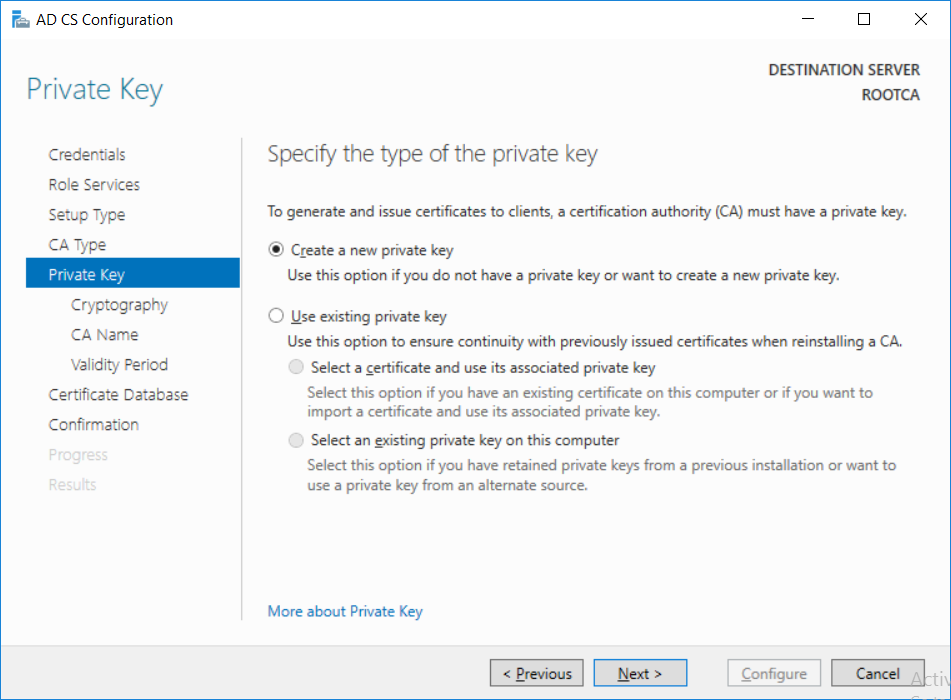
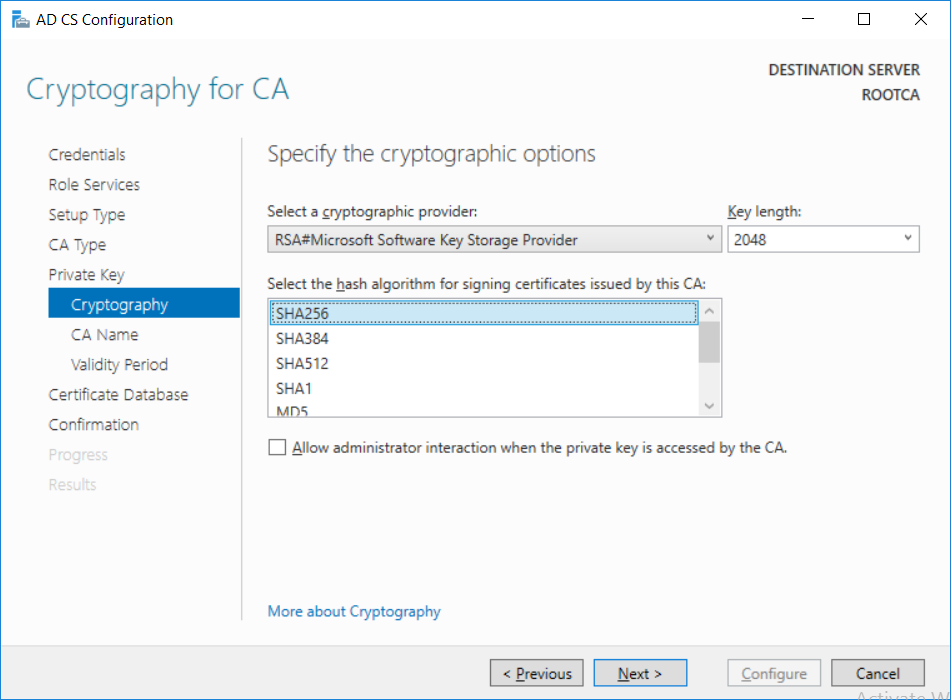
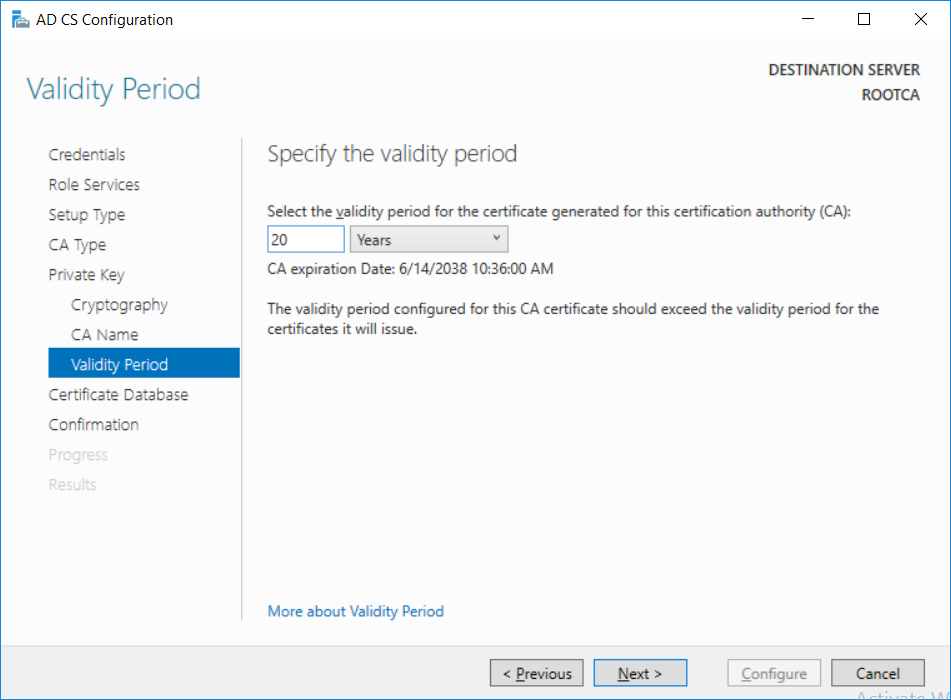
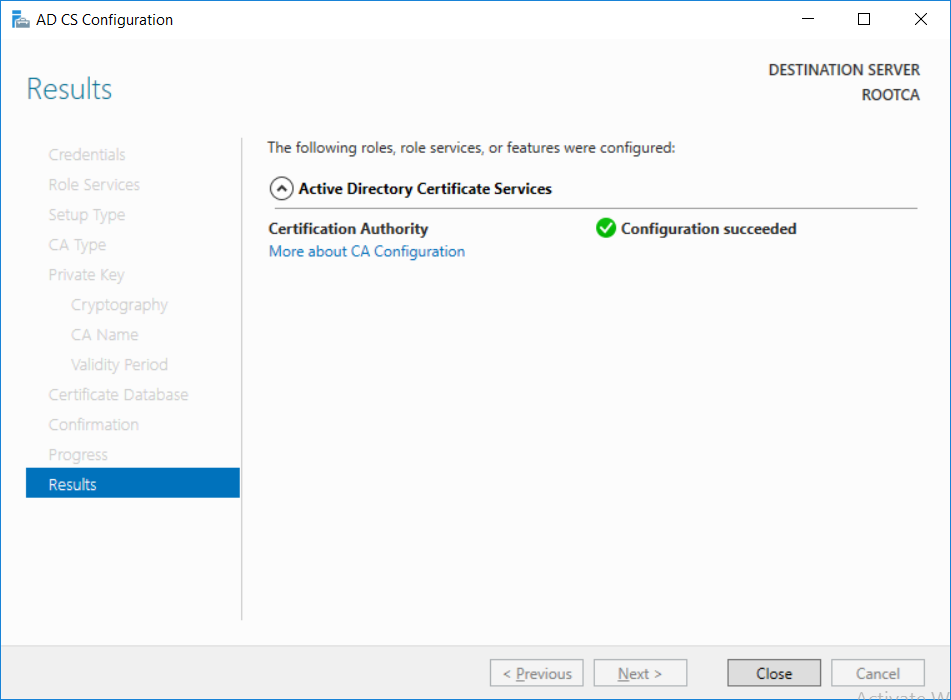
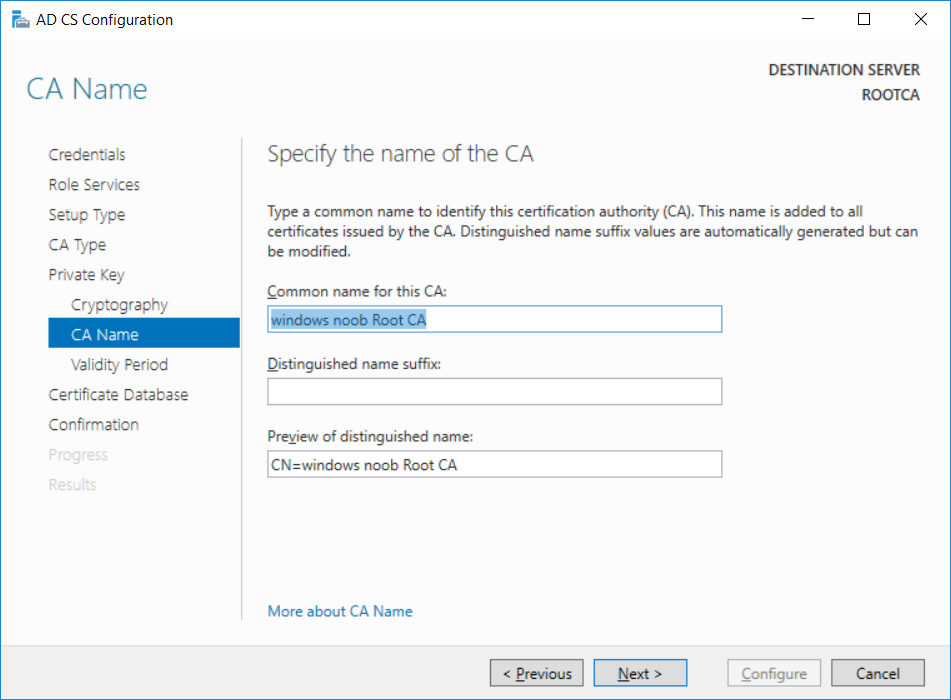
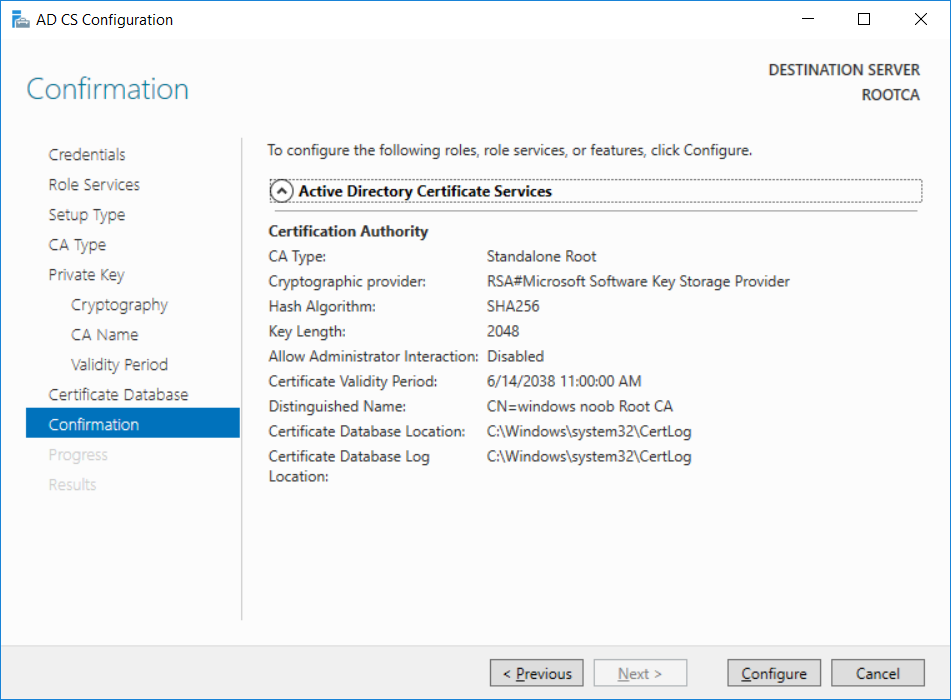
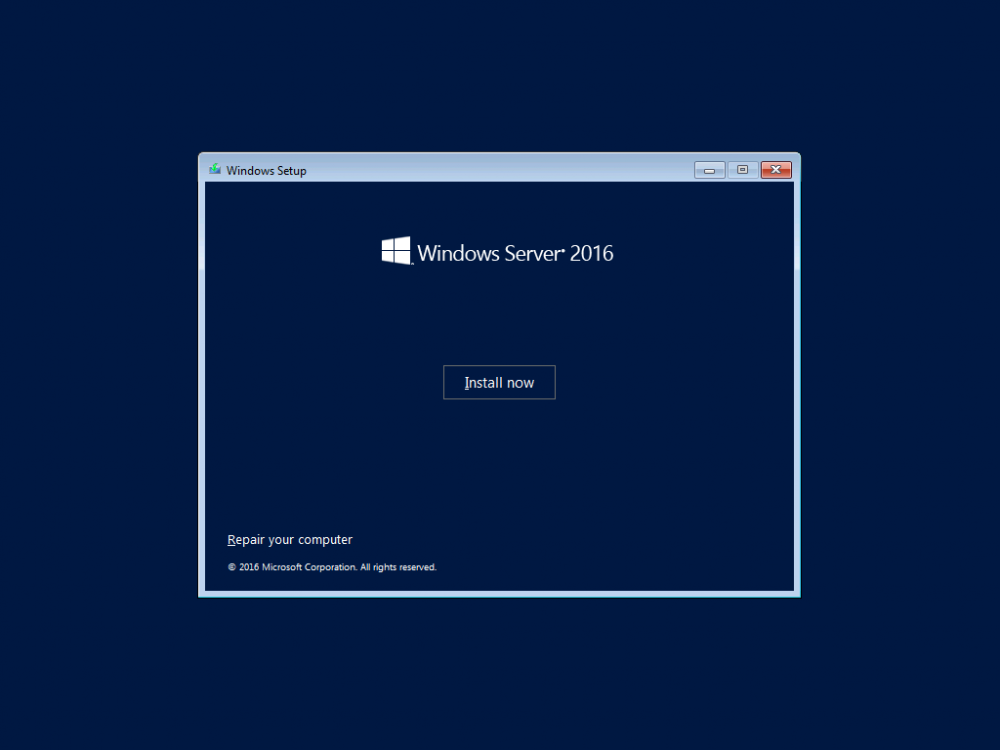
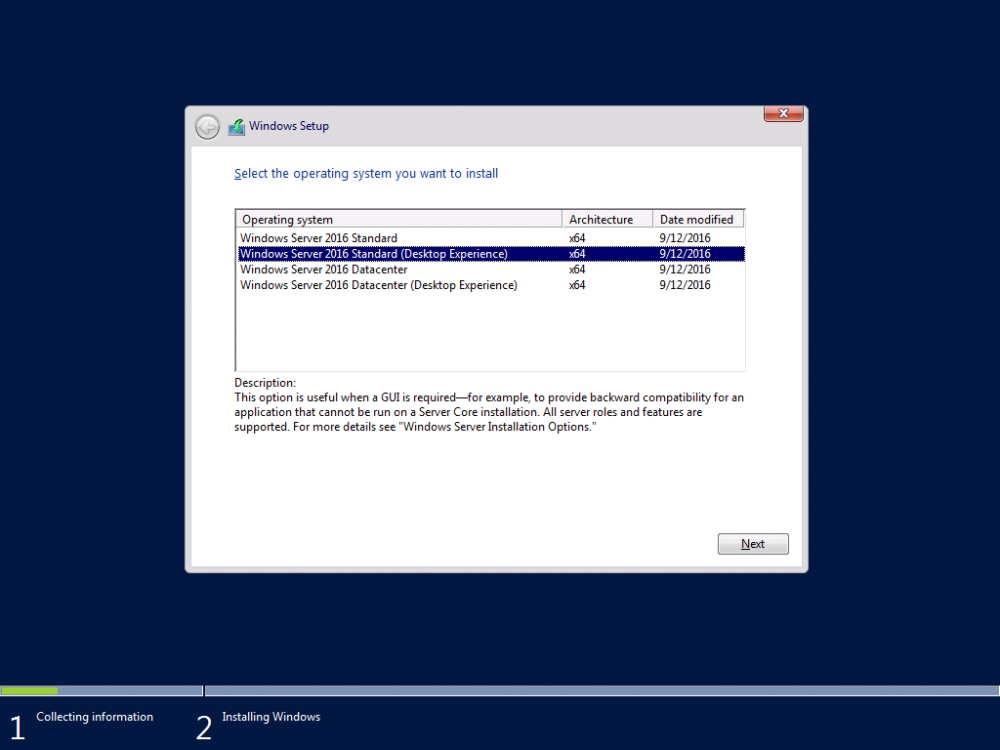
This series is comprised of different parts, listed below. Part 1 - Introduction and server setup Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA (this part) Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication Part 4 - Post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 5 - Installing the Enterprise Issuing CA Part 6 - Perform post installation tasks on the Issuing CA Part 7 - Install and configure the OCSP Responder role service Part 8 - Configure AutoEnroll and Verify PKI health In part 1 of this series, you configured your LAB for a 2 tier PKI hierarchy running on Windows Server 2016. You used PowerShell to create some virtual machines, and then installed Windows Server 2016, Windows 10 Enterprise version 1803 and optionally Smoothwall 3.1 before configuring the IP address scheme and Computer Names on the virtual machines. Finally you configured ADDS on DC01 so that you have a working Domain Controller for the rest of this LAB. In this part you'll install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA. What is a Standalone Offline Root CA ? If you've never dealt with PKI before you are probably wondering what a Standalone Offline Root CA is and why do you need it. I'll quote the following paragraph from the excellently written article about a Standalone Offline Root CA here. If you don't read the article itself, at least read the Quote below. To cut a long story short, you should use a Standalone Offline Root CA because it lowers the possibility of compromise and ensures reliability of your Certificate Authority infrastructure. Step 1. Create a CAPolicy.inf file Before installing the Standalone Offline Root CA, you should create a CAPolicy.inf to define 'default' settings for CA templates, some of these settings cannot be changed later and you want them in place before creating any certificates on the Standalone Offline Root CA. So now that you know that you should create the file as a first step, let's go and do that. On the #11_RootCA virtual machine (RootCA), login as Administrator using the password specified. Open an administrative command prompt and type the following: notepad C:\Windows\CAPolicy.inf and press ENTER, when prompted to create new file, click Yes. Paste in the following text into the new CAPolicy.inf file. [Version] Signature="$Windows NT$" [Certsrv_Server] RenewalKeyLength=4096 RenewalValidityPeriod=Years RenewalValidityPeriodUnits=20 AlternateSignatureAlgorithm=0 Once done, save the file. Note: Any misspellings or mistakes will be ignored, so please copy/paste carefully. To understand what these values are, and why you are using them please see the following link, but in a nutshell, you are telling the CA that by default the Root CA should issue certificates that are valid for 20 years, feel free to adjust accordingly if you think it's appropriate but be aware of the consequences (having to re-issue certificates etc.). I'd recommend your verify that the file is indeed correctly named and in the C:\Windows folder. You don't want .TXT appended to it or it will be ignored. To verify, do the following: dir C:\Windows\Capolicy.* The file has the right name and is in the right location. Step 2. Install Active Directory Certificate Services Now that you've created the CAPolicy.inf file you are ready to install Active Directory Certificate Services on the Standalone Offline Root CA. To do so, open Server Manager and select Add Roles and Features. Click Next and select Role-based or feature-based installation. Click Next and Select Select a server from the server pool, ensure that ROOTCA is selected. Click Next and select Active Directory Certificate Services from the choices available on the Select server roles page, if prompted to Add features that are required for Active Directory Certificate Services, click Add features. And here you see the Active Directory Certificate Services role is selected. Click Next to continue. on the Select features screen, click Next. Click Next, On the Active Directory Certificate Services introduction page, read the Things to note before clicking on Next. Insure that Certificate Authority is selected on the Confirmation screen, click on Install. Wait for the installation progress to finish successfully before clicking on Close. Click Close to close the wizard. Step 3. Configure Active Directory Certificate Services After the installation succeeded in the previous step, click on Configure Active Directory Certificate Services on the destination server in Server Manager. On the Specify credentials to configure role services screen, ensure your credentials are ROOTCA\Administrator and then click Next. Select the Certificate Authority role to configure… by default it is not selected. Click Next and select Standalone CA Click Next and on the Specify the type of the CA select Root CA Click Next. On the Specify the type of private key select Create a new private key and click Next. On the Specify the cryptographic options screen pay attention to the settings before clicking Next. For example, ensure that sha-256 is selected as sha-1 is dead (3). The key length defaults to 2048 but only change to 4096 if you are sure it doesn't break communication with your Switches and legacy applications. On the Specify the name for this CA, change Common Name for this CA to suit your needs, for example enter the following windows noob Root CA but do not change the other values. For more info about the CA Name see here (4). Click Next. On the Specify the validity period page, select 20 years instead of the default of 5. Click Next. On the Specify the database locations click Next. On the Confirmation screen review the details and change if necessary or if you are satisfied, click Configure. and you should see Configuration Succeeded. Click Close when done. Configuring the above with PowerShell To configure the above using PowerShell, use the following commands. First install the ADCS role Add-WindowsFeature Adcs-Cert-Authority -IncludeManagementTools Edit as necessary before running the below (which configures the ADCS role). Install-AdcsCertificationAuthority -CAType StandaloneRootCA -CACommonName "windows noob Root CA" -KeyLength 2048 -HashAlgorithm SHA256 -CryptoProviderName "RSA#Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider" -ValidityPeriod Years -ValidityPeriodUnits 20 -Force That's it for this part, in Part 3 you'll configure the Web server for CDP and AIA Publication. Recommended reading (1) - https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/2900.offline-root-certification-authority-ca.aspx (2) - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/networking/core-network-guide/cncg/server-certs/prepare-the-capolicy-inf-file (3) - https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/askpfeplat/2015/03/15/sha-1-deprecation-and-changing-the-root-cas-hash-algorithm/ (4) - http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=218063
-
- common name
- sha-1
-
(and 4 more)
Tagged with:
-
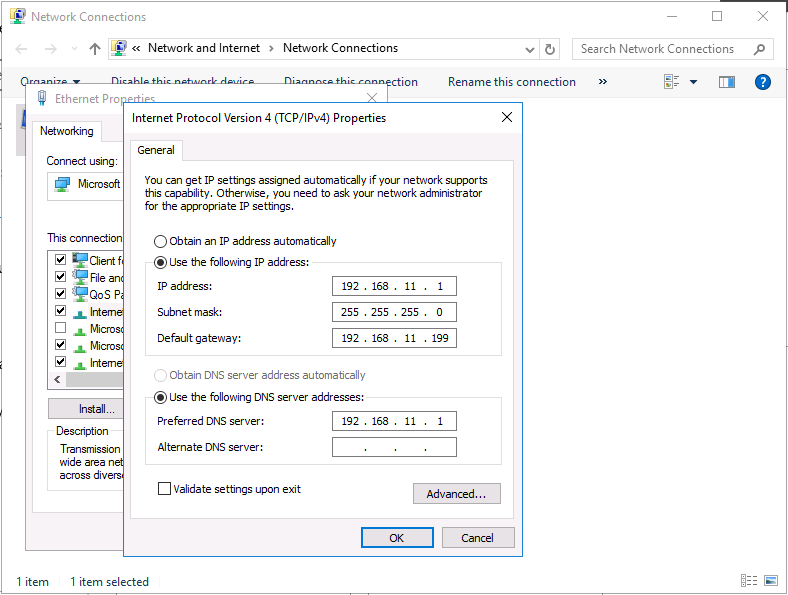
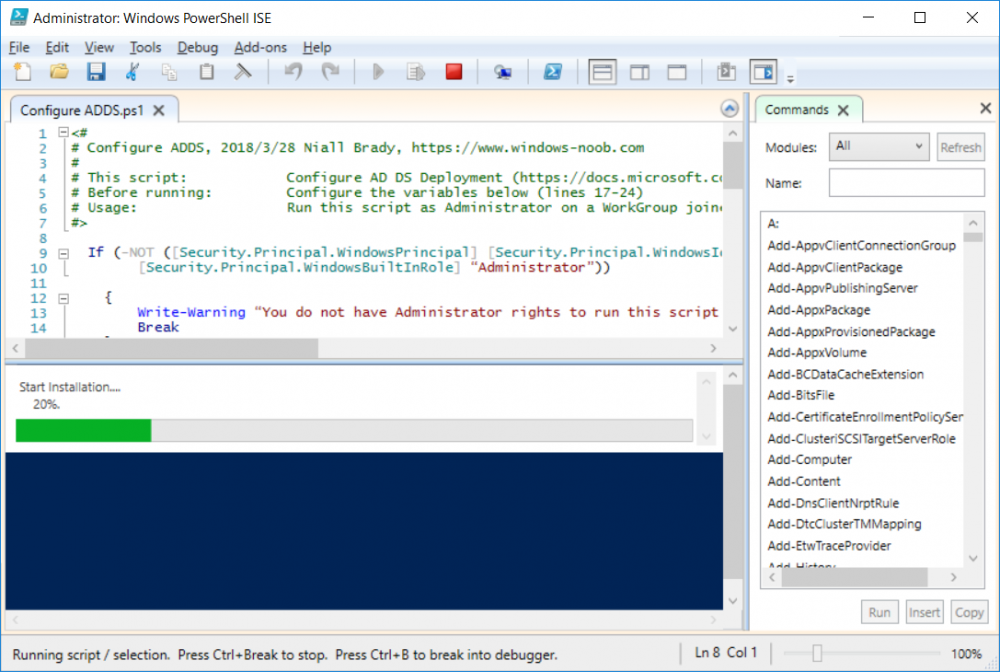
This series is comprised of different parts, listed below. Part 1 - Introduction and server setup (this part) Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication Part 4 - Post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 5 - Installing the Enterprise Issuing CA Part 6 - Perform post installation tasks on the Issuing CA Part 7 - Install and configure the OCSP Responder role service Part 8 - Configure AutoEnroll and Verify PKI health Introduction Security is everywhere, and a core component of security is certificates. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store, and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption (1). In this series of guides I will show you how to set up a 2 tier PKI hierarchy running on Windows Server 2016 and you can use this to set up your own LAB so that you can learn about PKI and later use it for related System Center Configuration Manager roles such as Co-Management (3). Note: I don't claim to be an expert on PKI and would absolutely advise you to consult with a PKI expert if you plan on setting up PKI in production. This guide is designed to help you setup your LAB, it's based on a Windows Server 2012 R2 PKI guide on Technet from here and kudos to those guys for writing it (2). The difference here is you'll be using Windows Server 2016 (or later) and you'll see more screenshots and hints to guide you through the experience. I'd highly recommend you go through this entire series at least twice, just to get a feel for how PKI works and to become familiar with the terms involved. The first time you complete this series will probably feel laborious, however the second time you do it things will start to make sense and you'll have a better understanding of why you are doing it. This series will be tough to wrap your head around especially if you are new to PKI, but take it one part at a time, one step at a time, methodically. If in any doubt, about any of the content then please ask your questions here by starting a new thread. Please note, Microsoft released a new updated PKI guide of their own, here June 2025. By the end of this series of guides you'll have the following setup and running in your windowsnoob.lab.local PKI LAB. Domain Controller (Windows Server 2016) - 192.168.11.1 Issuing CA (Windows Server 2016) - 192.168.11.2 Webserver (Windows Server 2016) - 192.168.11.3 Offline Root CA (Windows Server 2016) Windows 10 (Windows 10 Enterprise, version 1803) - 192.168.11.4 (Optional) Smoothwall NAT (linux) - 192.168.11.199 and MMC based applications like this screenshot from the Enterprise Issuing CA will become familiar to you Before we start the series let's list some of the terms you'll see popping up over and over. I will try to explain them as we move through the guide. PKI - Public Key Infrastructure AIA - Authority Information Access CDP - Certificate revocation list Distribution Point CRL - Certificate Revocation List OCSP - Online certificate status protocol CA - Certificate Authority Note: I'd recommend that you snapshot (checkpoint) the Virtual Machines at the end of each part of this series, so if you make a mistake, you can always back track to a known good state. Step 1. Create the Virtual Machines I use Hyper-V for my labs, as it's a role built into Windows Server 2016 (and even Windows 10), so as long as your computer is relatively new and the hardware supports virtualization, you can use it (simply enable the role, reboot, and start using it). You should have at least 16GB of ram and 500GB of SSD storage to set this lab up comfortably. To quickly create the virtual machines I use a PowerShell script which I wrote, you can download it here. Download the script - Create HyperV VMv2.ps1 Virtual Machine Names For this LAB, please use the following naming convention for your virtual machines (note this is not the computer name but the virtual machine name). #11_DC01 #11_IssuingCA #11_RootCA #11_W10_1803 #11_Webserver #11_Smoothwall Note: The #11 prefix is simply a method I use in Hyper-V to separate my labs visually in Hyper-v manager, so #11 is one lab, and #10 is another (and so on). You don't have to use the same convention as I do, but it would make it easier for you to follow the entire series. I use the Smoothwall linux based NAT to provide Port Forwarding capability and to share internet into my various LABs. Virtual Machine Roles The Virtual Machines created will have the following functions #11_DC01 Roles: DC, DNS, LDAP CDP,AIA #11_IssuingCA Roles: Enterprise Issuing CA #11_RootCA Roles: Standalone Offline Root CA #11_W10_1803 Roles: A Windows client #11_Webserver Roles: Webserver HTTP CDP, AIA #11_Smoothwall Roles: Port Forward, Internet sharing Note: When prompted for a network switch, create a unique one (#11) for the first VM created, and use the same one for each of the other vm's (we will remove the network from the Offline Root CA). For generation type, use Gen 2. Below is how I created the virtual machines listed above. Note: After creating the virtual machines and before installing Windows Server 2016 on the Offline Root CA, you must remove the Network Card for the Offline Root CA virtual machine as it should not be connected to any network. Step 2. Install the virtual machines Install Server 2016 On DC01, RootCA, IssuingCA and Webserver, install Windows Server 2016. It's up to you how to do this, you can use an Automated MDT PowerShell script, or install them manually. To install all Windows Server 2016 on all 4 servers as WorkGroup joined computers do as follows.. Choose Windows Server 2016 Standard (Desktop Experience) Continue through the installation wizard until prompted for a password, use P@ssw0rd as the Administrator password Click Finish. And then logon using the Administrator username and password configured above. Once Windows is installed, set the IP address for each virtual machine as shown below. Note: Below are the Computer Name and IP addresses used in this guide. For the Offline Root CA, you must remove the Network card in the Hyper-V virtual machine settings. Computer Name: DC01, IP address: 192.168.11.1, Subnet mask 255.255.255.0, Default gateway: 192.168.11.199, Preferred DNS server: 192.168.11.1 Computer Name: IssuingCA, IP address: 192.168.11.2, Subnet mask 255.255.255.0, Default gateway: 192.168.11.199, Preferred DNS server: 192.168.11.1 Computer Name: Webserver, IP address: 192.168.11.3, Subnet mask 255.255.255.0, Default gateway: 192.168.11.199, Preferred DNS server: 192.168.11.1 Computer Name: RootCA, IP: <NO NETWORK> Computer Name: W101803, IP address: 192.168.11.4, Subnet mask 255.255.255.0, Default gateway: 192.168.11.199, Preferred DNS server: 192.168.11.1 Computer Name: smoothwall11, IP address: (Green, static) 192.168.11.199 (Red, DHCP internet IP) x.x.x.x Here's how you can set the IP address for DC01. And configure the Computer Name as per the list (in this example it's for the Domain Controller) Reboot when prompted. Install Windows 10 Enterprise version 1803 Install Windows 10 Enterprise, version 1803 on the remaining virtual machine (#11_W10_1803). Configure the Computer Name and IP address as specified. Leave it WorkGroup joined. Optionally install Smoothwall To learn how to setup Smoothwall express as a firewall see this blog post. Step 3. Configure ADDS on DC01 Now that you've installed the servers, it's time to make DC01 a domain controller, to do that we'll install Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) and to do that we'll use this PowerShell script, simply run the script as Administrator in Windows PowerShell ISE on DC01. Download the script -Configure ADDS.ps1 After running the script, DC01 is prompted to a Domain Controller and is ready for the next part of this series. Note: Please only run this script on the DC01 virtual machine. After running the script, the Domain Controller is ready for Part 2 (configured as dc01.windowsnoob.lab.local) and internet is working (via the Smoothwall) To continue with Part 2 of this series, click here. Recommended reading (1) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_key_infrastructure (2) - https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/15037.ad-cs-step-by-step-guide-two-tier-pki-hierarchy-deployment.aspx (3) - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/clients/manage/co-management-overview
- 2 replies
-
- 2
-

-
- co-mangement
- ca
-
(and 12 more)
Tagged with:
-
it's very easy just install smoothwall on a legacy (gen 1) hyperv vm and configure two nics, one for Green (lan) and one for Red (wan),
- 5 replies
-
- sccm
- windows server 2016
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-

Run Command not working in Task Sequence for OSD
anyweb replied to LiamMc18's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
"parsing" you are looking at the part of the smsts.log where it parses through the commands it has to execute, to see how your step performs, search for "start executing" instead and see what errors if any are present for the actual step, and not the 'parsed' step -
odd, my working ts has MDT integration, can you try adding a Use Toolkit Package and then MDT gather step before this, and see does it make any difference in your task sequence
- 242 replies
-
- 1702
- forced upgrade
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
so if you manually run the command in a command prompt, does it work ?
- 242 replies
-
- 1702
- forced upgrade
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
it's more than likely forcing to GPT due to the bios mode being in UEFI, and that's a good thing, looking at the small snippet of log file you provided doesn't really help troubleshoot this however, we need the entire smsts.log to be sure what is being detected, and then, what steps are running, so can you attach it please
-
I see you are using french, have you tried the equivalent word in French in case that's the issue ?
- 242 replies
-
- 1702
- forced upgrade
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
hi can you show the step in your task sequence please
- 242 replies
-
- 1702
- forced upgrade
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
training is always good but intense, and these types of training give you good info over the time frame of about a week, but what they don't give you is experience. That you get when working with SCCM in different organizations over the years, so don't expect to be an all singing, all dancing SCCM engineer after attending one of these courses for one week, sure, these courses will give you a great overview of the product, but SCCM is WAY TOO immense to understand or fully comprehend in just one week IMHO, I'd suggest you bookmark this link and start working your way through the guides to get familiar with various options in SCCM Current Branch (and technical preview) cheers niall
-
hi Thomas, I didn't create any separate discs for temp and transaction logs and didn't add it to the scripts either, that would be an exercise for you to undertake, p.s. you should really be working off the latest version of the guide here > How can I install System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1802 on Windows Server 2016 with SQL Server 2017 – Part 1






Issuedresubmittedbyrootcaadministrator.png.0054988f730b22e4791c69926ae8cea3.png)